April 30, 2025
2 min learn
Key takeaways:
- Hospital wastewater evaluation confirmed that scientific respiratory viruses and different pathogens look like correct.
- The accuracy of antimicrobial resistance genes didn’t align with scientific instances within the hospital.
ORLANDO — Wastewater surveillance is mostly performed at native, state and nationwide inhabitants ranges, however a examine introduced at SHEA Spring urged it could possibly be helpful for well being care amenities to conduct themselves.
Guillermo Rodriguez–Nava, MD, third-year infectious illnesses fellow at Stanford College, who introduced the examine at SHEA, advised Healio that he’s solely conscious of a handful of establishments in america that conduct their very own wastewater surveillance and whether or not extra needs to be doing so was one of many questions the examine was aiming to reply.

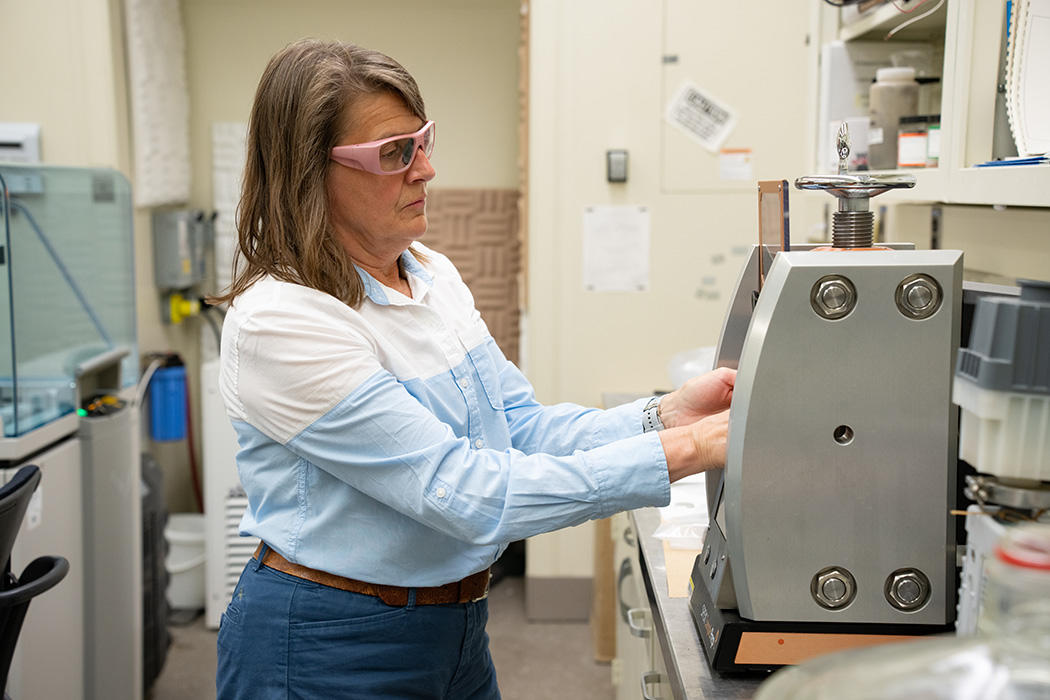
A wastewater surveillance trial program at Stanford Hospital urged the hassle could also be value it for bigger establishments, researchers stated at SHEA, however challenges to accuracy nonetheless stay. Picture: Adobe Inventory
“It might rely on the hospitals and what they’re attempting to do,” Rodriguez stated. “For respiratory viruses, maybe neighborhood wastewater is nice sufficient as normal, however for antibiotic resistant genes, perhaps some hospitals … [should] attempt to do it each 1 or 2 months to get an concept of what’s occurring when it comes to antimicrobial resistance.”
Early within the COVID-19 pandemic, the CDC began utilizing wastewater surveillance to detect upticks in SARS-CoV-2 instances. A number of research have proven that the surveillance technique can affirm spikes in scientific instances of COVID-19, influenza and RSV throughout respiratory virus season and a 2024 examine confirmed that detection of extremely pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza may have supplied consultants an early warning of its unfold.
Rodriguez and colleagues, in a pilot examine at Stanford Hospital, deployed a Teledyne ISCO 5800 wastewater autosampler to gather samples from the ultimate hospital outflow level earlier than the water merged with the neighborhood sewer system to find out if they might detect circulating pathogens amongst all folks within the facility.
The researchers programmed the sampler to gather 1,000 mL of water per week at a price of 15 mL each 151 minutes. They processed the samples inside 48 hours of assortment, separating solids utilizing centrifugation, and performed nucleic acid extraction and droplet digital PCR testing focusing on a set of pathogens.
The hospital wastewater nucleic acid concentrations had been then in contrast with the variety of constructive cultures on the hospital throughout the identical time interval and with neighborhood wastewater knowledge.
Based on Rodriguez, the researchers confronted a number of challenges, together with the situation of the wastewater outflow and the scale of the autosampler.
The samples paralleled the variety of scientific instances of an infection and had been just like neighborhood wastewater developments, he stated. He famous, nonetheless, that whereas mecA confirmed some alignment, most antimicrobial genes, together with vanA, and carbapenemase genes, together with KPC, NDM, OXA-48 and VIM, confirmed restricted alignment with scientific instances on the hospital.
Hospital wastewater additionally had a better focus of resistant genes than neighborhood wastewater, he stated.
General, Rodriguez stated the flexibility to trace scientific respiratory virus developments by facility wastewater could possibly be helpful, however that figuring out developments for antimicrobial resistance is tougher due to a spread of potential extra influences. These may embrace the variety of colonized sufferers, bacterial load within the hospital’s sewage system, hospital antimicrobial use and drug residues within the water.
Relating to particular person amenities and well being techniques making a call on wastewater surveillance, Rodriguez stated it doubtless comes all the way down to the ability itself, their dimension and their wants, in addition to modifications to public well being funding and packages — which regularly pay for these kinds of efforts.
“It relies upon,” Rodriguez stated. “Some amenities could profit from it, maybe some wouldn’t. We’re fortunate sufficient that we’re in an space the place there may be plenty of biotech corporations to take a position on this. So, maybe this may be outsourced to the business facet to distribute prices to non-public sources reasonably than the federal government.”
For extra data:
Guillermo Rodriguez–Nava, MD, might be reached at guiro@stanford.edu.