Our brains start to create inside representations of the world round us from the primary second we open our eyes. We perceptually assemble elements of scenes into recognizable objects due to neurons within the visible cortex.
This course of happens alongside the ventral visible cortical pathway, which extends from the first visible cortex in the back of the mind to the temporal lobes.
It is lengthy been thought that particular neurons alongside this pathway deal with particular kinds of info relying on the place they’re situated, and that the dominant circulation of visible info is feedforward, up a hierarchy of visible cortical areas. Though the reverse course of cortical connections, also known as suggestions, has lengthy been recognized to exist, its purposeful position has been little understood.
Ongoing analysis from the lab of Rockefeller College’s Charles D. Gilbert is revealing an necessary position for suggestions alongside the visible pathway.
As his crew demonstrates in a paper printed in PNAS, this countercurrent stream carries so-called “high down” info throughout cortical areas that’s knowledgeable by our prior encounters with an object.
One consequence of this circulation is that neurons on this pathway aren’t mounted of their responsiveness however can adapt second to second to the knowledge they’re receiving.
“Even on the first levels of object notion, the neurons are delicate to way more advanced visible stimuli than had beforehand been believed, and that functionality is knowledgeable by suggestions from greater cortical areas,” says Gilbert, head of the Laboratory of Neurobiology.
A special circulation
Gilbert’s lab has investigated basic facets of how info is represented within the mind for a few years, primarily by finding out the circuitry underlying visible notion and perceptual studying within the visible cortex.
“The classical view of this pathway proposes that neurons at its starting can solely understand easy info reminiscent of a line phase, and that complexity will increase the farther up the hierarchy you go till you attain the neurons that may solely reply to a selected degree of complexity,” he says.
Earlier findings from his lab point out that this view could also be incorrect. His group has, for instance, discovered that the visible cortex is able to altering its purposeful properties and circuitry, a top quality referred to as plasticity. And in work executed together with his Rockefeller colleague (and Nobel Prize winner) Torsten N. Wiesel, Gilbert found long-range horizontal connections alongside cortical circuits, which allow neurons to hyperlink bits of data over a lot bigger areas of the visible discipline than had been thought.
He is additionally documented that neurons can swap their inputs between these which can be task-relevant and people which can be task-irrelevant, underscoring the dexterity of their purposeful properties.
“For the present examine, we had been attempting to ascertain that these capabilities are a part of our regular means of object recognition,” he says.
Seeing is knowing
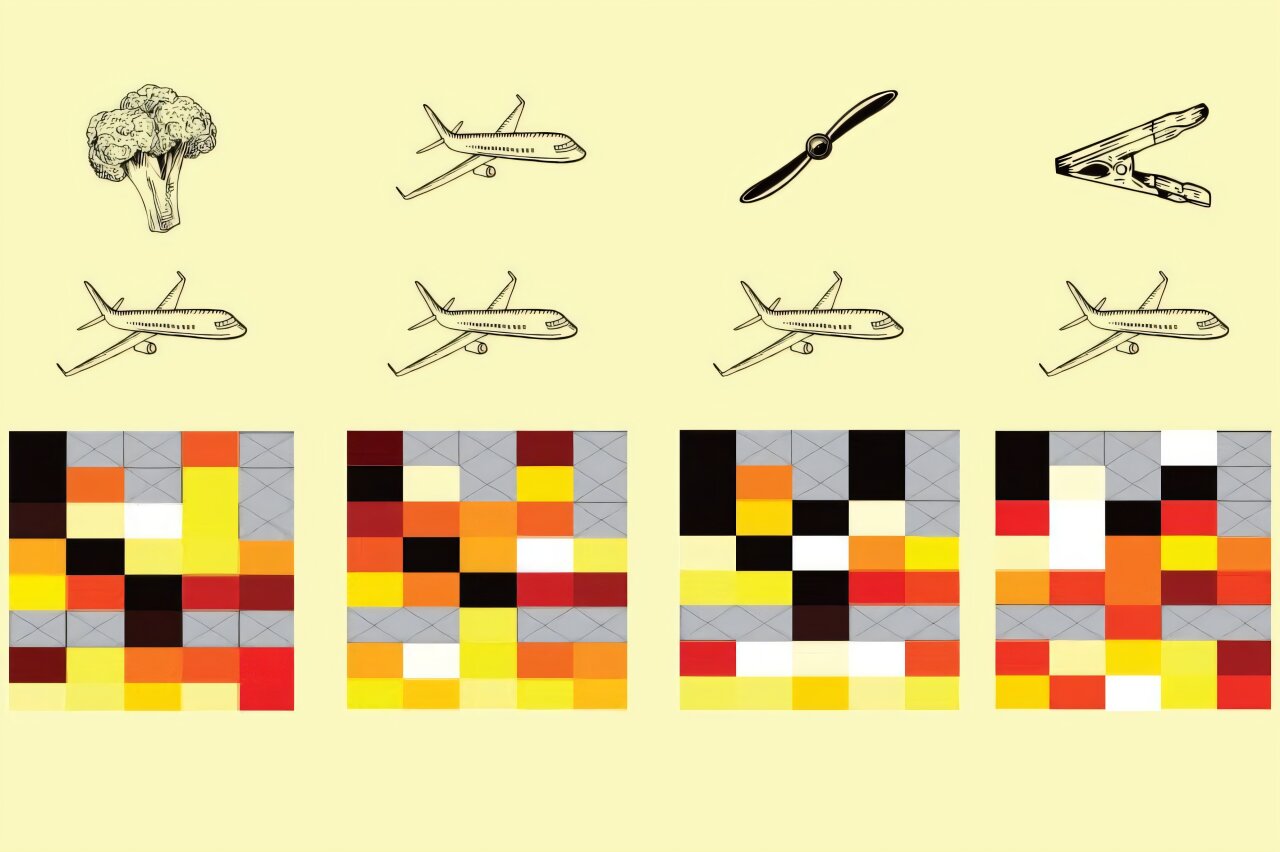
Gilbert’s lab spent a number of years finding out a pair of macaques that had been educated in object recognition utilizing photos of a wide range of objects the animals might or might not have had familiarity with, reminiscent of fruits, greens, instruments, and machines.
Because the animals discovered to acknowledge these objects, the researchers monitored their mind exercise utilizing fMRI to determine which areas responded to the visible stimuli. (This methodology was pioneered by Gilbert’s Rockefeller colleague Winrich Freiwald, who has used it to determine areas of the mind which can be conscious of faces.)
They then implanted electrode arrays, which enabled them to file the exercise of particular person nerve cells because the animals had been proven photos of the objects they’d been educated to acknowledge. Generally they had been proven the total object, and different instances a partial or tightly cropped picture. Then they had been proven a wide range of totally different visible stimuli and indicated whether or not they discovered a match to the unique object or not.
“These are referred to as delayed match-to-sample duties as a result of there’s a delay between after they see an object cue and when they’re proven a second object or object element, to which they’re educated to report whether or not the second picture corresponds to the preliminary cue,” Gilbert says.
“Whereas they’re trying by way of all of the visible stimuli to discover a match, they’ve to make use of their working reminiscence to remember the unique picture.”
Adaptive processing
The researchers discovered that over a variety of visible targets, a single neuron could also be extra responsive to 1 goal, and with one other cue, they will be extra conscious of a distinct goal.
“We discovered these neurons are adaptive processors that change on a moment-to-moment foundation, taking up totally different capabilities which can be acceptable for the instant behavioral context,” Gilbert says.
In addition they demonstrated that the neurons discovered firstly of the pathway, considered restricted to responding to easy visible info, weren’t really so constrained of their skills.
“These neurons are delicate to way more advanced visible stimuli than had beforehand been believed,” he says. “There would not appear to be as massive of a distinction when it comes to the diploma of complexity represented within the early cortical areas relative to the upper cortical areas as beforehand thought.”
These findings bolster what Gilbert believes is a novel view of cortical processing: that grownup neurons should not have mounted purposeful properties however are as a substitute dynamically tuned, altering their specificities with various sensory expertise.
Remark of cortical exercise additionally revealed a possible purposeful position of reciprocal suggestions connections in object recognition, the place the circulation of data from greater cortical areas to those decrease ones contributes to their dynamic capabilities.
“We found that these so-called ‘top-down’ suggestions connections convey info from areas of the visible cortex that symbolize beforehand saved details about the character and id of objects, which is acquired by way of expertise and behavioral context,” he says.
“In a way, the higher-order cortical areas ship an instruction to the decrease areas to carry out a specific calculation, and the return sign—the feedforward sign—is the results of that calculation. These interactions are more likely to be working frequently as we acknowledge an object and, extra broadly talking, make visible sense of our environment.”
Autism analysis purposes
The findings are a part of an growing recognition of the significance and prevalence of suggestions info circulation within the visible cortex—and maybe far past.
“I’d argue that top-down interactions are central to all mind capabilities, together with different senses, motor management, and better order cognitive capabilities, so understanding the mobile and circuit foundation for these interactions might develop our understanding of the mechanisms underlying mind problems,” Gilbert says.
To that finish, his lab is starting to analyze animal fashions of autism each on the behavioral and the imaging degree. Will Snyder, a analysis specialist in Gilbert’s lab, will examine perceptual variations between autism-model mice and their wild-type littermates.
In conjunction, the lab will observe massive neuronal populations within the animals’ brains as they have interaction in pure behaviors utilizing the extremely superior neuroimaging applied sciences within the Elizabeth R. Miller Mind Observatory, an interdisciplinary analysis middle situated on Rockefeller’s campus.
“Our purpose is to see if we will determine any perceptual variations between these two teams and the operation of cortical circuits which will underly these variations,” Gilbert says.
Extra info:
Tiago S. Altavini et al, Expectation-dependent stimulus selectivity within the ventral visible cortical pathway, Proceedings of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences (2025). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2406684122
Quotation:
Object recognition formed by prior expertise as mind adapts to new visible info, examine reveals (2025, Could 2)
retrieved 2 Could 2025
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2025-05-recognition-prior-brain-visual.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.