Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed what they are saying is a “vital design flaw” in delegated Managed Service Accounts (dMSAs) launched in Home windows Server 2025.
“The flaw can lead to high-impact assaults, enabling cross-domain lateral motion and chronic entry to all managed service accounts and their assets throughout Lively Listing indefinitely,” Semperis mentioned in a report shared with The Hacker Information.
Put in a different way, profitable exploitation may permit adversaries to sidestep authentication guardrails and generate passwords for all Delegated Managed Service Accounts (dMSAs) and group Managed Service Accounts (gMSAs) and their related service accounts.
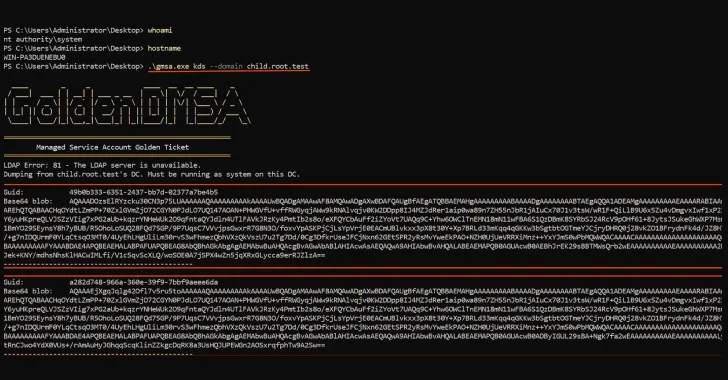
The persistence and privilege escalation methodology has been codenamed Golden dMSA, with the cybersecurity firm deeming it as low complexity owing to the truth that the vulnerability simplifies brute-force password era.
Nevertheless, to ensure that unhealthy actors to take advantage of it, they have to already be in possession of a Key Distribution Service (KDS) root key that is usually solely accessible to privileged accounts, reminiscent of root Area Admins, Enterprise Admins, and SYSTEM.
Described because the crown jewel of Microsoft’s gMSA infrastructure, the KDS root key serves as a grasp key, permitting an attacker to derive the present password for any dMSA or gMSA account with out having to connect with the area controller.
“The assault leverages a vital design flaw: A construction that is used for the password-generation computation accommodates predictable time-based elements with just one,024 attainable combos, making brute-force password era computationally trivial,” safety researcher Adi Malyanker mentioned.
Delegated Managed Service Accounts is a brand new function launched by Microsoft that facilitates migration from an present legacy service account. It was launched in Home windows Server 2025 as a method to counter Kerberoasting assaults.
The machine accounts bind authentication on to explicitly licensed machines in Lively Listing (AD), thus eliminating the potential for credential theft. By tying authentication to machine identification, solely specified machine identities mapped in AD can entry the account.
Golden dMSA, just like Golden gMSA Lively Listing assaults, performs out over 4 steps as soon as an attacker has obtained elevated privileges inside a site –
- Extracting KDS root key materials by elevating to SYSTEM privileges on one of many area controllers
- Enumerating dMSA accounts utilizing LsaOpenPolicy and LsaLookupSids APIs or by way of a Light-weight Listing Entry Protocol (LDAP)-based strategy
- Figuring out the ManagedPasswordID attribute and password hashes by means of focused guessing
- Producing legitimate passwords (i.e., Kerberos tickets) for any gMSA or dMSA related to the compromised key and testing them by way of Move the Hash or Overpass the Hash strategies
“This course of requires no further privileged entry as soon as the KDS root key’s obtained, making it a very harmful persistence methodology,” Malyanker mentioned.
“The assault highlights the vital belief boundary of managed service accounts. They depend on domain-level cryptographic keys for safety. Though automated password rotation supplies wonderful safety towards typical credential assaults, Area Admins, DnsAdmins, and Print Operators can bypass these protections completely and compromise all the dMSAs and gMSAs within the forest.”
Semperis famous that the Golden dMSA method turns the breach right into a forest-wide persistent backdoor, on condition that compromising the KDS root key from any single area inside the forest is sufficient to breach each dMSA account throughout all domains in that forest.
In different phrases, a single KDS root key extraction could be weaponized to attain cross-domain account compromise, forest-wide credential harvesting, and lateral motion throughout domains utilizing the compromised dMSA accounts.
“Even in environments with a number of KDS root keys, the system persistently makes use of the primary (oldest) KDS root key for compatibility causes,” Malyanker identified. “Which means the unique key we have compromised may very well be preserved by Microsoft’s design – making a persistent backdoor that might final for years.”
Much more regarding is that the assault utterly sidesteps regular Credential Guard protections, that are used to safe NTLM password hashes, Kerberos Ticket Granting Tickets (TGTs), and credentials in order that solely privileged system software program can entry them.
Following accountable disclosure on Might 27, 2025, Microsoft mentioned, “When you have the secrets and techniques used to derive the important thing, you’ll be able to authenticate as that consumer. These options have by no means been meant to guard towards a compromise of a site controller.” Semperis has additionally launched an open-source as proof-of-concept (PoC) to show the assault.
“What begins as one DC compromise escalates to proudly owning each dMSA-protected service throughout a complete enterprise forest,” Malyanker mentioned. “It is not simply privilege escalation. It is enterprise-wide digital domination by means of a single cryptographic vulnerability.”