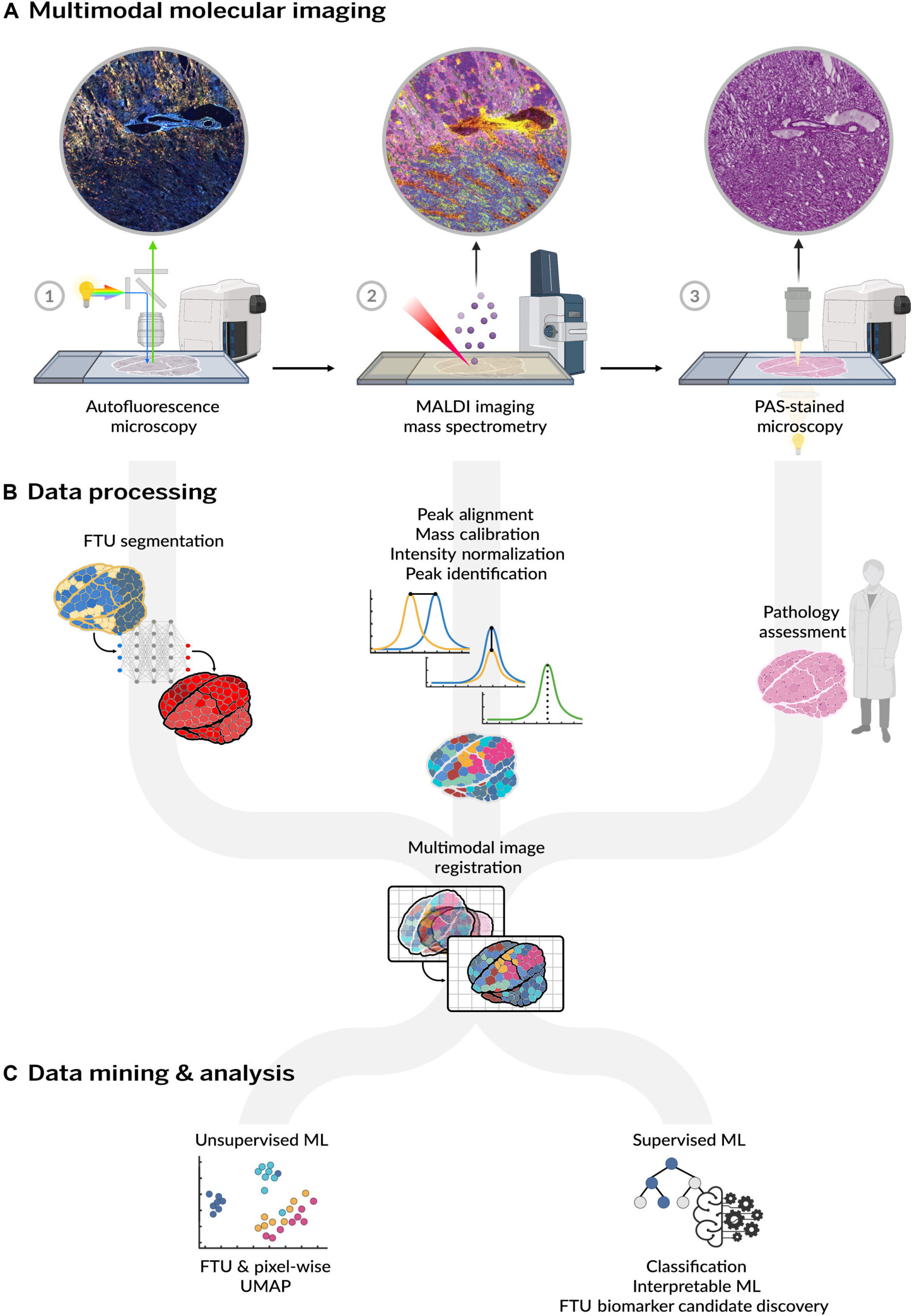
The kidney, a important organ for waste filtration and fluid regulation, is the topic of a molecular mapping mission that would reshape our understanding of renal well being. Regardless of advances in transcriptomics and proteomics, lipids—key structural and signaling molecules—have remained comparatively unexplored within the context of kidney perform.
That’s now altering because of a brand new examine revealed in Science Advances by researchers from the Mass Spectrometry Analysis Middle and the lab of Jeff Spraggins at Vanderbilt College and Raf Van de Plas’ group at Delft College of Expertise. Within the new paper, the staff created a high-resolution molecular atlas of the human kidney, leveraging a cutting-edge imaging mass spectrometry method known as MALDI and interpretable machine studying.
This atlas is probably the most complete of its variety, incorporating information from 29 human kidney donors. The researchers mapped lipid species throughout tens of millions of mass spectrometry measurements from greater than 100,000 discrete useful tissue models, together with glomeruli, proximal and distal tubules, thick ascending limbs, and gathering ducts.
“This work has been our most bold and complete multimodal molecular imaging examine thus far,” stated Spraggins, senior writer and co-lead of the mission. “By spatially linking lipid composition to anatomical and useful areas of the kidney, we have been in a position to successfully generate a molecular bar code for every part of the human nephron.”
Among the many hanging findings: The atlas’ molecular view of kidney perform reveals spatially particular lipid biomarkers for distinct useful tissue models of the nephron.
Regardless of the pure variations between human donors, particular sphingomyelins—a sort of lipid—have been persistently enriched in glomeruli, suggesting a job in supporting cell sorts important for filtration. Different lipid courses, together with sulfatides and phosphatidylserines, have been strongly related to nutrient reabsorption and ion transport in constructions such because the loop of Henle and proximal tubules.

The staff additionally explored how lipid profiles differ by intercourse and physique mass index. Leveraging interpretable machine studying fashions, the staff recognized candidate biomarkers, together with arachidonic acid–containing phospholipids, that will mirror sex-specific physiology and hormonal regulation. Moreover, distinct phosphatidylcholines and sphingomyelins have been related to obesity-linked alterations in kidney tissue, together with markers of glomerular sclerosis.
“It is like giving everybody a Google Maps of the kidney, however as a substitute of streets and landmarks, we’re mapping mobile group and molecular signatures,” Spraggins stated. “And identical to maps, as soon as you may see the terrain, you can begin navigating and intervening with extra precision.”
The potential advantages are broad: an improved understanding of the relationships between mobile and molecular distributions of the kidney, extra exact stratification of affected person illness threat primarily based on molecular information, and finally, lipid-targeted interventions for illnesses.
Critically, the dataset and instruments can be found without cost by way of the Nationwide Institutes of Well being’s Human Biomolecular Atlas Program, which is often known as HuBMAP, which implies that the broader analysis group can mine this useful resource for brand spanking new hypotheses. The Biomolecular Multimodal Imaging Middle has been targeted on creating an atlas for the human kidney and different organ methods for six years. Along with Vanderbilt researchers, BIOMIC additionally contains clinicians from Vanderbilt College Medical Middle and information scientists from Delft College of Expertise within the Netherlands.
The examine’s insights may translate into new diagnostic markers or therapeutic targets for kidney-related illnesses. “This atlas establishes a molecular baseline,” Melissa Farrow, co-first writer and analysis affiliate professor of cell and developmental biology, stated. “By evaluating diseased tissue to this reference, we are able to start to pinpoint lipid perturbations that underlie pathology.”
Finally, this mission marks a pivotal step towards integrating lipidomics into the biomedical mainstream and redefines how we have a look at organs by means of a molecular lens.
Extra data:
Melissa A. Farrow et al, A lipid atlas of the human kidney, Science Advances (2025). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adu3730
Quotation:
Kidney atlas maps molecular panorama, unlocking clues to renal well being and illness (2025, June 17)
retrieved 17 June 2025
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2025-06-kidney-atlas-molecular-landscape-clues.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.