Key takeaways:
- Danger elements for dementia embody hypertension, dyslipidemia and diabetes.
- Autopsies included neuropathologic evaluations.
- Semantic and dealing reminiscence noticed slower declines with three treatment lessons.
Sufferers who used mixtures of cardiovascular therapies skilled slower cognitive decline and fewer neuropathologies associated to dementia, in response to knowledge offered on the Alzheimer’s Affiliation Worldwide Convention.
“Hypertension, dyslipidemia, and diabetes are frequent situations in older adults and are recognized dementia threat elements,” Roshni Biswas, MBBS, PhD, MPH, analysis scientist, Rush Alzheimer’s Illness Heart, informed Healio.

Information had been derived from Biswas R, et al. Affiliation of mixture cardiovascular therapies with cognitive decline and neuropathologies. Introduced at: Alzheimer’s Affiliation Worldwide Convention; July 27-31, 2025; Toronto.
Antihypertensive, lipid-lowering and antidiabetes drugs have been studied individually for his or her affect on dementia threat, she continued, however little is thought about their mixed results on cognition.
“Since older adults are sometimes on mixture therapies, we aimed to evaluate the affect of mixture therapies with these three frequent treatment lessons on cognitive decline,” Biswas mentioned. “We additionally examined the affect of those mixture therapies on mind modifications at post-mortem.”
The research included 4,651 older adults (common age = 77 years; 75% ladies; 28% Black) who had no baseline dementia however who nonetheless had two or extra international cognition measures collected yearly. Documentation of visible inspections of their drugs was collected yearly as properly.

Roshni Biswas
Additionally, autopsies of 1,896 of those sufferers who had been deceased included evaluations for dementia-related neuropathologies akin to cerebrovascular illness and Alzheimer’s illness.
Sufferers who used all three lessons of medicines — antihypertensive, lipid-lowering and antidiabetes — had slower decline in international cognition in contrast with those that used no drugs (P = .02), the researchers mentioned, particularly in semantic and dealing reminiscence.
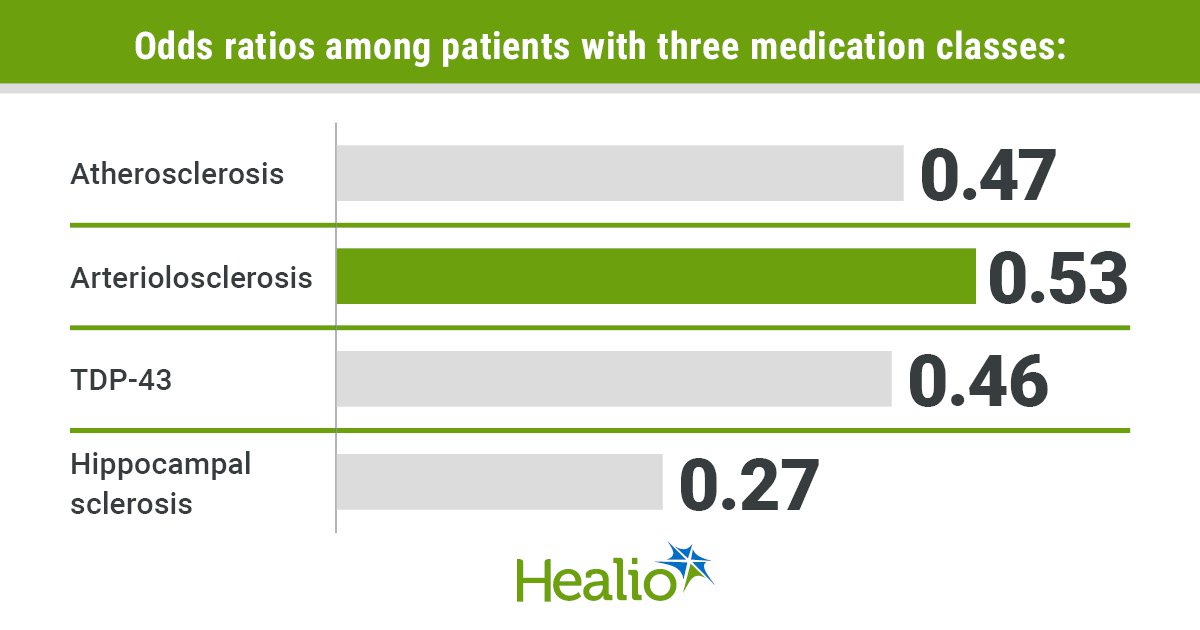
Amongst autopsied sufferers who had used all three lessons, odds for atherosclerosis (OR = 0.47; P < .01) and arteriolosclerosis (OR = 0.53; P = .01) had been decrease, however odds for mind infarcts (OR = 1.74; P = .01) had been greater, particularly macroinfarcts (OR = 1.66; P = .03).
Autopsied sufferers with all three lessons additionally had much less international Alzheimer’s illness pathology, primarily amyloid and tangles (P < .01). Odds ratios included 0.46 for TDP-43 (P < .01) and 0.27 (P = .03) for hippocampal sclerosis as properly.
Sufferers who used two lessons of medicines skilled slower declines in international cognition (P < .01), the researchers reported, particularly in semantic and dealing reminiscence.
Autopsied sufferers who had used two lessons included had decrease odds for atherosclerosis (OR = 0.63; P < .01) and TDP-43 (OR = 0.71; P = .02) in addition to much less international Alzheimer’s illness pathology (P = .03) and fewer tangles (P = .03).
Sufferers with one class of treatment had slower semantic reminiscence decline (P = .02), with autopsied sufferers who had used one class demonstrating fewer tangles (P = .02) and decrease odds for TDP-43 (OR = 0.73; P = .02) as properly.
These findings point out associations between mixture cardiovascular therapies and slower cognitive decline and fewer neuropathologies associated to dementia, the researchers mentioned, suggesting potential roles for these therapies in stopping dementia.
“Our research means that early interventions with mixture therapies concentrating on a number of vascular metabolic threat elements might probably delay or forestall cognitive decline and dementia,” Biswas mentioned. “Nonetheless, these associations have to be studied additional earlier than making scientific suggestions.”
Noting that this research examined using mixture therapies at baseline, Biswas mentioned that future analysis will study mixtures of therapies that focus on metabolic threat elements and their associations with dementia threat over time.
“Moreover, as a subsequent step, we might study amongst every of the treatment lessons which subclass works higher,” she mentioned. “For instance, amongst antihypertensive drugs which subclass works higher; and the identical factor for lipid-lowering and antidiabetes drugs.”
For extra info:
Roshni Biswas, MBBS, PhD, MPH, might be reached at neurology@healio.com.