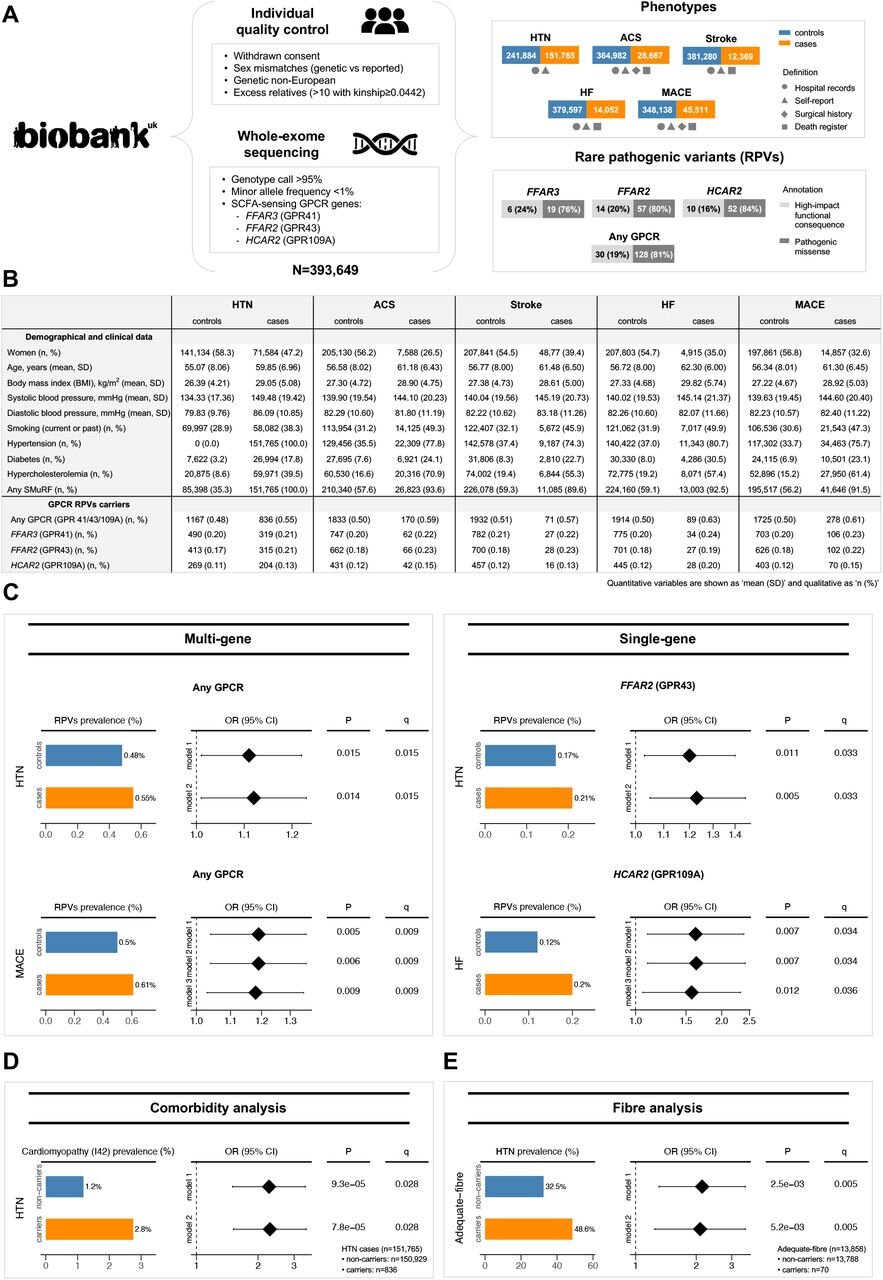
A Monash College research of just about 400,000 folks, printed within the journal Cardiovascular Analysis , is the primary to point, in people, that the signaling of gear referred to as short-chain fatty acids or SCFAs, launched when intestine micro organism break down dietary fiber, considerably protects towards heart problems and hypertension by as much as 20%.
A earlier medical trial by the Monash group, led by Professor Francine Marques, has proven that these SCFAs—when offered as a complement—result in lowered blood stress. One other trial is underway.
The present research used information from the UK Biobank database and located uncommon genetic variants that profoundly influence the operate of receptors that bind to SCFAs basically stop folks from using the cardiovascular safety provided by their very own intestine microbes.
“We needed to find out whether or not folks with these genetic modifications had an elevated danger of hypertension and main hostile cardiac occasions, together with acute coronary syndrome, coronary heart failure, and ischemic stroke,” stated Professor Marques.
For this, the researchers in contrast people with these genetic variants and their cardiovascular medical historical past to controls, discovering that this affected cohort had a considerably greater incidence of hypertension and long-term danger of heart problems, together with coronary heart assaults, coronary heart failure and stroke.
Dr. Leticia Camargo Tavares was the main writer of the research.
“The research discovered that disruption in these receptors is related to as much as 20% elevated prevalence of hypertension and coronary heart illness or stroke—even after accounting for different danger components like physique weight and smoking,” Dr. Tavares stated.
“Nevertheless, it’s price mentioning these uncommon genetic variants happen in lower than 1% of people,” Professor Marques stated.
Importantly, the researchers additionally appeared into what occurred to this affected cohort—with out the cardioprotective capability—when fiber consumption adopted dietary tips.
“In the event that they consumed satisfactory dietary fiber, however have been unable to show this into safety towards coronary heart illness, then this is able to show the significance of short-chain fatty acids signaling in cardio-protection,” Professor Marques stated.
“Per our speculation, the prevalence of hypertension was considerably greater on this cohort, even amongst those that ate a weight loss plan wealthy in fiber,” Dr. Tavares added.
The analysis group is presently within the strategy of creating a commercially out there product that may ship SCFAs orally. As well as, the group goals to develop medication that activate these receptors, which can present a novel technique to decrease blood stress and stop coronary heart illness.
Extra info:
Leticia Camargo Tavares et al, Uncommon pathogenic variants in G-protein-coupled receptor genes concerned in gut-to-host communication are related to heart problems danger, Cardiovascular Analysis (2025). DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvaf070
Quotation:
Activation of receptors concerned in intestine microbial breakdown of fiber might lower coronary heart illness danger by as much as 20% (2025, Might 23)
retrieved 23 Might 2025
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2025-05-receptors-involved-gut-microbial-breakdown.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.