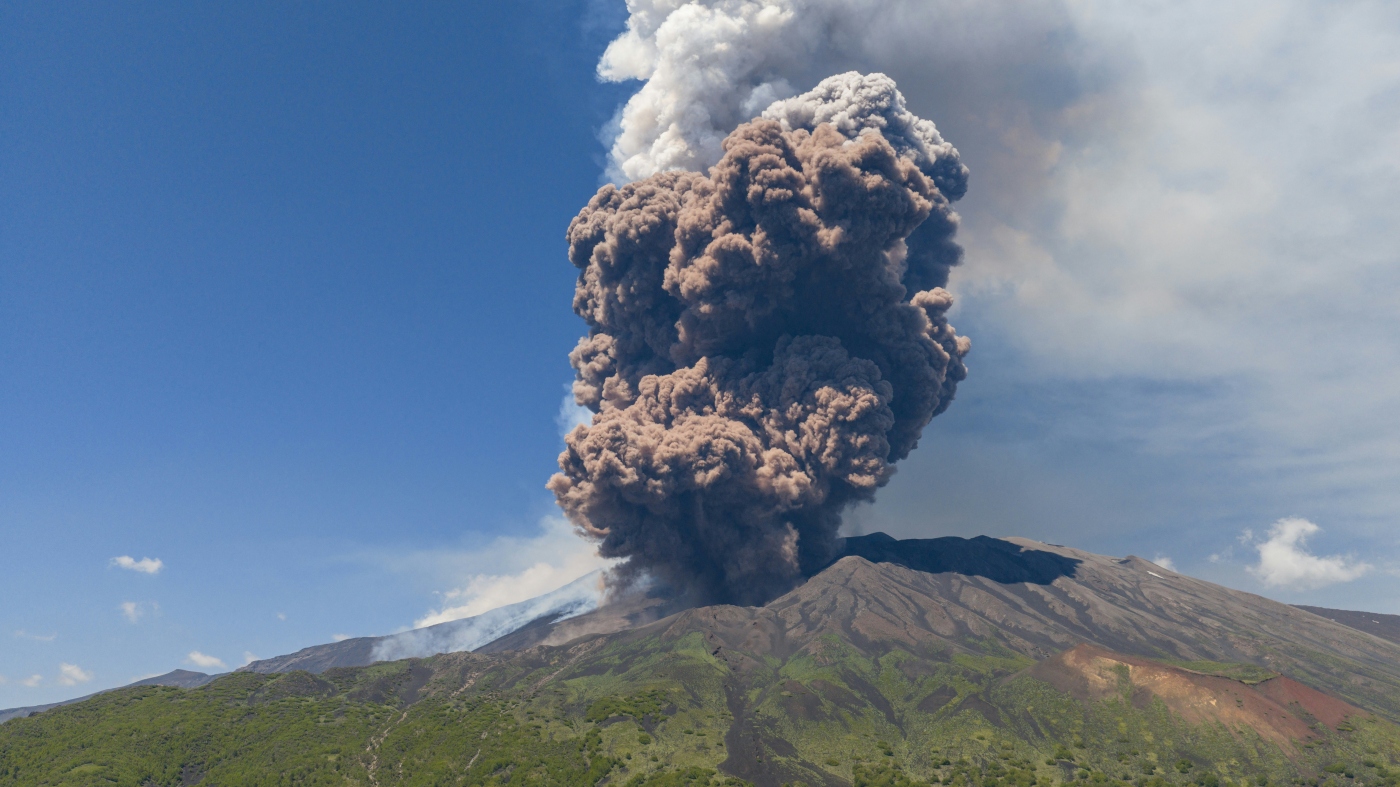
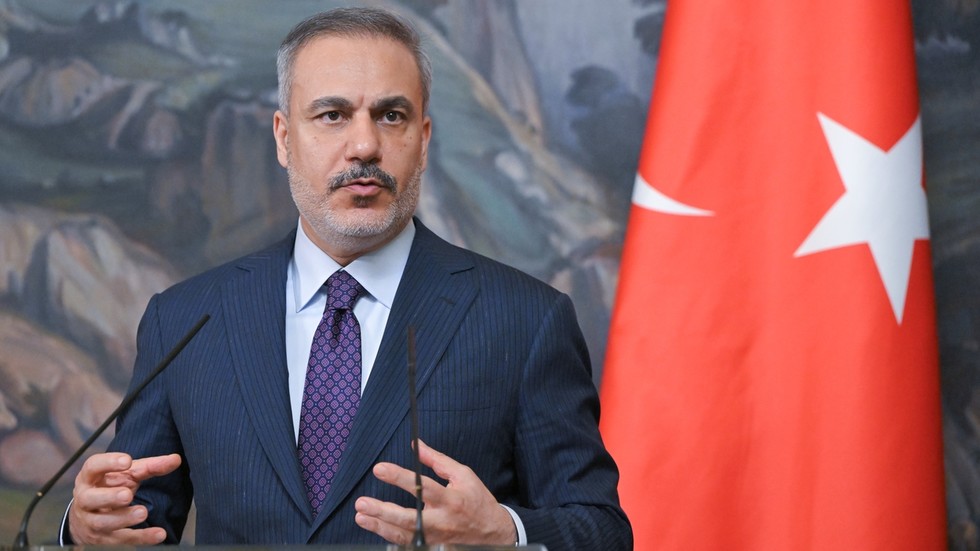
Smoke rises from the crater of the Etna volcano because it erupts, on Mount Etna close to Catania, Italy, on Monday. An enormous plume of ash, gasoline and rock spewed forth from Europe’s highest energetic volcano.
Giuseppe Distefano/AFP through Getty Pictures
disguise caption
toggle caption
Giuseppe Distefano/AFP through Getty Pictures
Italy’s Mount Etna produced a spectacularly explosive eruption Monday morning, sending a ripple of reddish clouds down from its summit. The hovering ash rose to kind a mushroom cloud excessive above Etna, Europe’s highest energetic volcano, triggering a crimson alert for aviation crews within the area.
The Nationwide Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology’s Etna Observatory in Catania estimated the volcanic cloud’s peak at about 21,325 ft. The large ash cloud was transferring in a west-southwest course, in response to the company, generally known as INGV.
YouTube
The dramatic scene at Etna’s southeast crater was caught on a number of webcams, spreading rapidly throughout social media. As seen in a Climate Sicily webcam video, the eruption quickly grew from a couple of lava flows to cascades of boiling ash and smoke that rose into a big cloud.
Fortunately, the eruption would not appear to have had any speedy influence on individuals within the space, apart from forcing officers to halt vacationers’ visits to the volcano, which is a well-liked vacation spot and is situated on the east coast of Sicily.
Officers consider that a big portion of the crater collapsed, in response to the Italian information company ANSA.
Aviation alerts have been eased afterward Monday because the INGV stated volcanic exercise and ash emissions have been lastly reducing. With the ash cloud transferring towards the west, operations at Vincenzo Bellini Catania Airport, due south of Etna, weren’t affected.
It is commonplace for Etna to emit lava and gases from its summit craters. Etna is “essentially the most energetic stratovolcano on this planet that has repeatedly pumped ash and lava” for hundreds of years, in response to the United Nations. (A stratovolcano, also referred to as a composite volcano, is usually steep and conical, in response to the U.S. Geological Survey. In distinction, protect volcanoes, like Hawaii’s Mauna Loa, are bigger however with a extra gradual slope.)
Etna has an extended historical past of frequent eruptions, documented no less than to 1500 B.C.
Most of Etna’s eruptions are “Strombolian eruptions” — ejections of cinder, gasoline and molten lava that outcome from repeated, however comparatively small, explosions.
“The Strombolian exercise typically impacts a restricted space across the vent and isn’t an agent of danger [to] constructed up areas” round Etna, in response to Italy’s Civil Safety Division. Etna’s lava flows are additionally usually viscous and slow-moving, usually permitting authorities to intervene to redirect flows that threaten communities.
Etna’s eruptions have produced placing scenes through the years, from a vivid nighttime show in 2011 to an outburst that preceded an earthquake in 2018.