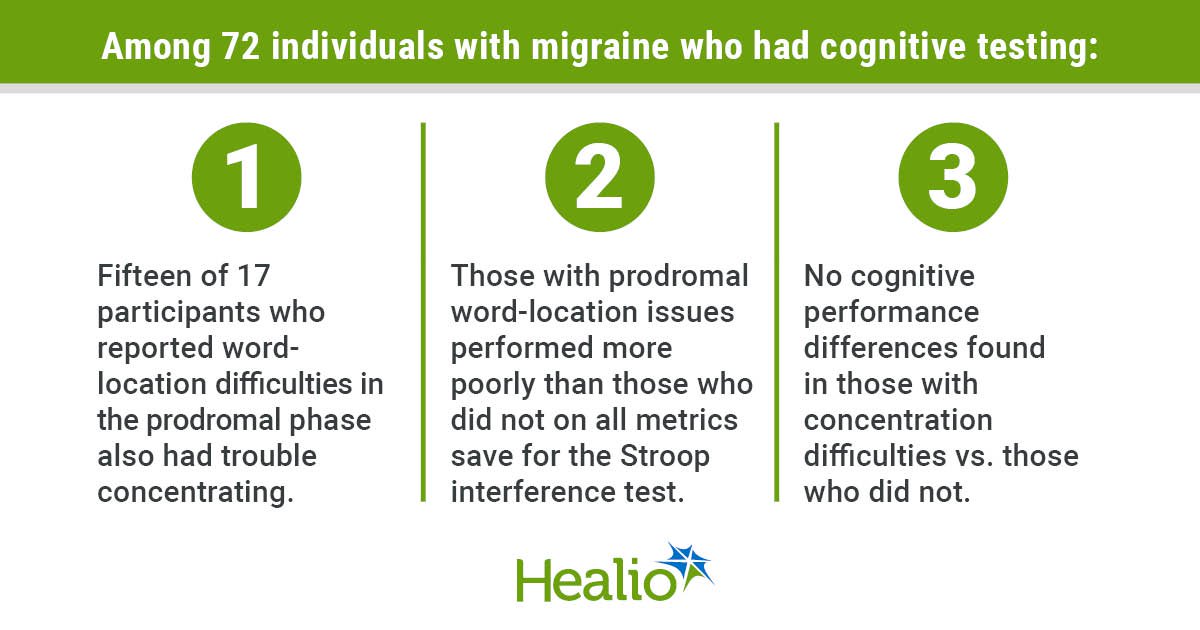
Key takeaways:
- IOP measurements with Tono-Vera had ‘sturdy correlation and settlement’ with the Ocular Response Analyzer.
- The system is moveable and consists of options to scale back operator errors.
IOP measurements taken with Tono-Vera, a brand new handheld rebound tonometer, carefully align with these taken with the Ocular Response Analyzer, in response to a cross-sectional examine revealed in Journal of Glaucoma.
“The Ocular Response Analyzer (ORA, Reichert Applied sciences) is a noncontact tonometer that estimates IOP by analyzing corneal responses to deformation induced by an air pulse,” Luiz A.F. Beniz, MD, of Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, and colleagues wrote. “The Tono-Vera (Reichert Applied sciences) is a new rebound tonometer that implements vital enhancements to presently obtainable tonometers, together with a proprietary camera-based positioning system that mixes a colour view of the attention with interactive prompts that guarantee correct angulation, distance and centration, decreasing operator-dependent measurement errors.”

IOP measurements taken with Tono-Vera, a handheld rebound tonometer, carefully align with these taken with the Ocular Response Analyzer. Picture: Adobe Inventory
Beniz and colleagues used each instruments a number of occasions on 54 eyes, 50 with glaucoma and 4 regular. The measurements had been performed consecutively on the identical go to by the identical technician.
“Because the measurements on this examine had been acquired with a pre-market uncalibrated model of the system, an preliminary calibration was crucial to permit a significant comparability,” the researchers wrote. “To deal with this, our pattern was cut up on the affected person degree into calibration [46% of eyes] and validation [54% of eyes] teams.”
In keeping with the outcomes, there was “sturdy correlation and settlement” between measurements from the 2 units. The common distinction between them was “near zero” at –0.4 ± 2.5 mm Hg.
Within the validation pattern, 96.5% of the Tono-Vera measurements had been inside 5 mm Hg of the ORA, 79.3% had been inside 3 mm Hg, and 58.6% had been inside 2 mm Hg.
“These outcomes point out that the Tono-Vera could present correct IOP measurements whereas having some great benefits of portability and user-friendly operation,” Beniz and colleagues wrote. “The Tono-Vera represents a promising addition to the arsenal of moveable medical units in a position to measure IOP.”