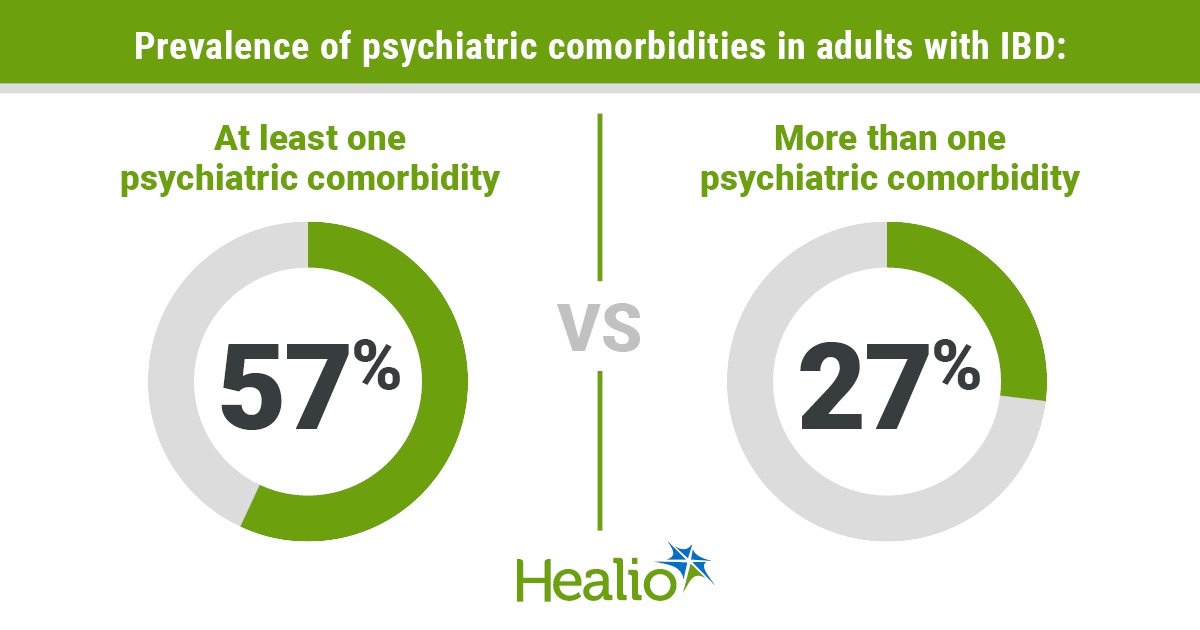
Key takeaways:
- An evaluation of blood biomarkers revealed that an omega-6 fatty acid could assist decrease dangers for CVD and sort 2 diabetes.
- Researchers mentioned it might assist cut back irritation.
ORLANDO — Linoleic acid, an omega-6 fatty acid, could assist decrease dangers for sort 2 diabetes and CVD, highlighting the dietary potential for seed oils, in keeping with a presentation on the annual NUTRITION assembly.
Prior observational proof signifies there’s a connection between omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids and a diminished danger for sort 2 diabetes, Kevin C. Maki, PhD, an adjunct professor on the Indiana College College of Public Well being-Bloomington and chief scientist at Midwest Biomedical Analysis, and colleagues wrote in a latest research. And linoleic acid — present in plant meals and vegetable oils, particularly seed oils like corn and soybean — is the first supply of omega-6 fatty acid in individuals’s diets, in keeping with a press launch.

“There was rising consideration on seed oils, with some claiming these oils promote irritation and lift cardiometabolic danger,” Maki mentioned within the launch.
Maki and colleagues carried out a cross-sectional evaluation to guage potential hyperlinks between omega-6 and serum linoleic acid with BMI and glucose homeostasis biomarkers.
“Our research, based mostly on nearly 1,900 individuals, discovered that larger linoleic acid in blood plasma was related to decrease ranges of biomarkers of cardiometabolic danger, together with these associated to irritation,” Maki mentioned within the launch. “Though different research have assessed relationships between linoleic acid and cardiometabolic danger elements, our research used goal biomarkers reasonably than weight loss program information or meals frequency questionnaires to evaluate linoleic acid consumption. We additionally measured a variety of markers of irritation and indicators of glucose metabolism.”
Greater ranges of linoleic acid had been constantly linked to decrease ranges of identified danger elements for sort 2 diabetes and CVD, like insulin and glucose. Additionally they noticed decrease ranges of biomarkers for irritation like serum amyloid A, glycoprotein acetyls and C-reactive protein.
“We noticed constant outcomes throughout the completely different biomarkers measured,” Maki mentioned within the launch. “Folks with larger ranges of linoleic acid of their blood tended to have a more healthy general danger profile for coronary heart illness and diabetes.”
The findings “help the necessity for extra intervention research” to see if rising consumption of linoleic acid would enhance cardiometabolic danger elements and decrease the incidence of stroke, sort 2 diabetes and coronary heart assaults, in keeping with the discharge. The researchers plan to guage how completely different oils with various fatty acid ranges could influence cardiometabolic danger elements.
Reference:
- Maki KC, et al. Summary PTFS04-06-25. Introduced at: NUTRITION; Might 31-June 3, 2025; Orlando.