9to5Mac is delivered to you by Incogni: Shield your private information from prying eyes. With Incogni, you’ll be able to scrub your deeply delicate data from information brokers throughout the net, together with folks search websites. Incogni limits your telephone quantity, tackle, e-mail, SSN, and extra from circulating. Combat again in opposition to undesirable information brokers with a 30-day a reimbursement assure.
In case you’ve by no means heard about iCloud Non-public Relay, it’s principally a privateness function that Apple launched in 2021 as a part of the iCloud+ subscription. It allows you to shield your information when looking the net in Safari. Right here’s the way it works, and whether or not you ought to be utilizing it.
First issues first. Is Non-public Relay a VPN?
Brief reply, no.
Barely longer reply, there are just a few key variations between iCloud Non-public Relay and a VPN. The primary distinction is that whereas a VPN usually encrypts and reroutes your complete web site visitors throughout apps and web sites, iCloud Non-public Relay provides sure privateness layers when utilizing Safari.
Which privateness layers?
Glad you requested.
While you browse the net, each your web supplier and the web sites you go to can see your IP tackle. Over time, this data might be collected to construct a profile for, amongst different issues, focused promoting.
Likewise, once you entry an internet site, your machine makes a DNS request that sometimes goes via your web supplier. This offers them perception into the web sites you’re attempting to succeed in and, mixed along with your IP tackle, a clearer image of who you’re over time. That’s plenty of information it’s possible you’ll be handing over simply by looking.
What iCloud Non-public Relay does is cut up your looking exercise on Safari into “two separate, safe web relays.” Right here’s Apple on the way it handles your Safari exercise as soon as iCloud Non-public Relay is turned on:
- Your IP tackle is seen to your community supplier and to the primary relay, which is operated by Apple. Your DNS information are encrypted, so neither celebration can see the tackle of the web site you’re attempting to go to.
- The second relay, which is operated by a third-party content material supplier, generates a short lived IP tackle, decrypts the title of the web site you requested, and connects you to the positioning.

In different phrases, no person has full visibility into who you’re and what web site you’re visiting. Your web supplier and Apple know you’re attempting to go someplace, however they don’t know the place, whereas the third-party relay is aware of the place you’re going, however not who you’re.
What are the drawbacks?
Does the web pace get affected?
Apple says that since pace checks open simultaneous connections to check your web pace, that goes in opposition to the best way iCloud Non-public Relay works, which is on a “single, safe connection to take care of privateness and efficiency.” In observe, although, the reality is that whereas there could also be a small impression on pace, web connections these days are quick sufficient for that to not be noticeable.
Will I’ve connectivity issues?
When you may sometimes run into points with sure web service suppliers (like these on airplanes or in lodges), that’s the exception. I’ve used iCloud Non-public Relay for years, and I can’t bear in mind the final time I needed to flip it off to repair a connectivity subject. It’s price preserving Non-public Relay in thoughts as a troubleshooting step, nevertheless it’ll not often be the wrongdoer.
What about geolocation points?
iCloud Non-public Relay at all times makes use of IP addresses based mostly in your nation and time zone, so it is rather unlikely that you’ll run into geoblocking points when utilizing it. However like with web connectivity issues, maintain it in thoughts when troubleshooting your connection.
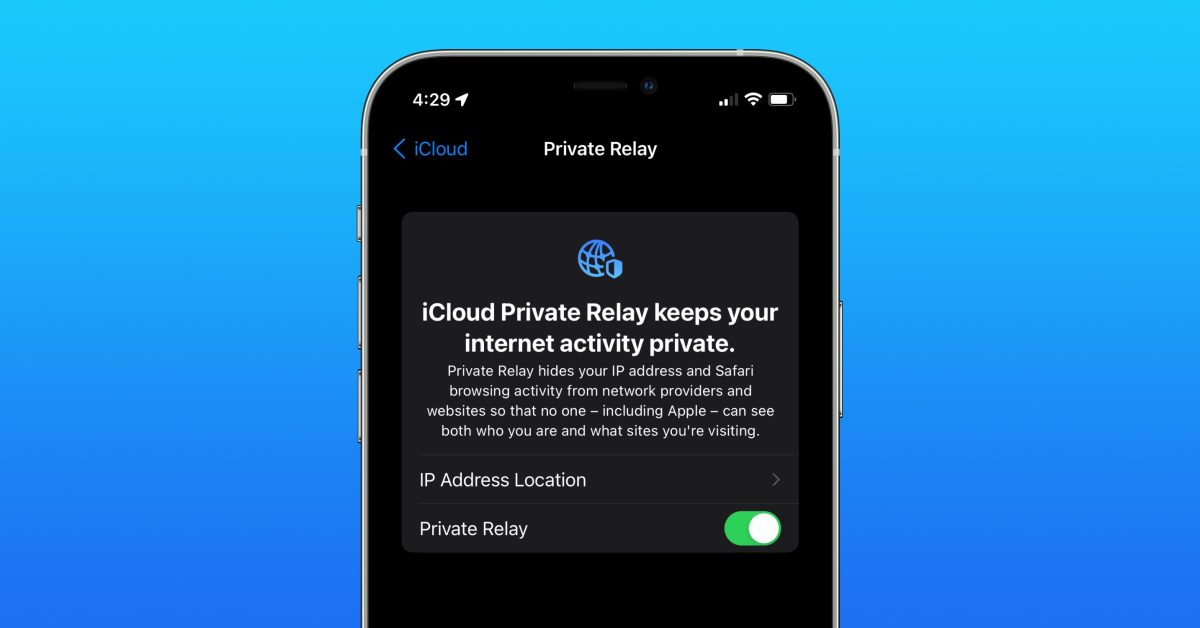
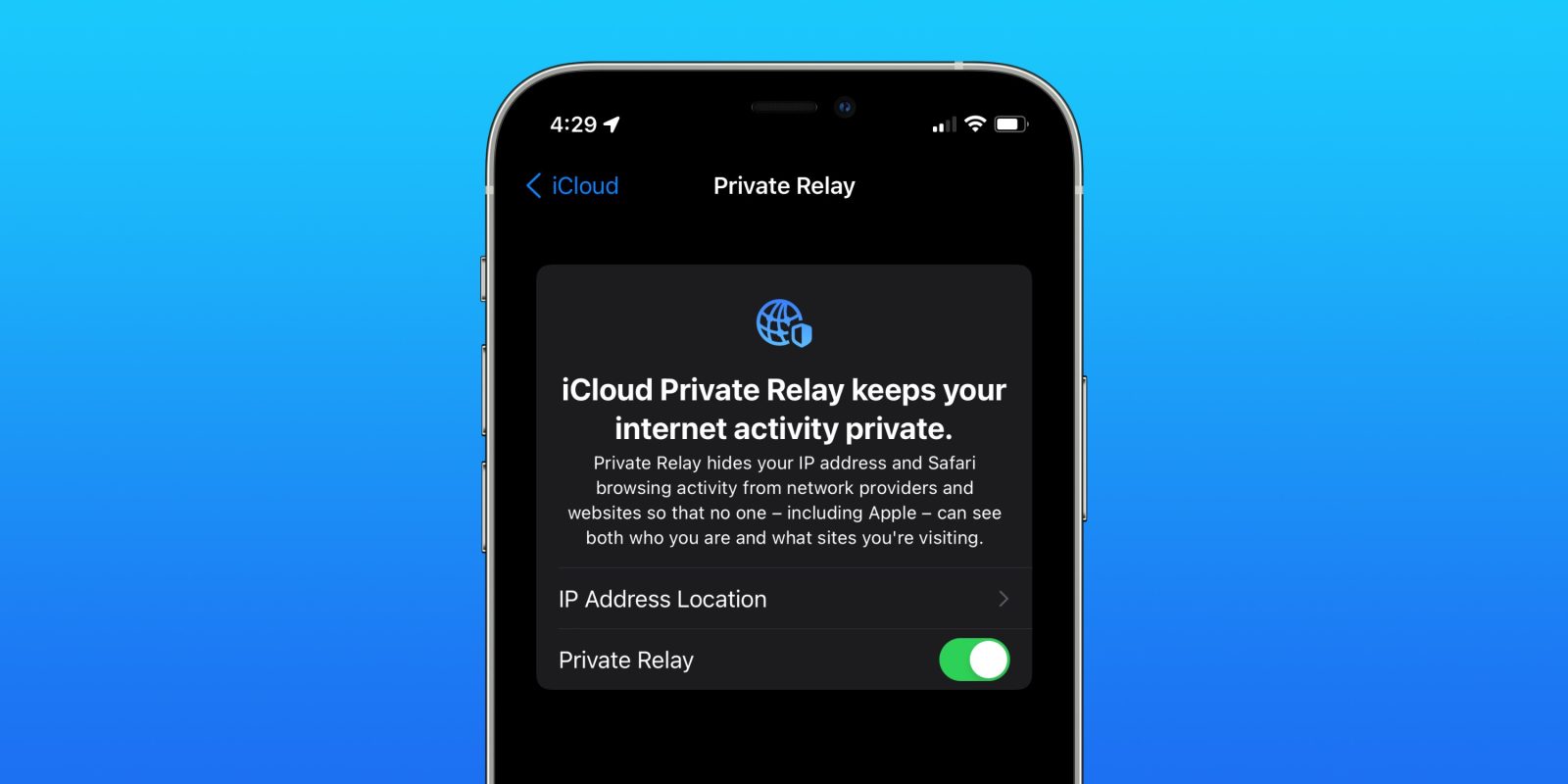
Establishing iCloud Non-public Relay
It’s price noting that the function requires an energetic iCloud+ subscription, whether or not a person or household plan, and it solely works in Safari.
Listed here are Apple’s official directions on the way to arrange iCloud Non-public Relay in your iPhone or iPad
- In your iPhone or iPad, go to Settings > [your name] > iCloud.
- Faucet Non-public Relay, then activate Non-public Relay.
- To vary your location settings, faucet IP Deal with Location.
And right here’s the way to arrange iCloud Non-public Relay in your Mac
- In your Mac, select Apple menu > System Settings, then click on your title on the high of the sidebar.
If you don’t see your title, click on “Sign up”, enter your Apple Account e-mail tackle or telephone quantity, then enter your password. - Click on iCloud, click on Non-public Relay, then activate Non-public Relay.
- To vary your location settings, click on Choices.
9to5Mac take: Do you have to use Non-public Relay?
As I prefer to say, right here is no person’s favourite reply: it relies upon.
Non-public Relay presents complete safety in opposition to monitoring your actions throughout the net, so it is likely to be price turning it on and observing whether or not it impacts your looking exercise.
Likelihood is, the impression shall be minimal, with an upside that your information shall be safer, supplied that you’re a Safari person.

9to5Mac is delivered to you by Incogni: Shield your private information from prying eyes. With Incogni, you’ll be able to scrub your deeply delicate data from information brokers throughout the net, together with folks search websites. Incogni limits your telephone quantity, tackle, e-mail, SSN, and extra from circulating. Combat again in opposition to undesirable information brokers with a 30-day a reimbursement assure.
Accent offers on Amazon
FTC: We use earnings incomes auto affiliate hyperlinks. Extra.