A person in his 50s has died from lyssavirus in New South Wales after being bitten by a bat a number of months in the past.
That is Australia’s fourth human case of bat lyssavirus and the primary confirmed case in NSW for the reason that virus was first recognized in 1996 in a black flying fox in Queensland.
So what’s lyssavirus? And how are you going to shield your self should you come into contact with a bat?
A detailed relative of rabies
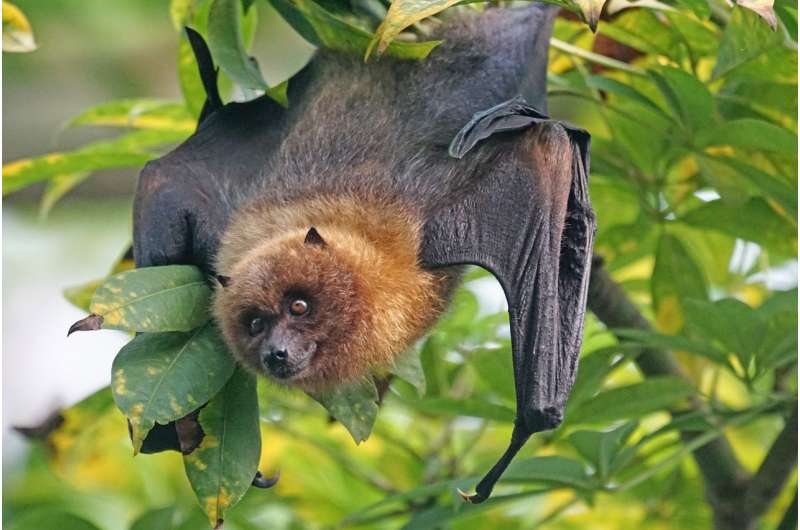
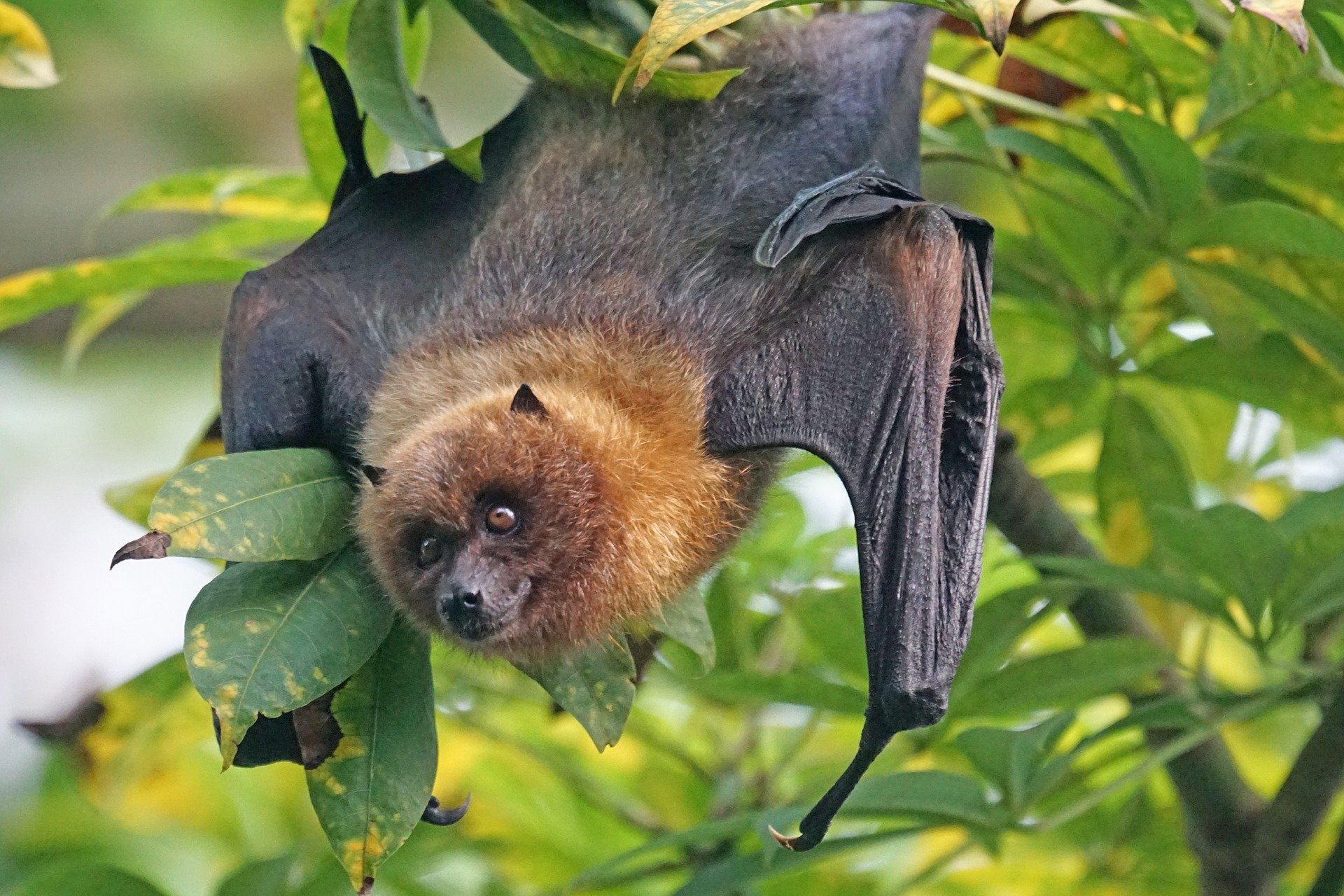
Australian bat lyssavirus belongs to the Rhabdoviridae household, the identical group of viruses that causes rabies.
It primarily infects bats. Energetic monitoring suggests fewer than 1% of wholesome bats carry the virus, although the prevalence rises to five–10% in sick or injured bats.
In bats, the virus usually causes no apparent signs, although some present neurological indicators reminiscent of disorientation, aggression, muscle spasms and paralysis. Some will die.
The virus has been confirmed in all 4 mainland flying fox species (Pteropus alecto, P. poliocephalus, P. scapulatus and P. conspicillatus) in addition to the yellow-bellied sheathtail bat (Saccolaimus flaviventris), a species of microbat.
Nonetheless, serological proof—the place scientists check for antibodies in bats’ blood—suggests different microbats might be vulnerable too. So we needs to be cautious of all Australian bat species in relation to lyssavirus.
Uncommon, however probably lethal
Not like rabies, which causes roughly 59,000 human deaths yearly, predominantly in Africa and Asia, human an infection with bat lyssavirus is extraordinarily uncommon.
Australian bat lyssavirus, because the identify suggests, is exclusive to Australia. However different bat lyssaviruses, reminiscent of European bat lyssavirus, have equally brought about uncommon human infections.
Human an infection with bat lyssavirus happens by direct contact with contaminated bat saliva through bites, scratches or open pores and skin. It could actually additionally happen if our mucous membranes (eyes, nostril, mouth) are uncovered to bat saliva.
There isn’t any threat related to bat feces, urine, blood, or informal proximity to roosts.
If somebody has been uncovered, there’s an incubation interval which might vary from weeks to greater than two years. Throughout this time, the virus slowly strikes by the physique’s nerves to the mind, staying hidden and symptom-free.
Treating the virus through the incubation interval can stop the sickness. But when it is not handled, signs are severe and it is invariably deadly.
The character of the sickness in people mirrors rabies, starting with flu-like signs (fever, headache, fatigue), then rapidly progressing to extreme neurological illness, together with paralysis, delirium, convulsions, and lack of consciousness. Demise usually happens inside one to 2 weeks of symptom onset.
All 4 recorded human circumstances in Australia—three in Queensland (in 1996, 1998 and 2013) and the current NSW case—have been deadly.
There isn’t any efficient remedy as soon as signs develop
If somebody is probably uncovered to bat lyssavirus and seeks medical consideration, they are often handled with post-exposure prophylaxis, consisting of rabies antibodies and the rabies vaccine.
This intervention is extremely efficient if initiated promptly—ideally inside 48 hours, and no later than seven days post-exposure—earlier than the virus enters the central nervous system.
However no efficient remedy exists for Australian bat lyssavirus as soon as signs develop. Rising analysis on monoclonal antibodies presents potential future therapies, nonetheless these should not but out there.
So what’s one of the best safety? And what if a bat bites you?
Pre-exposure rabies vaccination, involving three doses over one month, is really helpful for high-risk teams. This contains veterinarians, animal handlers, wildlife rehabilitators, and laboratory employees dealing with lyssaviruses.
It is vital for members of the general public to keep away from all direct contact with bats. Solely vaccinated, educated professionals, reminiscent of wildlife caregivers or veterinarians, ought to deal with bats.
Public schooling campaigns are important to scale back dangerous interactions, particularly in bat-populated areas.
In case you get bitten or scratched by a bat, it is vital to behave instantly. Wash the wound completely with cleaning soap and water for at the least quarter-hour, apply an antiseptic (reminiscent of betadine), and search pressing medical consideration.
This tragic case in NSW underscores that, whereas extraordinarily uncommon, bat lyssavirus is a vital public well being menace. We have to see enhanced public consciousness and guarantee vaccination for high-risk teams, alongside ongoing bat monitoring and analysis into new therapies.
This text is republished from The Dialog beneath a Artistic Commons license. Learn the authentic article.![]()
Quotation:
Lyssavirus is uncommon, however lethal: What do you have to do if a bat bites you? (2025, July 4)
retrieved 5 July 2025
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2025-07-lyssavirus-rare-deadly.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.