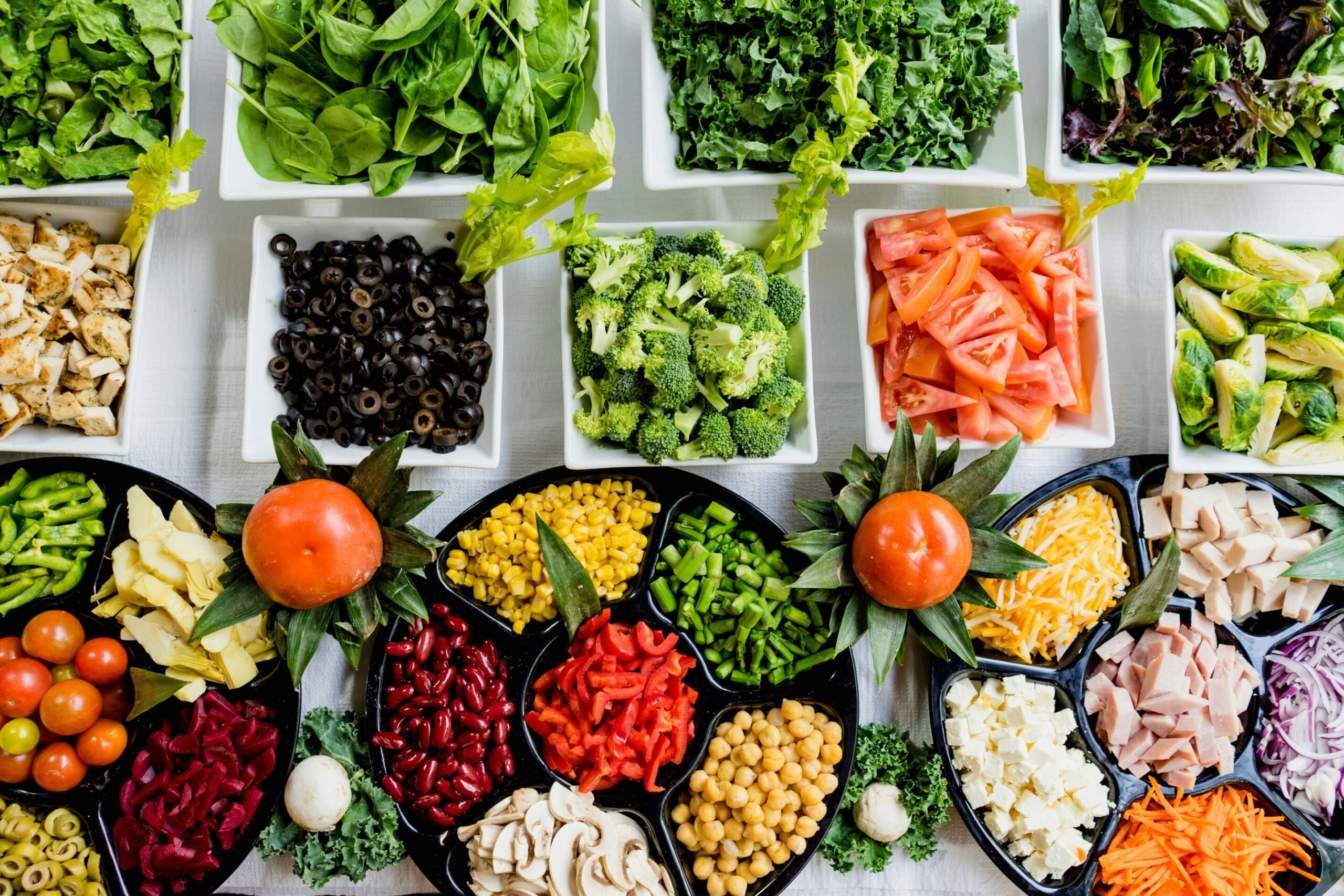
A significant research of U.Okay. dietary habits has discovered that the meals we eat accommodates a mean of not less than 49 completely different species every week.
Researchers used modern algorithms to determine the quantity and sort of distinctive elements in 6,000-plus food and drinks objects within the Nationwide Weight-reduction plan and Diet Survey (NDNS) nutrient databank then cross-referenced hundreds of four-day meals diaries.
They discovered a mean of 29 distinctive species on the primary day—with 9 extra added on day two, 5 on day three and 4 on the final day—suggesting the weekly quantity would high 50.
The species included completely different forms of meat, seafood, fruit, greens, herbs and spices—with solely excluding sure extracts and flavorings not counted within the rating.
The peer-reviewed paper, revealed in Public Well being Diet, demonstrates that this novel methodology can be utilized to make sturdy scientific calculations concerning the number of parts that make up what we eat and offers a case research for international locations which have a comparatively excessive consumption of processed meals as a part of Western-style diets.
It offers vital new insights into the science of food plan biodiversity, which is gaining consideration as a strategy to measure the well being and local weather impacts of what we eat.
And it reinforces the worth of current dietary recommendation, discovering DSR is “considerably greater in these adhering to dietary pointers for fruit and greens, fish and fiber.”
The analysis was carried out by a workforce on the Rowett Institute, College of Aberdeen in collaboration with colleagues from the Unilever Meals Innovation Middle, Wageningen within the Netherlands and from Robert Gordon College in Aberdeen.
Lead creator Professor Baukje de Roos stated, “Consuming extra ‘species’ is probably going to enhance the standard of our diets, and subsequently our well being.
“Our analysis clearly exhibits that sticking to current dietary pointers to eat 5 parts of vegetables and fruit a day, and not less than one or two fish meals every week, is a vital strategy to maximize the variety of species we eat as a part of our food plan.”
A spokesperson for the Unilever Meals Innovation Middle added, “We’re proud to be a part of a challenge that makes use of cutting-edge algorithms to validate dietary species richness and discover how elevated variety of species in our diets can enhance vitamin and public well being.”
The concept consuming a assorted food plan advantages well being is effectively established however has historically been measured by counting meals teams, reasonably than particular person parts inside them.
Now there’s a rising deal with meals biodiversity (completely different crops, animals, fungi, bugs, and so forth.)—each for human and planetary well being.
Latest analysis which related a better DSR with decrease dying charges has led to options it’s included in public well being methods as a brand new metric for wholesome and sustainable meals and diets.
Some business vitamin packages already encourage prospects to eat a minimal variety of several types of sure foodstuffs per week, as this will likely assist to enhance the range of their intestine microbiome.
However, the paper notes, questions stay about how DSR can greatest be measured, its actual relationship with food plan high quality and what rating is required for optimum well being.
For instance, whereas a better DSR was usually related to a small enchancment in food plan high quality, maybe unexpectedly, the brand new research discovered that avoiding sugar and salt truly tends to be linked to a decrease DSR.
DSR was additionally discovered to be greater in youthful individuals, these with greater family incomes and people dwelling within the least disadvantaged areas—however with no important variation between women and men or between individuals of various ethnicities.
The paper concludes: “It’s important to know how meals biodiversity is related to dietary high quality and well being outcomes to justify its use as a significant new metric that may hyperlink diets to human and planetary well being, complementing current indicators for wholesome and sustainable diets.
“To extend DSR in U.Okay. diets in a simply method, we might want to be certain that we preserve pure biodiversity worldwide by means of our dietary selections and preserve the affordability of high-DSR meals and diets, which requires integration of environmental and public well being insurance policies.
“An important energy of this research is the sturdy bottom-up evaluation of DSR in U.Okay. diets, utilizing four-day meals consumption knowledge collected from 3,558 members throughout intercourse, age, ethnicity and socio-economic teams over a latest interval of three years.”
Extra data:
Magaly Aceves-Martins et al, The measurement of dietary species richness reveals {that a} greater consumption of dietary fibre, fish, vegetables and fruit, is related to higher meals biodiversity in UK diets, Public Well being Diet (2025). DOI: 10.1017/S1368980025000473
Quotation:
Weight-reduction plan variety: Common Brit eats not less than 49 completely different species every week (2025, July 1)
retrieved 1 July 2025
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2025-07-diet-diversity-average-brit-species.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.