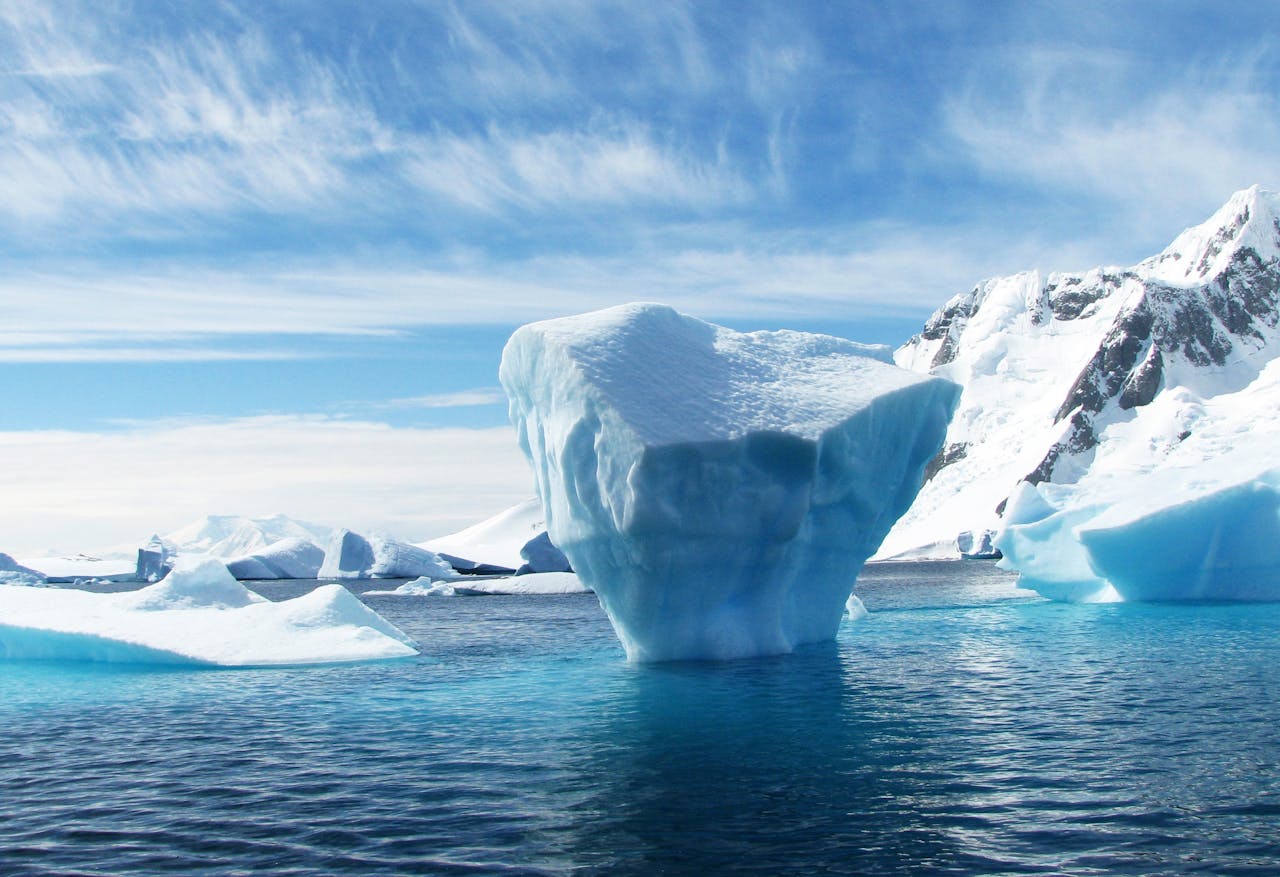
Researchers for the primary time have used seismic sensors to trace meltwater flowing by means of glaciers and into the ocean, a necessary step to understanding the way forward for the world’s largest glaciers as local weather modifications.
Researchers for the primary time have used seismic sensors to trace meltwater flowing by means of glaciers and into the ocean, a necessary step to understanding the way forward for the world’s largest glaciers as local weather modifications.
Meltwater transferring by means of a glacier into the ocean is critically necessary as a result of it could actually enhance melting and destabilize the glacier in a lot of methods: The water can pace the glacier’s movement downhill towards the ocean; it could actually transfer rocks, boulders, and different sediments towards the terminus of the glacier alongside its base; and it could actually churn and stir heat ocean water, bringing it in touch with the glacier.
“It’s like once you drop an ice dice right into a pot of heat water. It is going to finally soften, however it’s going to soften lots sooner in the event you stir that water,” says Timothy Bartholomaus, a postdoctoral fellow on the College of Texas at Austin Jackson College of Geosciences. “Subglacial discharge supplies that stirring.”
Tidewater Glaciers
The brand new approach, described within the journal Geophysical Journal Letters, affords scientists a instrument for monitoring meltwater at glaciers that finish within the ocean, known as tidewater glaciers.
In contrast to landlocked glaciers, the place scientists can merely measure the meltwater flowing in glacial rivers, there beforehand had not been a technique out there to trace what’s occurring inside tidewater glaciers.
“All the greatest glaciers in Greenland, the entire greatest glaciers in Antarctica, they finish within the ocean,” says Bartholomaus, the research’s lead writer.
“We have to perceive how these glaciers are transferring and the way they’re melting at their entrance. If we need to reply these questions, we have to know what’s occurring with the meltwater being discharged from the glacier.”
Iceberg Calving
Researchers found the brand new technique whereas making an attempt to review earthquakes brought on by iceberg calving—when giant chunks of ice break off glaciers. The power to establish these earthquakes, often known as icequakes, diverse over the season, and so they had been far more tough to detect throughout summer time as a result of seismic background noise was obscuring the icequake alerts.
The staff set about making an attempt to find out what was making the background noise, investigating potential causes reminiscent of rainfall, iceberg calving, and the motion of the glacier over the bottom.
Finally, because the researchers discounted these theories, they found that the seismic vibrations being detected by the gear was brought on by meltwater percolating down by means of the glacier and weaving its manner by means of the difficult plumbing system within the inside of the ice.
Researchers examined the idea on glaciers with meltwater rivers and located that the timing of the meltwater and the seismic alerts synced completely. The tactic is superb at figuring out when the glacial discharge is flowing into the ocean, however it’s going to take extra analysis to find out precisely how a lot water is flowing out, Bartholomaus says.
“Now that we all know when subglacial discharge is quicker or slower, we are able to make higher measurements of glacier change. My hope is that this technique will actually assist us perceive how the glaciers and the oceans are coupled, and the way the ocean is likely to be affecting the conduct of tidewater glaciers.”
Researchers from the College of Alaska Southeast, the College of Alaska Fairbanks, and the US Geological Survey contributed to the research.
Supply: College of Texas at Austin. Republished from Futurity.org beneath Inventive Commons License 4.0.
In case you discovered this text fascinating, please take into account supporting conventional journalism
Our first version was revealed 25 years in the past from a basement in Atlanta. At this time, The Epoch Occasions brings fact-based, award-winning journalism to thousands and thousands of People.
Our journalists have been threatened, arrested, and assaulted, however our dedication to impartial journalism has by no means wavered. This 12 months marks our twenty fifth 12 months of impartial reporting, free from company and political affect.
That’s why you’re invited to a limited-time introductory supply — simply $1 per week — so you’ll be able to be a part of thousands and thousands already celebrating impartial information.