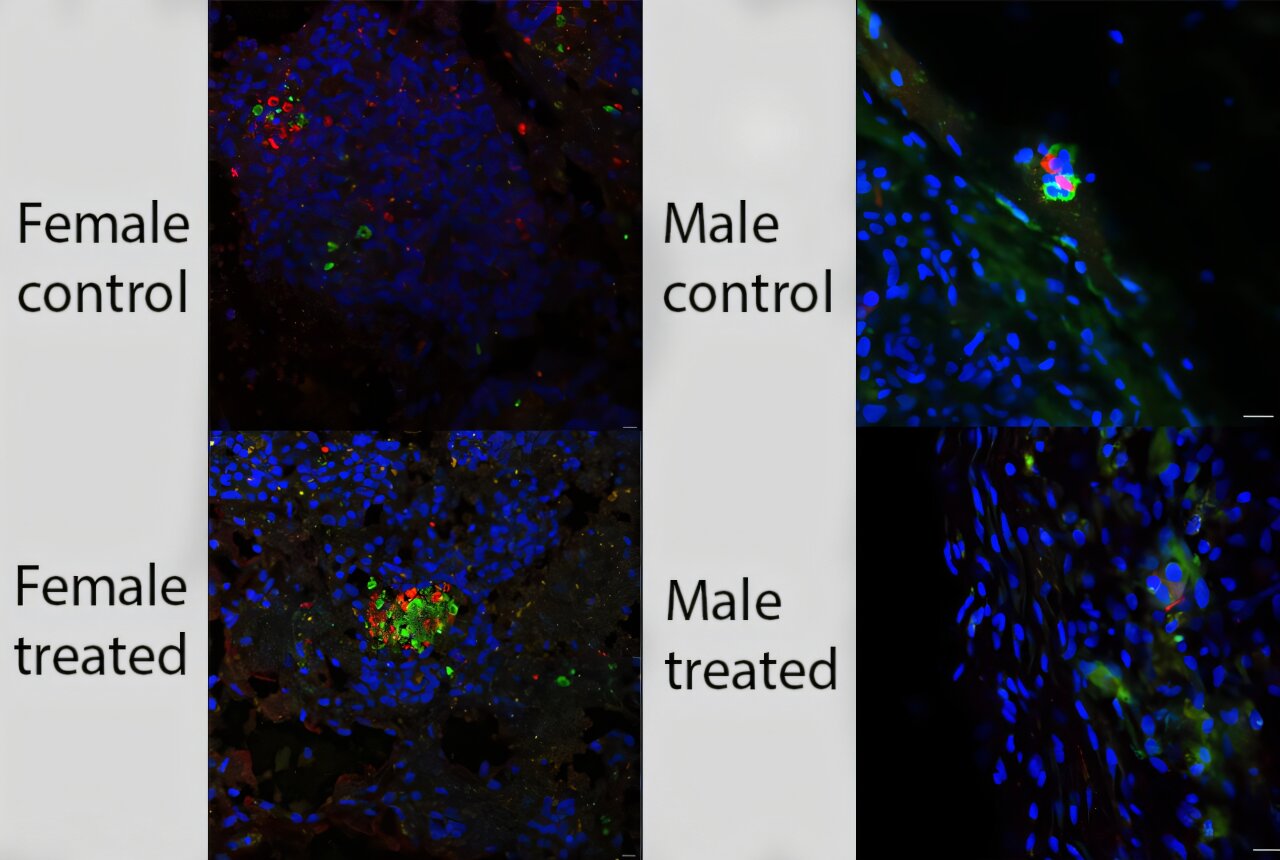
A pretreatment step might assist transplanted pancreatic islets survive longer in sufferers with sort 1 diabetes, based on a brand new preclinical research from Weill Cornell Medication investigators. One mixture of small molecules prolonged the cells’ lives in feminine mice, and including two molecules to the combination boosted cell survival in male mice.
The findings, revealed on June 24 in Cell Stem Cell, might permit physicians to deal with extra sufferers with fewer cells.
In sort 1 diabetes, autoimmune cells assault the pancreatic islets, destroying the insulin-producing beta cells and leaving sufferers depending on insulin injections. The present FDA-approved transplant process replaces these cells with pancreatic islet cells from a number of deceased organ donors. It usually takes as much as 48 hours to isolate islets from the donor for injection right into a vein that carries them to the recipient’s liver. As soon as within the liver, the islet cells start producing insulin, simply as they’d in a wholesome pancreas.
Nevertheless, many transplanted cells die quickly after the process, and issues can come up from focusing on the liver. Transplanting the cells underneath the pores and skin, an choice with some potential benefits, additionally has challenges with dying cells. Dr. Shuibing Chen, the Kilts Household Professor of Surgical procedure and director of the Heart for Genomic Well being at Weill Cornell Medication, famous analysis by others displaying that pretreating a sort of cell used to replenish blood cell populations throughout a six-hour interval improves their survival after a transplant, so she explored the same strategy for islet cells.
“With our new technique, we must always solely want one donor per affected person, or perhaps one donor might contribute cells to 2 sufferers, lessening the ready time for sufferers to obtain the remedy,” mentioned Dr. Chen, who can be a member of the Hartman Institute for Therapeutic Organ Regeneration at Weill Cornell Medication.
Small molecule cocktails
Figuring out the perfect pretreatment strategy usually requires a number of costly and labor-intensive drug screens, however J. Jeya Vandana, graduate pupil within the Tri-Institutional Ph.D. Program in Chemical Biology and first creator of the paper, had an concept.

“Jeya mixed chemical screens with single cell RNA-sequencing expertise in order that we might test a number of readouts in a single experiment,” mentioned Dr. Chen.
With their system, which they name ChemPerturb-Seq, every cell in an experiment receives a singular barcode and is handled for 48 hours with a singular small molecule drug. After the therapy, the group swimming pools the cells and sequences the RNA. The barcode tells the researchers which cells responded properly to a sure molecule. All the information are made publicly out there by means of an internet site known as ChemPerturbDB, which is powered by a man-made intelligence assistant that’s just like ChatGPT.
Intercourse variations
Performing ChemPerturb-Seq with a human beta cell line led to the invention of a pretreatment they known as LIP. This mixture of beta-lipotropin, insulin progress factor-1 and prostaglandin E2 boosted the survival of beta cells and human islets from donors when transplanted subcutaneously in a type-1 diabetes mouse mannequin in comparison with controls. However there was a catch.
“Jeya first transplanted every thing into feminine mice, and the strategy labored very properly, however when she transplanted the pretreated cells into male mice, it failed,” mentioned Dr. Chen.
Going again to the drafting board, the group used ChemPerturb-Seq to foretell different small molecules that might assist the cells stay longer in males. The consequence was a cocktail known as LIPHS, which included the three LIP molecules plus histamine and serotonin, that was profitable in males.
Armed with their new approach, Dr. Chen’s group will conduct extra research to see whether or not the outcomes maintain for added preclinical fashions. The group can be including much more small-molecule knowledge to the web site.
Dr. Shuibing Chen is the co-founder of Oncobeat and iOrganBio, Inc.
Extra info:
J. Jeya Vandana et al. ChemPerturb-Seq Display Identifies a Small Molecule Cocktail Enhancing Human Beta Cell Survival After Subcutaneous Transplantation, Cell Stem Cell (2025). DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2025.06.002. www.cell.com/cell-stem-cell/fu … 1934-5909(25)00224-3
Quotation:
Small molecule therapy might make islet transplantation remedy more practical (2025, June 24)
retrieved 24 June 2025
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2025-06-small-molecule-treatment-islet-transplantation.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.