Columbia scientists have discovered that boosting the efficiency of a self-cleansing system within the mind helps flush amyloid and tau toxins from the brains of mice and improves the animals’ cognition.
Their research, printed in Neuron, additionally discovered that the mind cleaning system might be enhanced with medicine referred to as PERK inhibitors, already in medical trials for most cancers, and suggests the medicine may additionally be useful for Alzheimer’s and different neurodegenerative ailments.
“The glymphatic system—typically referred to as the mind’s dishwasher—was solely found a few decade in the past and has captured the eye of many scientists,” says Guang Yang, affiliate professor of anesthesiological sciences at Columbia College’s Vagelos Faculty of Physicians and Surgeons, who led the research.
Mind cleansing and Alzheimer’s
Alzheimer’s has been linked to a weak glymphatic system, so Yang and her group needed to see how the 2 are related, data that might yield new methods to deal with or stop the illness.
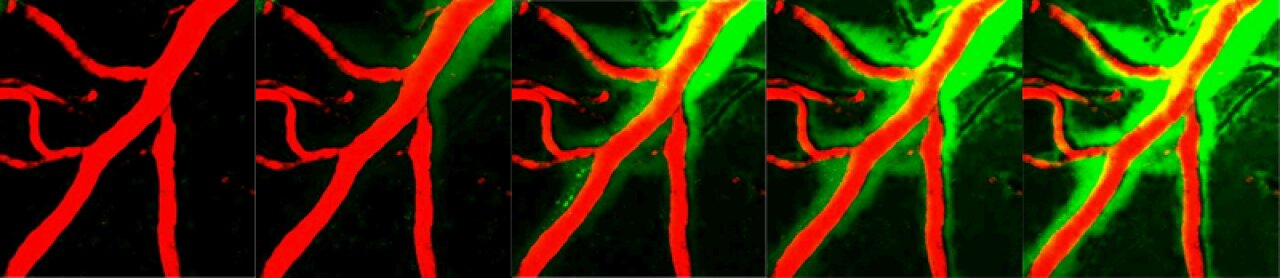
The researchers measured the efficiency of the mind’s cleaning cycle by injecting a tracer into the cerebrospinal fluid of mice and utilizing high-resolution microscopy to seize time-lapse photographs of the tracer within the glymphatic system.
In mice with Alzheimer’s, the group discovered that the cleansing system turns into sluggish as a result of channels that assist drain metabolic waste from the mind are misplaced.
“It appears to be like just like the cells have sufficient of those AQP4 channels, however they are not in the appropriate areas within the cells,” Yang says.
Usually, the channels are positioned on the endfeet of the astrocytes, star-shaped mind cells that management the glymphatic system. However in mice and folks with Alzheimer’s, the researchers discovered the channels distributed throughout the astrocytes, which hindered waste elimination from the cells.
The channels are misplaced in mice, the group discovered, as a result of a protein referred to as PERK is overactive. The researchers discovered that deleting the PERK gene or inhibiting it with a drug restored the channels to their correct location, elevated amyloid and tau clearance, and improved the animals’ cognitive efficiency.
A job for sleep?
Yang says there’s nonetheless extra to study concerning the connection between the glymphatic system and Alzheimer’s that might result in new therapies. “That is simply the place to begin. We all know PERK is essential for controlling localization of the channel, however the particulars should be labored out,” she says.
Sleep may additionally assist the glymphatic system clear the mind. Some research recommend the glymphatic system is most energetic throughout sleep, and Alzheimer’s is understood to be related to sleep problems.
“We’re trying to see if PERK exercise is linked to sleep, which could assist clarify how poor sleep may improve Alzheimer’s pathology,” Yang provides.
“Glymphatic impairment could also be a standard pathway in all neurodegenerative ailments, so our findings may additionally apply to different circumstances.”
Extra data:
Kai Chen et al, Selective elimination of astrocytic PERK protects in opposition to glymphatic impairment and reduces poisonous aggregation of β-amyloid and tau, Neuron (2025). DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2025.04.027
Quotation:
Boosting mind’s self-cleansing system helps clear Alzheimer’s toxins in mice (2025, June 4)
retrieved 4 June 2025
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2025-06-boosting-brain-cleansing-alzheimer-toxins.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.