Key takeaways:
- Researchers in contrast aloe vera and sodium hypochlorite as disinfectants for dental unit water strains.
- Aloe vera was superior as an antibacterial, whereas sodium hypochlorite was more practical as an antifungal.
PHOENIX — Aloe vera could possibly be an efficient possibility for disinfecting water strains with information offered on the Affiliation for Professionals in An infection Management and Epidemiology annual assembly displaying it was akin to sodium hypochlorite.
“We wished to discover safer, ecofriendly options to sodium hypochlorite for disinfecting dental unit waterlines (DUWLs),” Hagar L. Mowafy, MD, CIC, an infection management advisor at Cairo College Hospital, informed Healio. “Aloe vera was chosen for its well-documented antimicrobial and antifungal properties, and its current use in oral care merchandise, although its use in DUWLs hasn’t been effectively studied.”

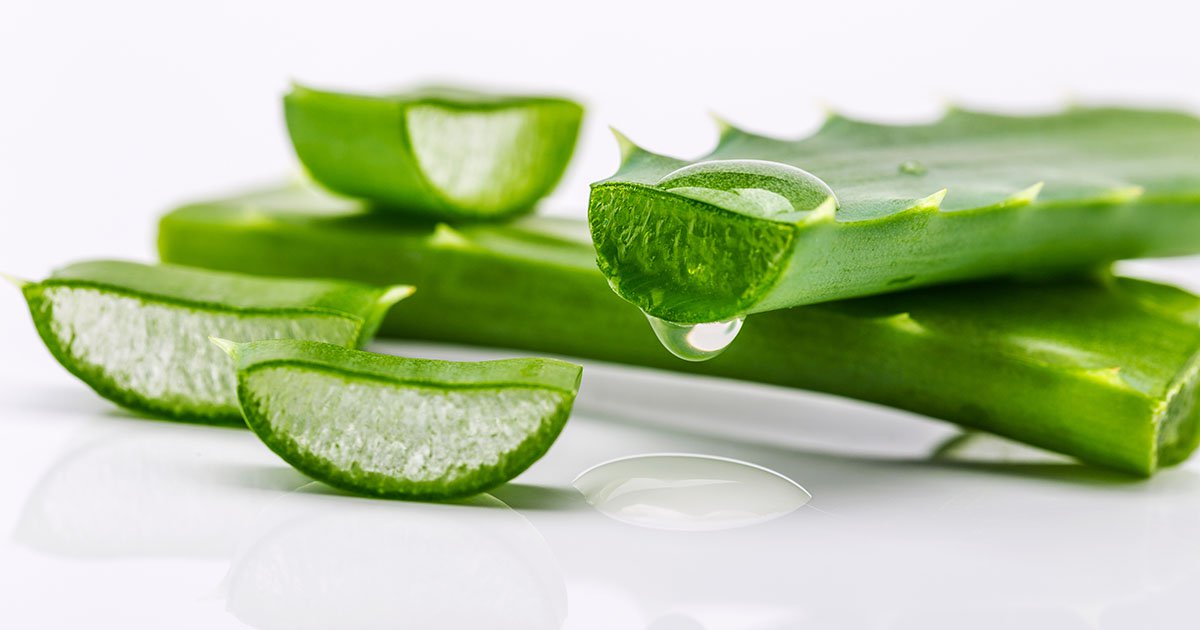
Researchers in contrast aloe vera and sodium hypochlorite as disinfectants for dental unit water strains, with aloe vera appearing as a superior antibacterial disinfectant, whereas sodium hypochlorite was more practical as an antifungal. Picture: Adobe Stocok.
To evaluate the antimicrobial impact of aloe vera on DUWLs and examine it towards generally used sodium hypochlorite, Mowafy and colleagues utilized the disinfectants to the DUWLs for two hours.
Pre- and post-treatment water samples have been from DUWL bottles and air/water syringes and each units of samples have been then analyzed for bacterial and fungal colony-forming models. In keeping with the research, the researchers then performed a statistical evaluation to check the disinfection efficacy of aloe vera vs. sodium hypochlorite.
Total, the research confirmed that aloe vera considerably decreased bacterial colony-forming models in DUWL samples, with comparable outcomes to sodium hypochlorite.
Particularly, the information confirmed that aloe vera demonstrated superior antibacterial efficacy, reaching a better discount in bacterial colony-forming models in contrast with sodium hypochlorite (P < .05), though sodium hypochlorite was more practical in lowering fungal colony-forming models (P < .05).
Based mostly on these outcomes, Mowafy mentioned that aloe vera could possibly be a “promising pure adjunct” or various for water line disinfection — significantly for bacterial management.
“It’s not but a full alternative for chemical disinfectants, however it could possibly be a beneficial part of multimodal disinfection methods,” she mentioned. “Future research are wanted to find out optimum focus, frequency, contact time, and to evaluate any long-term results or compatibility with dental gear.”
Moreover, Mowafy mentioned that utilizing aloe vera to disinfect water strains could possibly be an possibility at different amenities if finished correctly and “particularly if standardized industrial formulations are developed.”
“Our preparation was guide, which isn’t sensible for every day use, however aloe vera could possibly be particularly helpful in lower-resource settings or the place affected person consolation and gear longevity are priorities,” she mentioned.
For extra data:
Hagar L. Mowafy, MD, CIC, could be reached at hagarmowafy@kasralainy.edu.eg.