BBC Information Local weather and Science
It has been one of many strongest earthquakes ever recorded – however to date has not introduced the catastrophic tsunami that many feared.
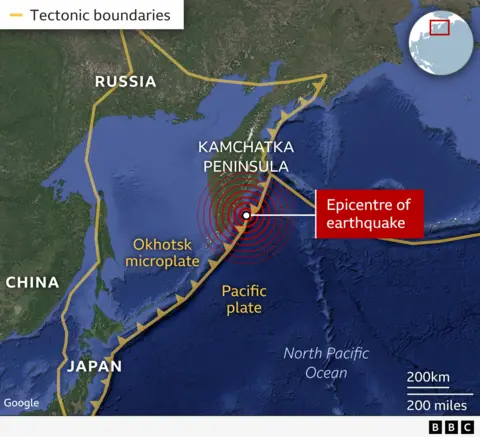
When the 8.8-magnitude quake struck japanese Russia at 11:25 native time on Wednesday (00:25 BST), it raised considerations for coastal populations throughout the Pacific.
Thousands and thousands of individuals had been evacuated, as minds forged again to the devastating tsunami of Boxing Day 2004 within the Indian Ocean and Japan 2011, each triggered by equally giant earthquakes.
However immediately’s tsunami has been a lot much less extreme, although it is introduced some injury.
So what precipitated the earthquake and tsunami – and why wasn’t it as dangerous as initially feared?
What causes a mega earthquake?
The Kamchatka Peninsula is distant however lies within the “Pacific Ring of Fireplace” – so referred to as due to the excessive variety of earthquakes and volcanoes that happen right here.
The higher layers of the Earth are break up into sections – tectonic plates – that are all transferring relative to at least one one other.
The “Pacific Ring of Fireplace” is an arc of those plates that extends across the Pacific. Eighty % of the world’s earthquakes happen alongside the ring, in response to the British Geological Survey.
Simply off the coast of the Peninsula, the Pacific plate is transferring north-west at about 8cm (3in) per yr – solely about twice the speed that your fingernails develop, however quick by tectonic requirements.
There it comes into contact with one other, smaller plate – referred to as the Okhotsk microplate.
The Pacific plate is oceanic, which suggests it has dense rocks and desires to sink beneath the much less dense microplate.
Because the Pacific plate sinks in the direction of the centre of the Earth, it heats up and begins to soften, successfully disappearing.
However this course of shouldn’t be at all times clean. Typically the plates can get caught as they transfer previous one another and the overriding plate is dragged downwards.
This friction can construct up over hundreds of years, however can then be instantly launched in simply a few minutes.
This is named a megathrust earthquake.
“After we usually take into consideration earthquakes, we think about an epicentre as a small level on a map. Nonetheless, for such giant earthquakes, the fault could have ruptured over many a whole lot of kilometres,” defined Dr Stephen Hicks, lecturer in environmental seismology at College School London.
“It’s this huge quantity of slip and space of the fault that generates such a excessive earthquake magnitude.”
The biggest earthquakes recorded in historical past, together with the three strongest in Chile, Alaska and Sumatra, had been all megathrust earthquakes.
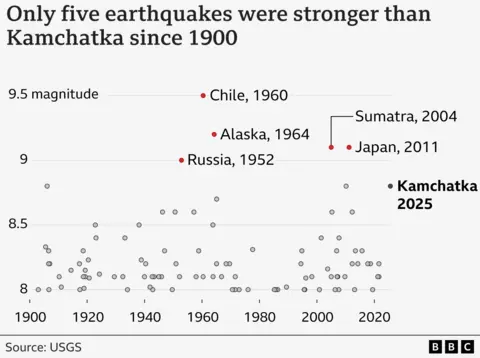
And the Kamchatka Peninsula is liable to sturdy quakes.
The truth is, one other excessive magnitude 9.0 earthquake struck lower than 30km (19mi) from immediately’s earthquake in 1952, the US Geological Survey says.
Why wasn’t this as dangerous as earlier tsunamis?
This sudden motion can displace water above the plates, which might then journey to the shoreline as tsunami.
Within the deep ocean, tsunami can journey at greater than 500mph (800km/h), about as quick as a passenger aeroplane.
Right here, the space between waves could be very lengthy and the waves aren’t very excessive – not often greater than a metre.
However as a tsunami enters shallow water close to land, it slows down, usually to about 20-30mph.
The gap between waves shortens, and waves develop in top, which might successfully create a wall of water close to the coast.
But it surely’s on no account assured {that a} very sturdy earthquake will result in a very tall tsunami reaching far inland.
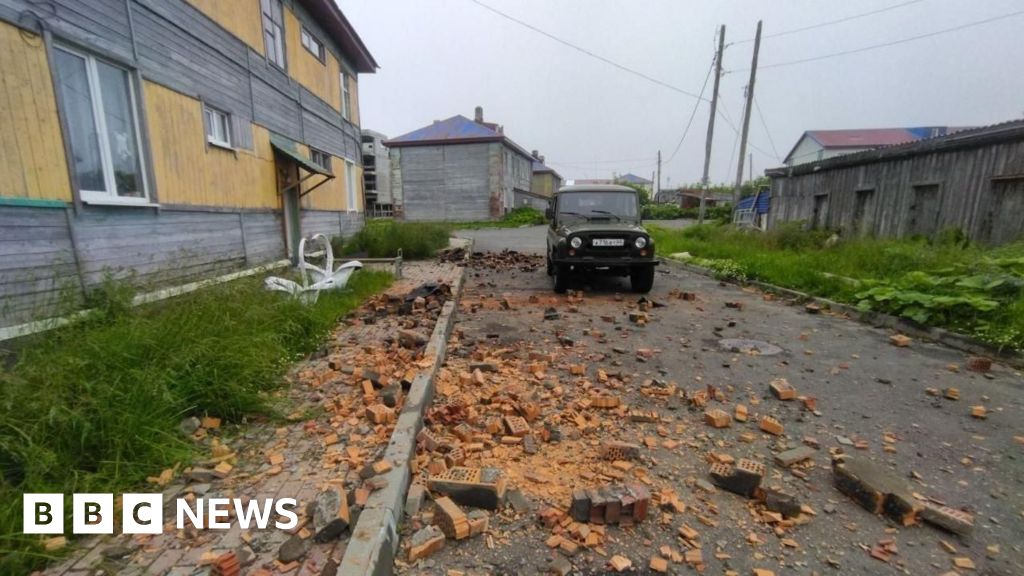
In the present day’s quake introduced tsunami waves of 4m (13ft) in components of japanese Russia, in response to authorities there.
However they do not come near the waves tens-of-metres excessive of Boxing Day 2004 within the Indian Ocean and Japan 2011.
“The peak of the tsunami wave can be affected by native shapes of the seafloor close to the coast and the [shape] of the land the place it arrives,” mentioned Prof Lisa McNeill, professor of tectonics on the College of Southampton.
“These elements, together with how populated the coast is, have an effect on how severe the affect is,” she added.
Preliminary reviews from the US Geological Survey mentioned that the earthquake was centred at fairly a slim depth, about 20.7km (12.9 miles) beneath the Earth’s floor.
That may result in better displacement of the seafloor, and subsequently an even bigger tsunami wave, however it’s onerous to inform for positive so quickly after the occasion.
“One chance is that the tsunami fashions have possibly taken a conservative estimate on the earthquake depth,” Dr Hicks instructed BBC Information.
“Probably you would shift that earthquake one other 20 kilometres deeper, and that may truly cut back the amplitude of the tsunami waves fairly significantly.”
 Philip FONG/AFP/Getty Photographs
Philip FONG/AFP/Getty PhotographsHigher early warning techniques
One other vital component is the event of early warning techniques.
Because of the excessive prevalence of earthquakes within the Pacific area, many international locations have tsunami centres. They ship out warnings by way of public bulletins for populations to evacuate.
No such system was in place when the 2004 Boxing Day tsunami occurred – leaving many individuals with out time to evacuate.
Greater than 230,000 individuals died throughout 14 international locations within the Indian Ocean.
Early warning techniques are vital due to the restricted means of scientists to foretell when an earthquake will happen.
The US Geological Survey recorded an earthquake measuring 7.4 in the identical area ten days earlier than.
This will likely have been a foreshock – an early launch of vitality – however it’s not a predictor of actual timing of a future earthquake, defined Prof McNeill.
“Though we will use how briskly the plates are transferring, GPS to measure present actions and when earlier earthquakes occurred, we will solely use this info to make forecasts of likelihood of an earthquake,” she mentioned.
The Geophysical Survey of the Russian Academy of Sciences (GS RAS) will proceed to watch the area because it anticipates aftershocks may proceed for the subsequent month.