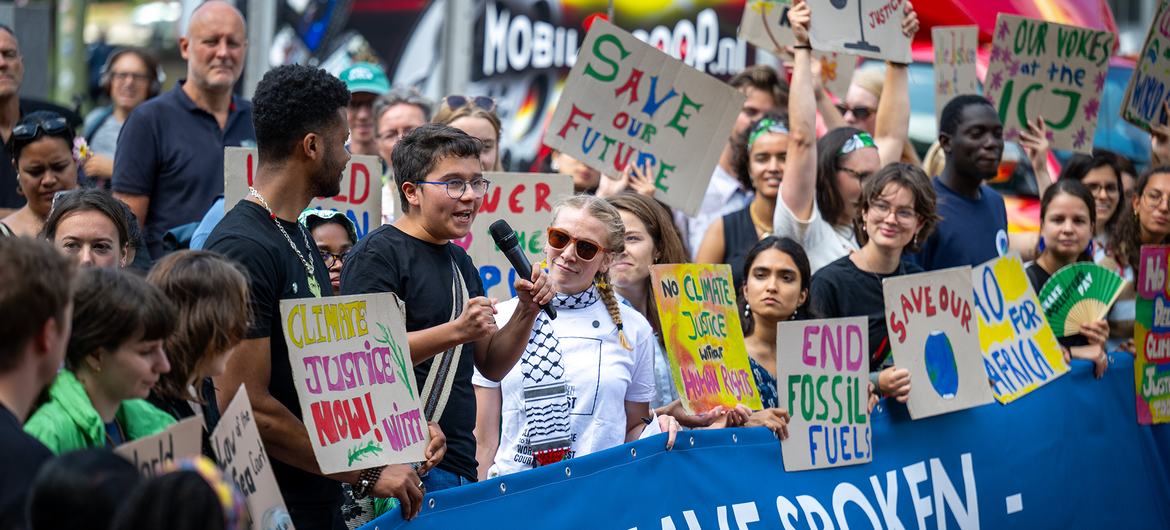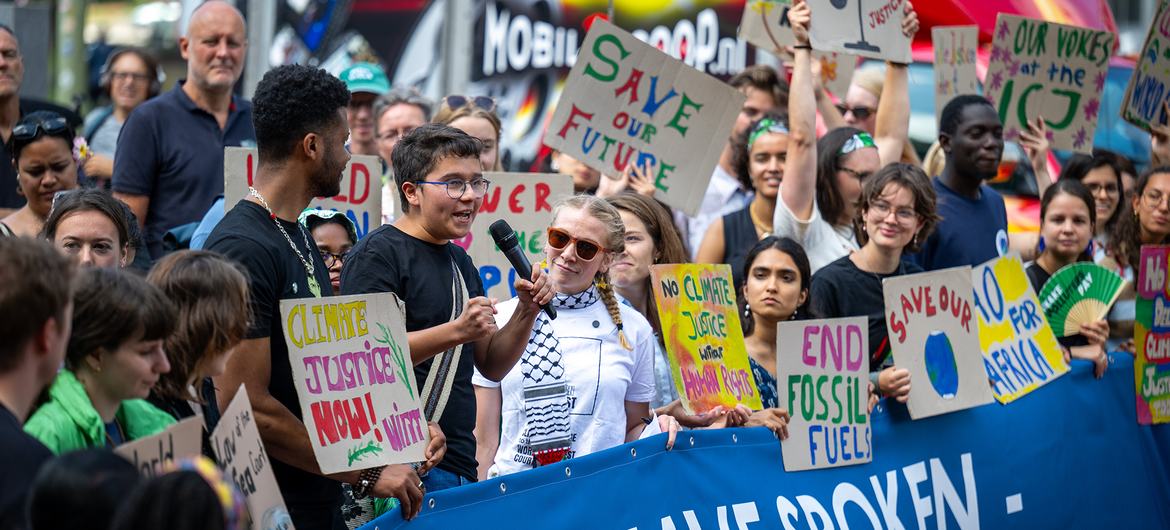
The UN’s principal judicial physique dominated that States have an obligation to guard the setting from greenhouse fuel (GHG) emissions and act with due diligence and cooperation to satisfy this obligation.
This consists of the duty underneath the Paris Settlement on local weather change to restrict world warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial ranges.
The courtroom additional dominated that if States breach these obligations, they incur obligation and could also be required to stop the wrongful conduct, supply ensures of non-repetition and make full reparation relying on the circumstances.
‘A victory for our planet’
UN Secretary-Basic António Guterres issued a video message welcoming the historic choice, which got here a day after he delivered a particular tackle to Member States on the unstoppable world shift to renewable vitality.
“This can be a victory for our planet, for local weather justice and for the facility of younger folks to make a distinction,” he mentioned.
Reasoning of the Courtroom
The courtroom used Member States’ commitments to each environmental and human rights treaties to justify this choice.
Firstly, Member States are events to a wide range of environmental treaties, together with ozone layer treaties, the Biodiversity Conference, the Kyoto Protocol, the Paris Settlement and lots of extra, which oblige them to guard the setting for folks worldwide and in future generations.
However, additionally as a result of “a clear, wholesome and sustainable setting is a precondition for the enjoyment of many human rights,” since Member States are events to quite a few human rights treaties, together with the UN’s Common Declaration of Human Rights, they’re required to ensure the enjoyment of such rights by addressing local weather change.
Case background
In September 2021, the Pacific Island State of Vanuatu introduced that it might search an advisory opinion from the courtroom on local weather change. This initiative was impressed by the youth group Pacific Island College students Preventing Local weather Change, which underscored the necessity to act to handle local weather change, notably in small island States.
After the nation lobbied different UN Member States to assist this initiative within the Basic Meeting, on 29 March 2023, it adopted a decision requesting an advisory opinion from the ICJ on two questions: (1) What are the obligations of States underneath worldwide legislation to make sure the safety of the setting? and (2) What are the authorized penalties for States underneath these obligations once they trigger hurt to the setting?
The UN Constitution permits the Basic Meeting or the Safety Council to request the ICJ to offer an advisory opinion. Though advisory opinions usually are not binding, they carry vital authorized and ethical authority and assist make clear and develop worldwide legislation by defining States’ authorized obligations.
That is the most important case ever seen by the ICJ, evident by the variety of written statements (91) and States that participated in oral proceedings (97).
The ‘world courtroom’
The ICJ, informally often known as the “world courtroom”, settles authorized disputes between UN Member States and provides advisory opinions on authorized questions which have been referred to it by UN organs and businesses.
It is without doubt one of the six predominant organs of the UN alongside the Basic Meeting, the Safety Council, the Financial and Social Council (ECOSOC), the Trusteeship Council and the Secretariat and is the one one not primarily based in New York.