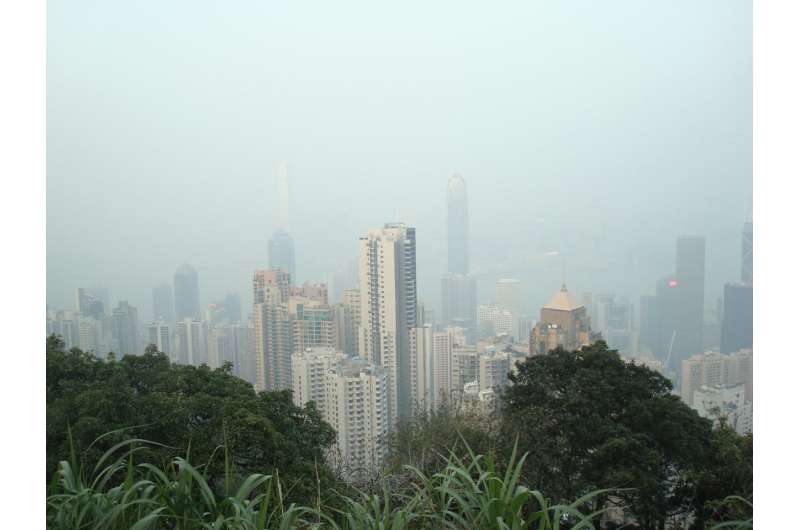
An evaluation of research incorporating information from nearly 30 million individuals has highlighted the function that air air pollution—together with that coming from automotive exhaust emissions—performs in elevated danger of dementia.
Dementias reminiscent of Alzheimer’s illness are estimated to have an effect on greater than 57.4 million individuals worldwide, a quantity that’s anticipated to nearly triple to 152.8 million circumstances by 2050. The impacts on people, households and caregivers, and society at giant are immense.
Whereas there are some indications that the prevalence of dementia is reducing in Europe and North America, suggesting that it might be potential to cut back the danger of the illness at a inhabitants degree, elsewhere the image is much less promising.
Air air pollution has not too long ago been recognized as a danger issue for dementia, with a number of research pointing the finger at numerous pollution. Nevertheless, the energy of proof and talent to find out a causal impact has various.
In a paper printed in The Lancet Planetary Well being, a crew led by researchers on the Medical Analysis Council (MRC) Epidemiology Unit, College of Cambridge, carried out a scientific overview and meta-analysis of present scientific literature to look at this hyperlink additional. This strategy allowed them to convey collectively research that on their very own could not present ample proof, and which generally disagree with one another, to offer extra sturdy overarching conclusions.
In whole, the researchers included 51 research, together with information from greater than 29 million contributors, largely from high-income nations. Of those, 34 papers have been included within the meta-analysis: 15 originated in North America, 10 in Europe, seven in Asia, and two in Australia.
The researchers discovered a constructive and statistically-significant affiliation between three kinds of air pollutant and dementia. These have been:
- Particulate matter with a diameter of two.5 microns or much less (PM2.5), a pollutant made up of tiny particles sufficiently small that they are often inhaled deep into the lungs. These particles come from a number of sources, together with car emissions, energy crops, industrial processes, wood-burning stoves and fireplaces, and building mud. Additionally they kind within the environment due to advanced chemical reactions involving different pollution reminiscent of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides. The particles can keep within the air for a very long time and journey a great distance from the place they have been produced.
- Nitrogen dioxide (NO2), one of many key pollution that come up from burning fossil fuels. It’s present in car exhaust, particularly diesel exhaust, and industrial emissions, in addition to these from gasoline stoves and heaters. Publicity to excessive concentrations of nitrogen dioxide can irritate the respiratory system, worsening and inducing situations like bronchial asthma and decreasing lung perform.
- Soot, from sources reminiscent of car exhaust emissions and burning wooden. It could lure warmth and have an effect on the local weather. When inhaled, it could penetrate deep into the lungs, aggravating respiratory illnesses and rising the danger of coronary heart issues.
In response to the researchers, for each 10 micrograms per cubic meter (μg/m³) of PM2.5, a person’s relative danger of dementia would improve by 17%. The common roadside measurement for PM2.5 in Central London in 2023 was 10 μg/m³.
For each 10 μg/m3 of NO2, the relative danger elevated by 3%. The common roadside measurement for NO2 in Central London in 2023 was 33 µg/m³.
For every 1 μg/m³ of soot as present in PM2.5, the relative danger elevated by 13%. Throughout the UK, annual imply soot concentrations measured at choose roadside areas in 2023 have been 0.93 μg/m³ in London, 1.51 μg/m³ in Birmingham and 0.65 μg/m³ in Glasgow.
Senior creator Dr. Haneen Khreis from the MRC Epidemiology Unit stated, “Epidemiological proof performs a vital function in permitting us to find out whether or not or not air air pollution will increase the danger of dementia and by how a lot. Our work offers additional proof to assist the commentary that long-term publicity to outside air air pollution is a danger issue for the onset of dementia in beforehand wholesome adults.
“Tackling air air pollution can ship long-term well being, social, local weather, and financial advantages. It could scale back the immense burden on sufferers, households, and caregivers, whereas easing stress on overstretched well being care methods.”
A number of mechanisms have been proposed to elucidate how air air pollution could trigger dementia, primarily involving irritation within the mind and oxidative stress (a chemical course of within the physique that may trigger harm to cells, proteins, and DNA). Each oxidative stress and irritation play a well-established function within the onset and development of dementia. Air air pollution is believed to set off these processes via direct entry to the mind or through the identical mechanisms underlying lung and cardiovascular illnesses. Air air pollution also can enter circulation from the lungs and journey to strong organs, initiating native and widespread irritation.
The researchers level out that almost all of individuals included within the printed research have been white and residing in high-income nations, despite the fact that marginalized teams are inclined to have the next publicity to air air pollution. On condition that research have urged that decreasing air air pollution publicity seems to be extra useful in decreasing the danger of early demise for marginalized teams, they name for future work to urgently guarantee higher and extra enough illustration throughout ethnicities and low- and middle-income nations and communities.
Joint first creator Clare Rogowski, additionally from the MRC Epidemiology Unit, stated, “Efforts to cut back publicity to those key pollution are possible to assist scale back the burden of dementia on society. Stricter limits on a number of pollution are more likely to be obligatory, focusing on main contributors such because the transport and business sectors. Given the extent of air air pollution, there’s an pressing want for regional, nationwide, and worldwide coverage interventions to fight air air pollution equitably.”
Additional evaluation revealed that whereas publicity to those pollution elevated the danger of Alzheimer’s illness, the impact appeared stronger for vascular dementia, a sort of dementia brought on by lowered blood circulate to the mind. Round 180,000 individuals within the UK are regarded as affected by this sort of dementia. Nevertheless, as there have been solely a small variety of research that examined this distinction, the researchers didn’t class it as statistically vital.
Joint first creator Dr. Christiaan Bredell from the College of Cambridge and North West Anglia NHS Basis Belief stated, “These findings underscore the necessity for an interdisciplinary strategy to dementia prevention. Stopping dementia is not only the duty of well being care: this examine strengthens the case that city planning, transport coverage, and environmental regulation all have a major function to play.”
Extra info:
Lengthy-term Air Air pollution Publicity and Incident Dementia: A Systematic Evaluation and Meta-Evaluation, The Lancet Planetary Well being (2025). DOI: 10.1016/S2542-5196(25)00118-4
Quotation:
Lengthy-term publicity to outside air air pollution linked to elevated danger of dementia (2025, July 24)
retrieved 24 July 2025
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2025-07-term-exposure-outdoor-air-pollution.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.