A China-linked unnamed risk actor dubbed Chaya_004 has been noticed exploiting a lately disclosed safety flaw in SAP NetWeaver.
Forescout Vedere Labs, in a report revealed right now, mentioned it uncovered a malicious infrastructure possible related to the hacking group weaponizing CVE-2025-31324 (CVSS rating: 10.0) since April 29, 2025.
CVE-2025-31324 refers to a crucial SAP NetWeaver flaw that enables attackers to attain distant code execution (RCE) by importing internet shells by way of a prone “/developmentserver/metadatauploader” endpoint.
The vulnerability was first flagged by ReliaQuest late final month when it discovered the shortcoming being abused in real-world assaults by unknown risk actors to drop internet shells and the Brute Ratel C4 post-exploitation framework.
In keeping with Onapsis, a whole lot of SAP programs globally have fallen sufferer to assaults spanning industries and geographies, together with power and utilities, manufacturing, media and leisure, oil and gasoline, prescribed drugs, retail, and authorities organizations.
The SAP safety agency mentioned it noticed reconnaissance exercise that concerned “testing with particular payloads towards this vulnerability” towards its honeypots way back to January 20, 2025. Profitable compromises in deploying internet shells had been noticed between March 14 and March 31.
Google-owned Mandiant, which can also be engaged in incident response efforts associated to those assaults, has proof of exploitation occurring on March 12, 2025.
In latest days, a number of risk actors are mentioned to have jumped aboard the exploitation bandwagon to opportunistically goal weak programs to deploy internet shells and even mine cryptocurrency.
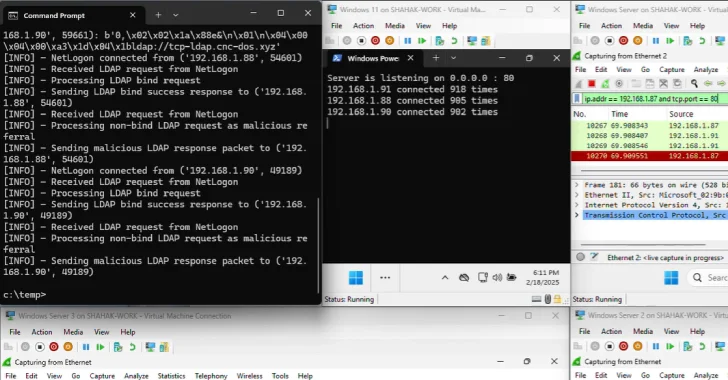
This, per Forescout, additionally contains Chaya_004, which has hosted a web-based reverse shell written in Golang known as SuperShell on the IP tackle 47.97.42[.]177. The operational know-how (OT) safety firm mentioned it extracted the IP tackle from an ELF binary named config that was put to make use of within the assault.
“On the identical IP tackle internet hosting Supershell (47.97.42[.]177), we additionally recognized a number of different open ports, together with 3232/HTTP utilizing an anomalous self-signed certificates impersonating Cloudflare with the next properties: Topic DN: C=US, O=Cloudflare, Inc, CN=:3232,” Forescout researchers Sai Molige and Luca Barba mentioned.
Additional evaluation has uncovered the risk actor must be internet hosting numerous instruments throughout infrastructure: NPS, SoftEther VPN, Cobalt Strike, Asset Reconnaissance Lighthouse (ARL), Pocassit, GOSINT, and GO Easy Tunnel.
“The usage of Chinese language cloud suppliers and several other Chinese language-language instruments factors to a risk actor possible primarily based in China,” the researchers added.
To defend towards assaults, it is important that customers apply the patches as quickly as potential, if not already, prohibit entry to the metadata uploader endpoint, disable the Visible Composer service if not in use, and monitor for suspicious exercise.
Onapsis CTO Juan Pablo JP Perez-Etchegoyen advised The Hacker Information that the exercise highlighted by Forescout is post-patch, and that it “will additional develop the specter of leveraging deployed internet shells not solely to opportunistic (and doubtlessly much less subtle) risk actors, but additionally extra superior ones appear to have been quickly reacting to this difficulty to leverage the prevailing compromises and additional develop.”