The human mind is comprised of two major kinds of cells, referred to as neurons and glia. The primary are accountable for transmitting electrical and chemical alerts, whereas the latter assist and shield neurons.
The communication between neurons and glia is central to the event of the mind and the upkeep of its features. Previous findings recommend that this communication takes place by way of the binding of ligands (i.e., signaling molecules) to particular proteins or receptors on the floor of a cell.
By finding out Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans), generally referred to as roundworms, researchers at Duke College Medical Middle have unveiled a brand new mechanism that would mediate neuron-glia communications throughout growing old.
Their findings, revealed in Nature Neuroscience, recommend that warmth shock proteins (i.e., proteins that play a task in defending cells from stress) can act as signaling molecules and mediate communications between neurons and glia as worms age.
“The mind is primarily composed of neurons and glial cells,” Jieyu Wu, first writer of the paper, advised Medical Xpress.
“In some mind areas, greater than half of the cells are glial cells. Quite a few research have proven that neuron–glia interactions play a vital position in mind improvement and performance. This raises an necessary query: how is neuron–glia communication concerned in mind growing old?”
Learning neuron-glia communication in reside organisms has thus far proved difficult, partly because of a scarcity of animal fashions which might be straightforward to look at within the lab, however that additionally mirror a number of the mechanisms noticed in people.
C. elegans has been discovered to be a very efficient mannequin for finding out growing old processes, thus Wu and his colleagues determined to pick it for his or her experiments.
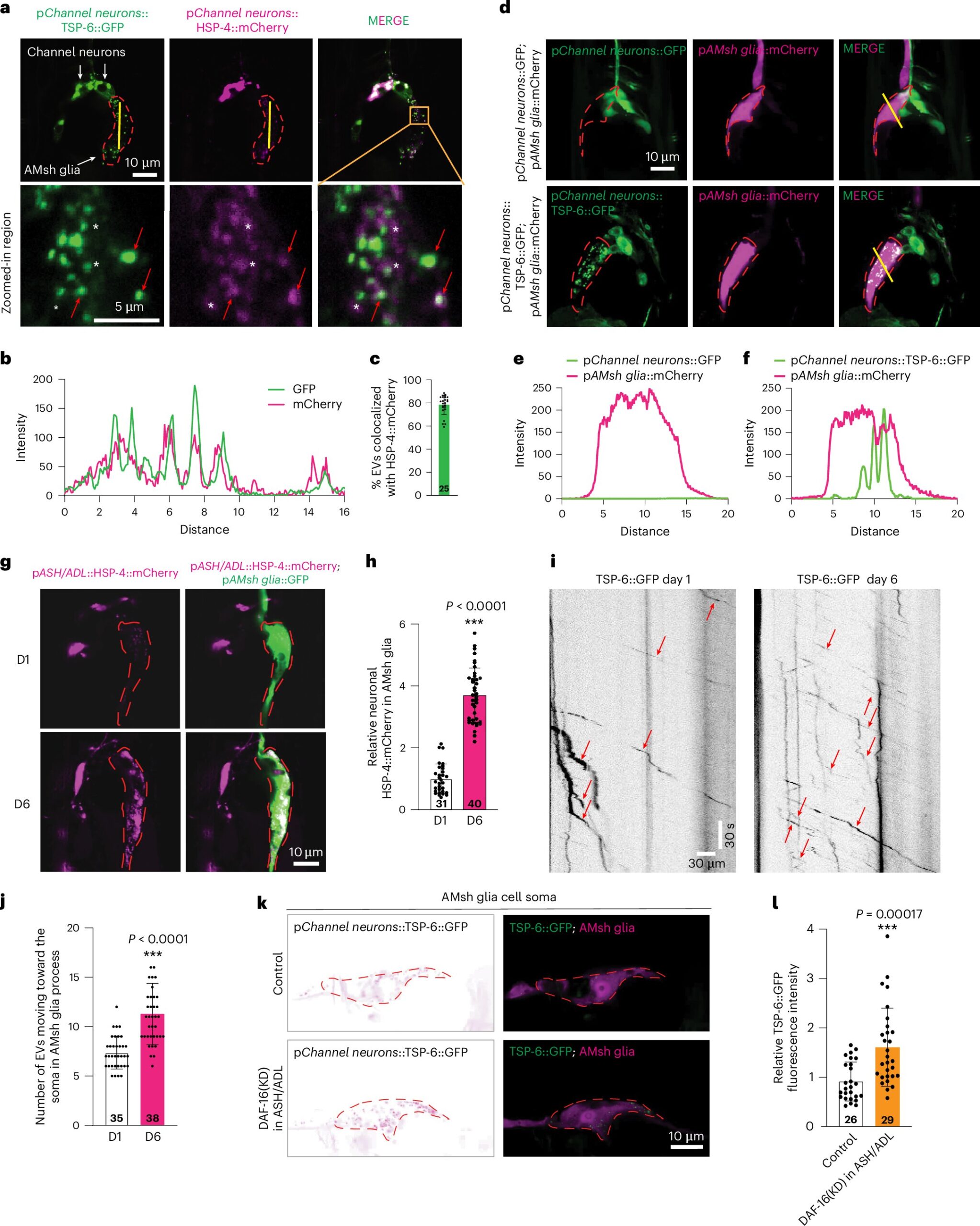
“After inspecting the complete nervous system of C. elegans, we recognized the amphid sensory organ as a promising mannequin to analyze neuron–glia communication throughout growing old in vivo,” defined Wu.
“We used chemotaxis assays and calcium imaging to guage sensory neuron operate. To control growing old in particular neurons, we employed the auxin-inducible system to deplete key regulatory components within the growing old signaling pathway.”
As a part of their experiments, Wu and his colleagues captured the proteins current inside glial cells (i.e., the glial cell-specific proteome) below totally different situations in reside roundworms. As well as, they checked out how this proteome responded to the growing old of neurons.
Subsequently, the researchers used molecular biology methods to change a number of the worms’ DNA/RNA. This allowed them to label particular proteins, guaranteeing that they’d glow below the microscope and to cut back or solely silence the exercise of particular genes.
“Our examine represents the primary in vivo occasion to indicate that protein transmission from neuron to glia by means of extracellular vesicles regulates mind growing old,” mentioned Wu.
“Moreover, we revealed that warmth shock proteins can act as signaling molecules to mediate neuron-glia communication and affect glial operate. These findings supply a brand new mannequin and open new prospects for the examine of neuron-glia communication.”
This examine provides new perception into the intricate neural mechanisms that would contribute to a decline or upkeep of mind operate throughout growing old.
The findings gathered by Wu and his colleagues might encourage additional analysis geared toward inspecting the distinctive contribution of warmth shock proteins to neuron-glia communication in additional depth.
“One among my future objectives is to analyze the purposeful significance of extracellular vesicles in mind growing old,” added Wu. “I’m at the moment in search of an assistant professor place, with the intention of focusing my analysis on dissecting the biology of extracellular vesicles within the nervous system and elucidating their roles in mind growing old.”
Written for you by our writer Ingrid Fadelli,
edited by Sadie Harley, and fact-checked and reviewed by Robert Egan—this text is the results of cautious human work. We depend on readers such as you to maintain impartial science journalism alive.
If this reporting issues to you,
please take into account a donation (particularly month-to-month).
You will get an ad-free account as a thank-you.
Extra info:
Jieyu Wu et al, Warmth shock proteins operate as signaling molecules to mediate neuron–glia communication in C. elegans throughout growing old, Nature Neuroscience (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s41593-025-01989-0.
© 2025 Science X Community
Quotation:
Roundworm examine identifies proteins that would mediate neuron-glia communication as mind ages (2025, July 8)
retrieved 8 July 2025
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2025-07-roundworm-proteins-neuron-glia-communication.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.