Cybersecurity researchers have offered new findings associated to a now-patched safety difficulty in Microsoft’s Home windows Distant Process Name (RPC) communication protocol that might be abused by an attacker to conduct spoofing assaults and impersonate a recognized server.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2025-49760 (CVSS rating: 3.5), has been described by the tech big as a Home windows Storage spoofing bug. It was fastened in July 2025 as a part of its month-to-month Patch Tuesday replace. Particulars of the safety defect had been shared by SafeBreach researcher Ron Ben Yizhak on the DEF CON 33 safety convention this week.
“Exterior management of file title or path in Home windows Storage permits a licensed attacker to carry out spoofing over a community,” the corporate stated in an advisory launched final month.
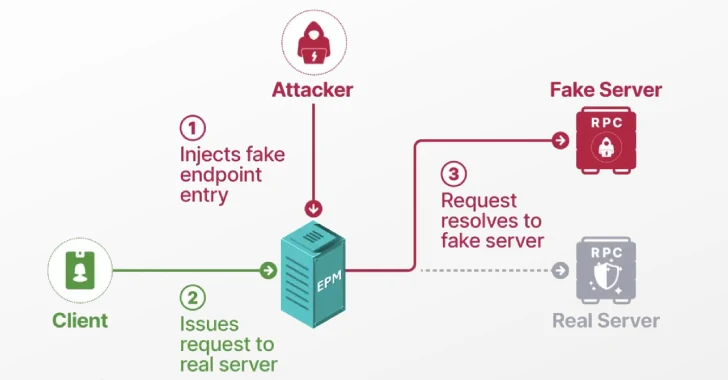
The Home windows RPC protocol makes use of universally distinctive identifiers (UUIDs) and an Endpoint Mapper (EPM) to allow using dynamic endpoints in client-server communications, and join an RPC consumer to an endpoint registered by a server.
The vulnerability basically makes it potential to control a core part of the RPC protocol and stage what’s known as an EPM poisoning assault that permits unprivileged customers to pose as a reliable, built-in service with the objective of coercing a protected course of to authenticate towards an arbitrary server of an attacker’s selecting.
Provided that the functioning of EPM is analogous to that of the Area Title System (DNS) – it maps an interface UUID to an endpoint, simply the DNS resolves a site to an IP tackle – the assault performs out like DNS poisoning, wherein a risk actor tampers with DNS information to redirect customers to malicious web sites –
- Poison the EPM
- Masquerade as a reliable RPC Server
- Manipulate RPC shoppers
- Obtain native/area privilege escalation by way of an ESC8 assault
“I used to be shocked to find that nothing stopped me from registering recognized, built-in interfaces that belong to core companies,” Ben Yizhak stated in a report shared with The Hacker Information. “I anticipated, for instance, if Home windows Defender had a singular identifier, no different course of would have the ability to register it. However that was not the case.”
“After I tried registering an interface of a service that was turned off, its consumer linked to me as a substitute. This discovering was unbelievable—there have been no safety checks accomplished by the EPM. It linked shoppers to an unknown course of that wasn’t even operating with admin privileges.”
The crux of the assault hinges on discovering interfaces that are not mapped to an endpoint, in addition to people who might be registered proper after the system boots by profiting from the truth that many companies are set to “delayed begin” for efficiency causes, and make the boot course of quicker.
In different phrases, any service with a guide startup is a safety threat, because the RPC interface would not be registered on boot, successfully making it prone to a hijack by permitting an attacker to register an interface earlier than the unique service does.
SafeBreach has additionally launched a software known as RPC-Racer that can be utilized to flag insecure RPC companies (e.g., the Storage Service or StorSvc.dll) and manipulate a Protected Course of Gentle (PPL) course of (e.g., the Supply Optimization service or DoSvc.dll) to authenticate the machine account towards any server chosen by the attacker.
The PPL know-how ensures that the working system solely masses trusted companies and processes, and safeguards operating processes from termination or an infection by malicious code. It was launched by Microsoft with the discharge of Home windows 8.1.
At a excessive degree, the whole assault sequence is as follows –
- Create a scheduled job that will likely be executed when the present person logs in
- Register the interface of the Storage Service
- Set off the Supply Optimization service to ship an RPC request to the Storage Service, leading to it connecting to the attacker’s dynamic endpoint
- Name the strategy GetStorageDeviceInfo(), which causes the Supply Optimization service to obtain an SMB share to a rogue server arrange by the attacker
- The Supply Optimization service authenticates with the malicious SMB server with the machine account credentials, leaking the NTLM hash
- Stage an ESC8 assault to relay the coerced NTLM hashes to the web-based certificates enrollment companies (AD CS) and obtain privilege escalation
To perform this, an offensive open-source software like Certipy can be utilized to request a Kerberos Ticket-Granting Ticket (TGT) utilizing the certificates generated by passing the NTLM data to the AD CS server, after which leverage it to dump all secrets and techniques from the area controller.
SafeBreach stated the EPM poisoning method might be additional expanded to conduct adversary-in-the-middle (AitM) and denial-of-service (DoS) assaults by forwarding the requests to the unique service or registering many interfaces and denying the requests, respectively. The cybersecurity firm additionally identified that there might be different shoppers and interfaces which might be probably susceptible to EPM poisoning.
To raised detect these sorts of assaults, safety merchandise can monitor calls to RpcEpRegister and use Occasion Tracing for Home windows (ETW), a safety characteristic that logs occasions which might be raised by user-mode purposes and kernel-mode drivers.
“Identical to SSL pinning verifies that the certificates is just not solely legitimate however makes use of a particular public key, the identification of an RPC server needs to be checked,” Ben Yizhak stated.
“The present design of the endpoint mapper (EPM) would not carry out this verification. With out this verification, shoppers will settle for information from unknown sources. Trusting this information blindly permits an attacker to manage the consumer’s actions and manipulate it to the attacker’s will.”