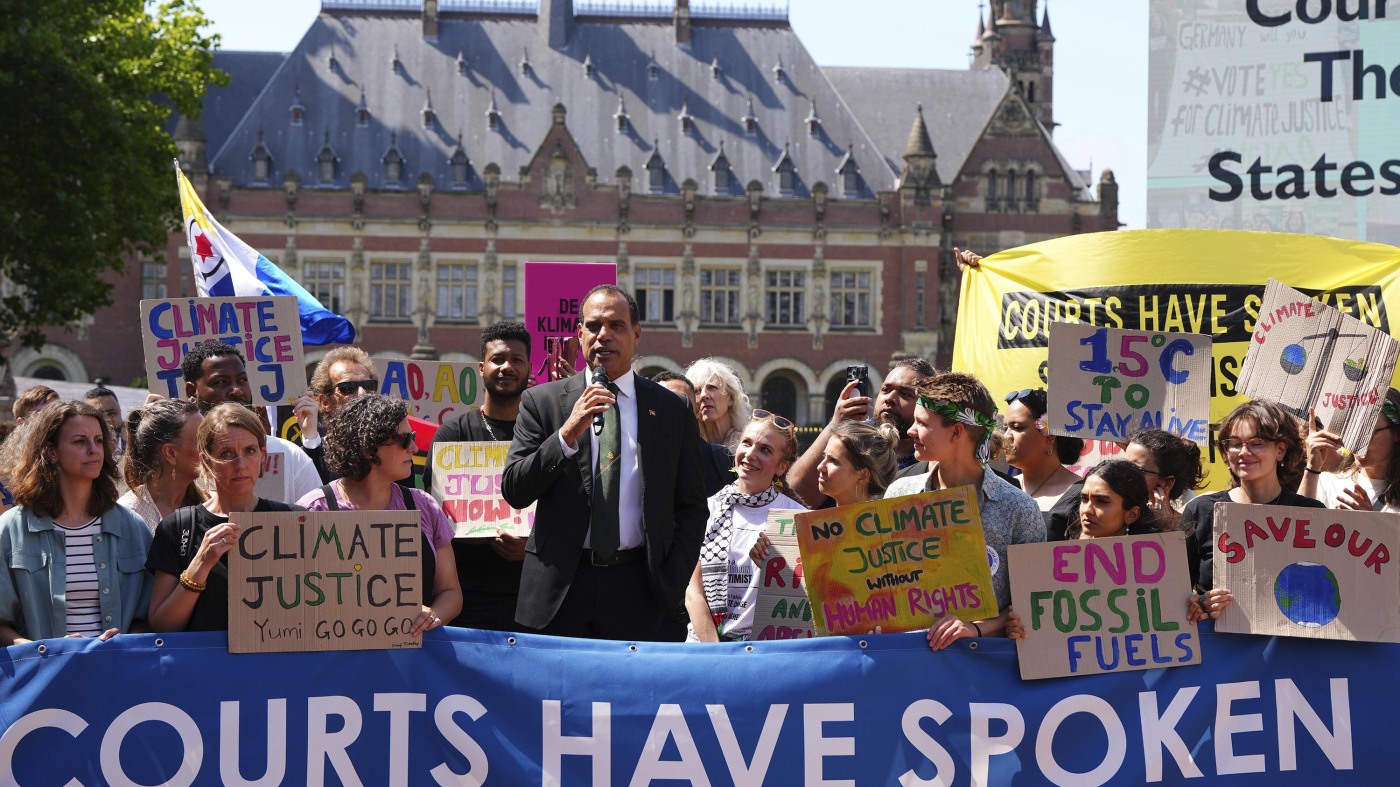
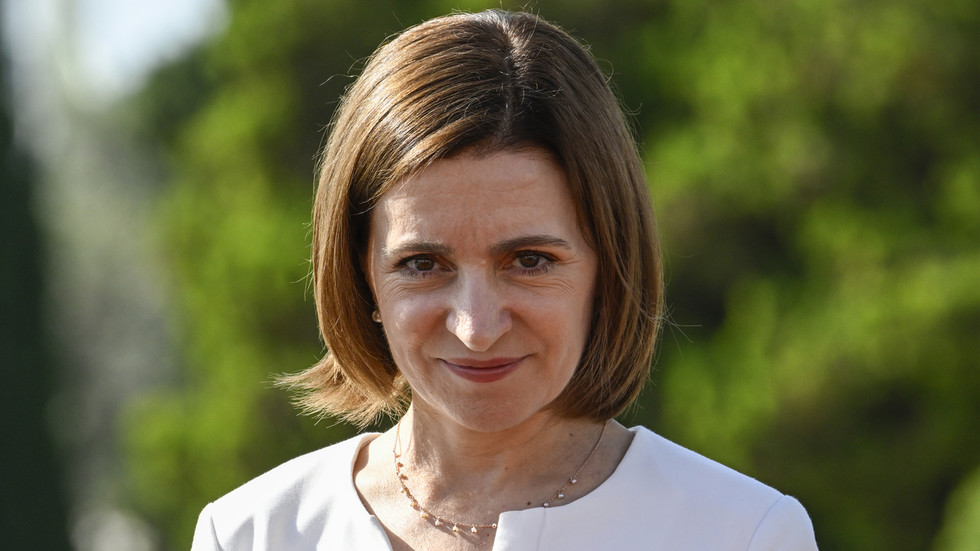
Ralph Regenvanu, Vanuatu’s minister for local weather change, is joined by local weather activists on the Worldwide Courtroom of Justice on Wednesday. The nation pushed for years for the court docket to listen to its first main local weather change case.
Peter Dejong/AP
disguise caption
toggle caption
Peter Dejong/AP
The highest United Nations court docket has dominated that nations are obligated beneath worldwide legislation to restrict local weather change, and nations that do not act may very well be held legally chargeable for local weather damages elsewhere.
The choice is a win for a lot of small nations weak to local weather impacts, which pushed for the problem to be heard by the Worldwide Courtroom of Justice (ICJ).
It is the court docket’s first main ruling on local weather change, however the choice is barely advisory, which means that nations are usually not legally sure by it. Nonetheless, authorized consultants say it may very well be a lift for different local weather change lawsuits pending in nationwide courts all over the world.
“It is actually groundbreaking,” says Maria Antonia Tigre, director of International Local weather Change Litigation at Columbia Regulation College. “I believe it is going to create this new wave of local weather litigation.”
The case was championed by the South Pacific island nation of Vanuatu, which has been among the many loudest voices calling for stronger worldwide local weather motion, alongside different island nations. The low-lying nations face dire dangers from rising sea ranges and extra intense cyclones.
In court docket proceedings in December, Vanuatu and different nations argued that nations have an obligation to behave on local weather change beneath worldwide legal guidelines defending the setting and human rights. In a ruling right this moment, the ICJ agreed.
“To be able to assure the efficient enjoyment of human rights, states should take measures to guard the local weather system and different elements of the setting,” Choose Yuji Iwasawa learn from the court docket’s opinion.
The court docket additionally discovered that if nations fail to curb their heat-trapping emissions from fossil fuels, they may very well be on the hook to pay for local weather change-related damages in different nations. These sorts of funds have been a degree of competition between main emitters and lower-income counties at annual local weather change negotiations.
The U.S. typically does not contemplate ICJ choices to be binding. Earlier this yr, President Trump additionally pulled the U.S. out of the most important worldwide local weather accord, the 2015 Paris local weather settlement.
Nonetheless, smaller nations say they hope the ICJ’s choice can be a turning level in worldwide local weather negotiations.
“Right now it has been a landmark milestone for local weather motion,” stated Vanuatu’s local weather minister Ralph Regenvanu. “It is an important course correction on this critically vital time.”
Island nations push for local weather change ruling
For years, low-lying nations all over the world have argued that local weather change is an existential menace. Sea ranges have already risen about 8 inches because the Industrial Revolution, and the tempo is accelerating. Vanuatu is relocating whole villages from the coast. Cyclones have taken a toll on the South Pacific nation and are getting extra intense because the local weather heats up.
With a inhabitants of round 300,000, Vanuatu has produced a comparatively tiny share of world emissions from burning fossil fuels, which entice warmth and heat the planet. The vast majority of emissions have come from bigger and richer nations such because the U.S., the European Union and China.
However Vanuatu officers argue it is bearing the brunt of the issue.
“We discover ourselves on the entrance strains of a disaster we didn’t create, a disaster that threatens our very existence,” Regenvanu stated earlier than the ICJ final December.
Vanutau led a coalition of nations to name for the ICJ to rule on local weather change, spurred on by a group of scholars from the Pacific Islands. The court docket, primarily based on the Hague, guidelines on worldwide legislation and disputes between nations. Near 100 nations filed testimonies, making it the largest case the court docket has heard.
Are nations obligated to behave on local weather change?
The court docket took up two questions: are nations obligated to behave on local weather change, and what are the authorized penalties in the event that they trigger hurt?
On the hearings, the U.S. argued that negotiations via worldwide agreements such because the Paris local weather accord are the easiest way to handle local weather change.
“Cooperative efforts via that regime present the very best hope for shielding the local weather system for the good thing about current and future generations,” stated Margaret Taylor, who represented the U.S. Division of State within the authorized proceedings beneath the Biden administration.
In its ruling right this moment, the ICJ discovered that nations are sure to curb emissions of greenhouse gases beneath worldwide legislation. That features taking actions corresponding to limiting the use and manufacturing of fossil fuels like coal, oil and pure fuel – and even authorities subsidies for these industries. It additionally discovered that states might be held chargeable for particular injury attributable to local weather change. That is made attainable by advances in local weather science which can be serving to to pinpoint how a lot local weather change contributes to particular disasters.
On the similar time, the ICJ acknowledged that the advisory ruling might have a minimal influence.
“Worldwide legislation… has an vital however finally restricted function in resolving this downside,” the judgment reads. “A whole resolution to this daunting, and self-inflicted, downside requires the contribution of all fields of human data, whether or not legislation, science, economics or every other.”
Potential worldwide impacts
The case might affect lots of of different local weather change lawsuits all over the world, including proof for plaintiffs who’re looking for to spur governments to behave. Circumstances have been filed within the U.S. and European nations just like the Netherlands, the place a court docket dominated that the Dutch state should reduce its greenhouse fuel emissions.
“This being actually the most important case that we now have seen in local weather litigation, the standing and the load of the court docket can actually affect a whole lot of these instances,” Tigre says.
The ICJ choice may be cited on the COP30 worldwide local weather negotiations this fall in Brazil. There, smaller nations like Vanuatu will proceed to make the case for compensation from wealthier nations for the damages from local weather change, generally known as “loss and injury” funds.
Local weather activists, like Vishal Prasad of Pacific Islands College students Preventing Local weather Change, say the choice offers new momentum for his or her motion.
“I believe it sends a powerful message for all of us and to younger folks all over the place,” Prasad says. “There may be nonetheless hope and there’s a probability and there is a cause for us to maintain preventing.”