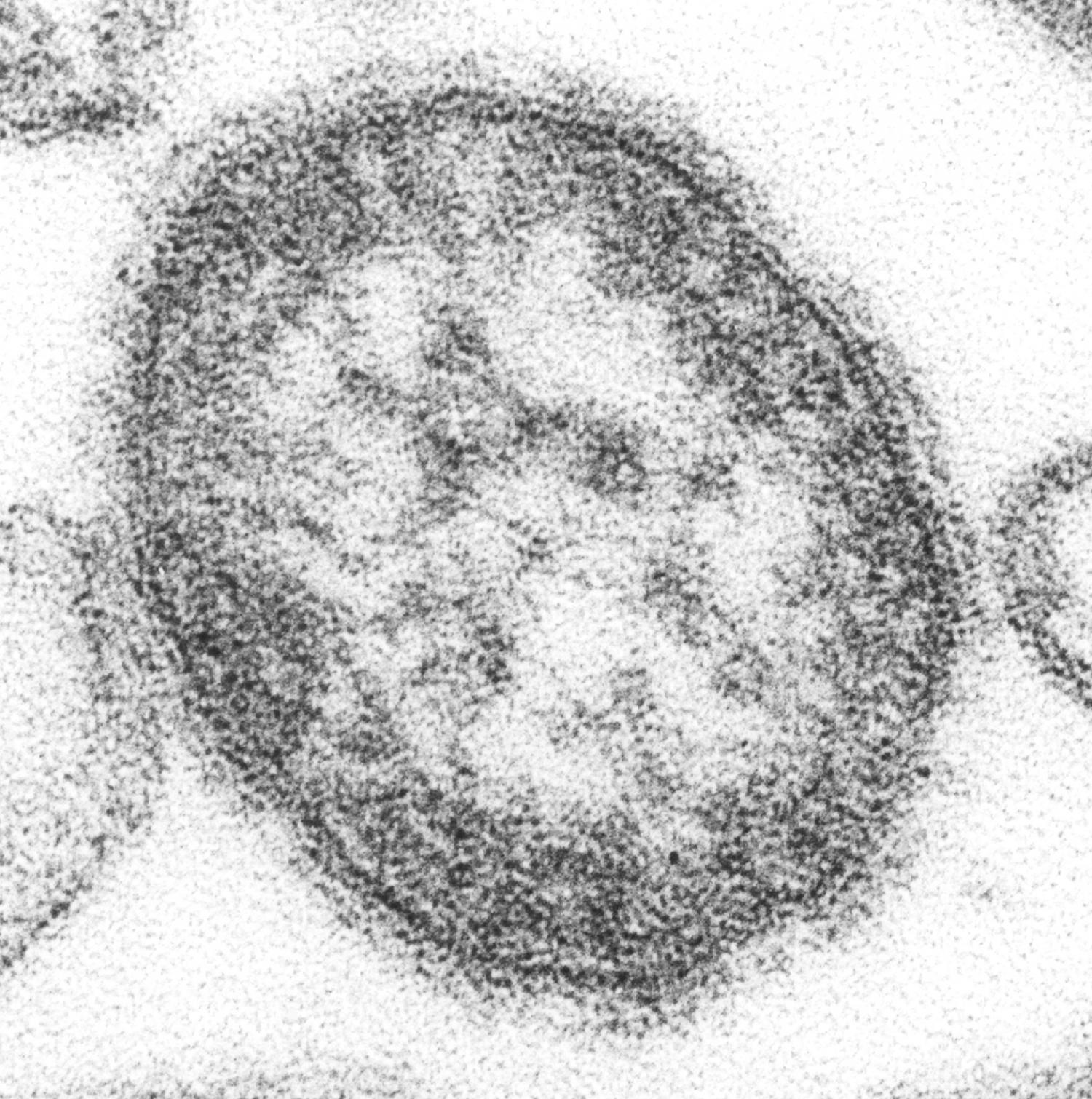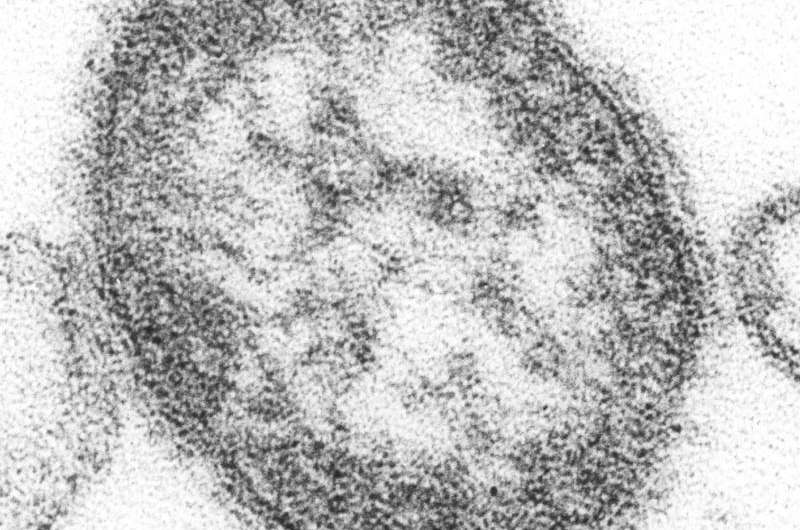
An modern outbreak detection program that tracks disease-causing viruses in wastewater recognized the measles virus in Houston samples collected in early January 2025, earlier than instances had been reported. The group that developed this system, which incorporates researchers at Baylor Faculty of Medication, the Faculty of Public Well being at College of Texas Well being Science Heart—Houston, the Houston Well being Division and Rice College, revealed their findings within the American Journal of Public Well being.
The researchers detected the virus in wastewater utilizing a sequencing-based strategy, a extremely delicate and particular technique that analyzes genetic materials. This technique might need broad implications for public well being, notably as a sentinel surveillance system to detect viruses earlier than widespread outbreaks happen. The findings are related and well timed as measles instances are rising in Texas and the remainder of the nation and the examine affords a promising technique to get forward of potential outbreaks.
“In 2023, we confirmed that systematically sequencing the genetic materials in wastewater reveals dynamic modifications in human viruses circulating in a neighborhood.
“Importantly, analyzing these viral modifications in wastewater can enhance our understanding of outbreaks and transmission and inform public well being preparedness, simply as one makes use of meteorological knowledge to raised perceive and predict climate patterns to anticipate probably harmful circumstances,” mentioned co-corresponding creator Dr. Anthony Maresso, Joseph Melnick Endowed Chair and Professor in Molecular Virology and Microbiology at Baylor.
Within the present examine, the researchers reported that their wastewater surveillance program detected the measles virus in samples collected on Jan. 7 in two Houston water therapy amenities serving greater than 218,000 residents. A parallel investigation confirmed on Jan. 17 the measles virus in two vacationers residing in the identical space serviced by the sampled water therapy vegetation.
“In such instances, our subsequent step is at all times validating the sign with a second technique, and we had been in a position to take action by way of a collaboration with the Houston Well being Division and Rice College,” mentioned co-first creator Dr. Sara Javornik Cregeen, assistant professor within the Alkek Heart for Metagenomics and Microbiome Analysis at Baylor. “They examined for the virus presence in samples from the identical date and assortment website and confirmed the sign utilizing one other approach, PCR.”
“As a reference, the 821 Houston wastewater samples we sequenced from the identical space had been damaging for measles virus within the earlier 31 months,” she added.
“As a result of no different instances have been reported and the detections occurred in the identical space the place the vacationers resided, it’s affordable to imagine that the measles sign detected in wastewater is from the 2 contaminated instances, which underscores the excessive sensitivity of the tactic,” Maresso mentioned.
“With classes realized from the Houston measles detection occasion, we at the moment are working with our public well being companions to collect knowledge on the present measles outbreak in West Texas. Though not reported right here, our program has been monitoring measles in wastewater from these websites as effectively, hoping the data will help officers get forward of this virus,” mentioned co-first creator Dr. Michael Tisza, assistant professor of molecular virology and microbiology at Baylor.
Presently, the researchers aren’t detecting measles viruses in wastewater in Houston however are detecting it in West Texas cities. The group continues to document the weekly exercise of attainable regarding viruses and report the leads to the primary of its form sequencing-based well being dashboard that’s publicly out there at https://tephi.texas.gov/early-detection.
Dr. Eric Boerwinkle, dean of the UTHealth Houston Faculty of Public Well being and co-corresponding creator, mentioned that “This work underscores the flexibility of subtle wastewater analyses to function an early detection system benefitting public well being, well being care and communities in stopping a measles outbreak in Houston.”
He goes on to remind us that “the most effective safety from contracting the measles virus is the MMR vaccine, which has been proven to be protected and efficient.”
Extra data:
Sara Javornik Cregeen et al, Sequencing-Primarily based Detection of Measles in Wastewater: Texas, January 2025, American Journal of Public Well being (2025). DOI: 10.2105/AJPH.2025.308146
Quotation:
Measles virus detected in Houston wastewater earlier than instances had been reported (2025, Could 12)
retrieved 13 Could 2025
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2025-05-measles-virus-houston-wastewater-cases.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.