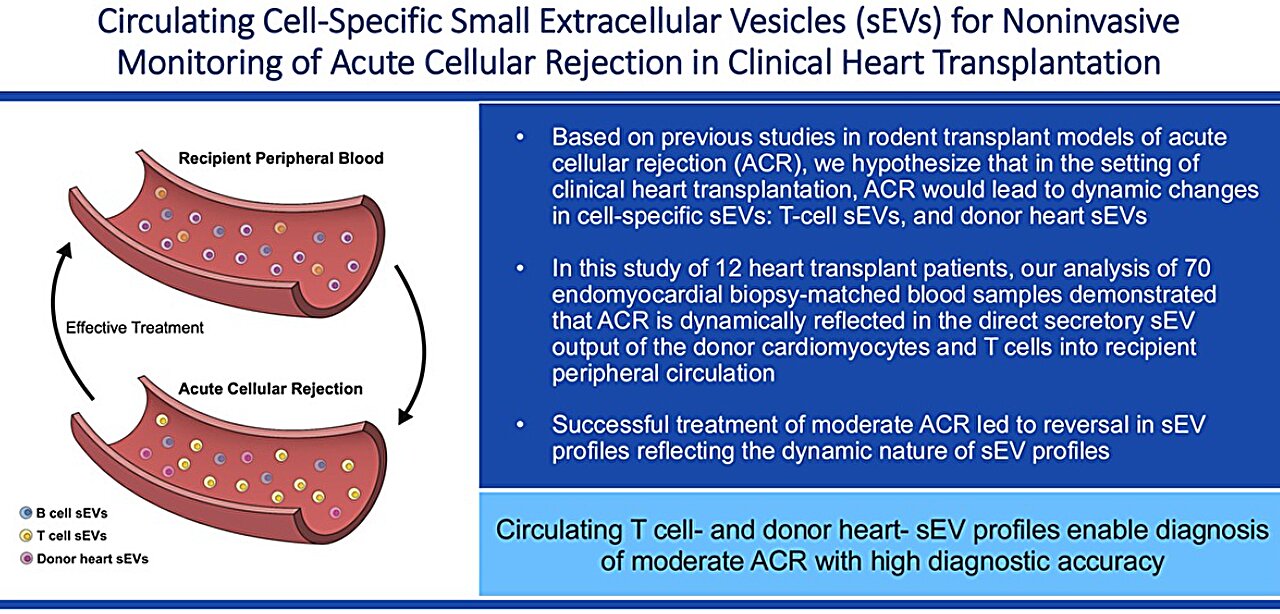
Following a coronary heart transplant, sufferers should bear surgical biopsies in order that clinicians can monitor for indicators of organ rejection. A brand new examine reveals the promise of a biomarker that would permit docs to exchange these invasive biopsies with a easy blood take a look at. The outcomes are printed within the journal Transplantation.
To speak with each other, cells launch exosomes—little organic packets containing varied molecules that switch data to different cells. Over the past decade, Yale College of Medication (YSM) researchers have been learning the potential of exosomes to function a biomarker for coronary heart transplant rejection in animal fashions.
The brand new examine in coronary heart transplant sufferers is a leap ahead in translating these ideas in animal research to coronary heart transplant sufferers, bringing new biomarker testing from the laboratory into the medical setting.
“Our sufferers have few choices for surveillance for rejection,” says examine co-author Sounok Sen, MD, medical director of the Yale Cardiac Transplantation and Mechanical Circulatory Help Program and assistant professor of drugs (cardiology) at YSM. “The gold normal has at all times been a coronary heart biopsy, however we at all times questioned if there have been higher methods to do that that did not require invasive procedures.”
The examine was led by principal investigator Prashanth Vallabhajosyula, MD, affiliate professor of surgical procedure (cardiac), together with Sen and first writer Laxminarayana Korutla, Ph.D., a analysis scientist at YSM.
“For the previous 50-plus years, ever since we began doing coronary heart transplants, there was a drive to exchange repeated coronary heart biopsies as a result of it isn’t sensible to maintain doing invasive biopsy process after process,” says Vallabhajosyula. “Having a noninvasive molecular window into what the cells of curiosity are doing with reference to the transplanted organ is crucial.”
Organ rejection related to coronary heart and T cell exosome modifications
Rejection happens when the affected person’s personal immune system acknowledges a transplanted organ as international and mounts an immune response in opposition to it. The most typical form of rejection is called acute mobile rejection, which is mediated by a sort of immune cell often known as T cells.
“T cells are continuously surveilling their setting, in search of infections and different issues which can be ‘non-self,'” Vallabhajosyula explains. “They see the transplanted coronary heart as non-self, so that they mount an assault.”
Clinicians grade acute mobile rejection as delicate, reasonable, or extreme. Gentle rejection is commonly asymptomatic, although some sufferers could expertise refined, flu-like signs. In reasonable or extreme circumstances, signs could embrace quick or irregular heartbeat, drop in blood strain, dizziness, and shortness of breath.
Utilizing a tissue biopsy, pathologists can search for indicators of rejection such because the presence of T cells and assign a grade based mostly on the severity of the extent of harm the T cells trigger to the transplanted coronary heart.
This grading helps information therapy choices. Remedy for reasonable or extreme acute mobile rejection contains growing immunosuppressive drugs to reverse rejection, whereas delicate circumstances usually simply require cautious monitoring of the affected person.
For the examine, the researchers took blood samples from 12 coronary heart transplant sufferers earlier than and after surgical procedure and examined the molecular cargo inside exosomes launched by T cells, one other kind of immune cell referred to as B cells, and the donor coronary heart. Six of those sufferers cumulatively skilled 11 reasonable acute mobile rejection episodes.
When the donor coronary heart was not being rejected by T cells, the researchers discovered particular portions of numerous molecular cargo contained by the exosomes from the guts and T cells. However when the guts was present process rejection, they noticed a rise in sure markers related to the rejection course of.
Importantly, one examine participant developed a special kind of organ rejection referred to as antibody-mediated rejection, which is mediated primarily by B cells with the assistance of T cells. By trying inside exosomes from the affected person’s B cells, the researchers have been capable of detect the sort of rejection as properly.
As a result of the therapies for acute mobile and antibody-mediated rejection are totally different, having a take a look at that may detect and distinguish between the varieties of transplant rejection could possibly be a great tool for aiding clinicians in figuring out a therapy plan.
“That is the primary time that we have had a noninvasive methodology to delineate between the several types of rejection which will happen throughout the coronary heart,” Sen says. The staff is additional learning this functionality of their new take a look at in ongoing analysis.
New take a look at detects early organ rejection and therapy efficacy
Over the previous couple of a long time, researchers have explored different biomarkers to exchange surgical biopsies. Most circumstances of acute mobile rejection occur throughout the first six months following the transplantation process. Nonetheless, the few blood assessments which can be commercially accessible are ineffective at detecting rejection throughout the first 30 days after the transplant.
Within the present examine, 10 out of the 11 rejection episodes occurred throughout the first 38 days post-transplant and the researchers efficiently detected all of them. “With the platform that we designed, we didn’t have any closing dates,” Vallabhajosyula says. “We will now begin in search of rejection from the very starting.”
Moreover, when a surgical biopsy detects reasonable or extreme rejection, clinicians have to deal with it by growing the affected person’s immunosuppressive drugs. However at present, there isn’t any good technique to noninvasively affirm if the therapy is working. “Generally, sufferers find yourself getting three, 4, 5 biopsies after we have detected rejection,” says Vallabhajosyula.
When sufferers within the present examine have been handled for rejection, the researchers noticed that the exosome profiles of the T cells and donor coronary heart cells reverted again towards baseline. “Not solely can we detect rejection, however our investigation additionally means that we will use our exosome platform to doubtlessly monitor the efficacy of therapy of rejection,” Vallabhajosyula says.
Bettering the lives of coronary heart transplant sufferers
Now, the YSM staff is analyzing biopsy samples from greater than 100 sufferers. With this bigger cohort, they’re amassing extra information on their platform’s capacity to check for various sorts of rejection, like antibody-mediated rejection. “There are thrilling alternatives to see the total potential of the sort of evaluation to assist transplant sufferers sooner or later,” says Sen.
At present, taking biopsies of the guts stays the gold normal for detecting transplant rejection, however it’s not with out its dangers. For instance, Vallabhajosyula remembers a affected person on whom he had carried out a coronary heart transplant. The transplant surgical procedure was profitable, however after a routine coronary heart biopsy seven days post-operation, the affected person suffered an issue together with her tricuspid valve that prompted renal failure. Vallabhajosyula needed to carry out extra surgical procedure to repair the harm.
Having a much less invasive technique to monitor a person’s immune response could be life-changing for recipients of transplanted organs, the Yale staff says. “As a doctor, once you undergo experiences like that along with your affected person, you always remember it,” Vallabhajosyula says. “If science like this may doubtlessly assist keep away from such conditions for our sufferers, what extra may I ask for as a doctor?”
Vallabhajosyula says this work would not have been potential with out the collaboration between his supportive laboratory employees, Sen and the Coronary heart Failure Program, the guts failure program on the College of Pennsylvania, and Korutla’s experience.
Extra data:
Laxminarayana Korutla et al, Circulating Tissue Particular Extracellular Vesicles for Noninvasive Monitoring of Acute Mobile Rejection in Scientific Coronary heart Transplantation, Transplantation (2025). DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000005369
Quotation:
For coronary heart transplant sufferers, blood take a look at could detect rejection earlier and extra simply (2025, June 30)
retrieved 30 June 2025
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2025-06-heart-transplant-patients-blood-earlier.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.