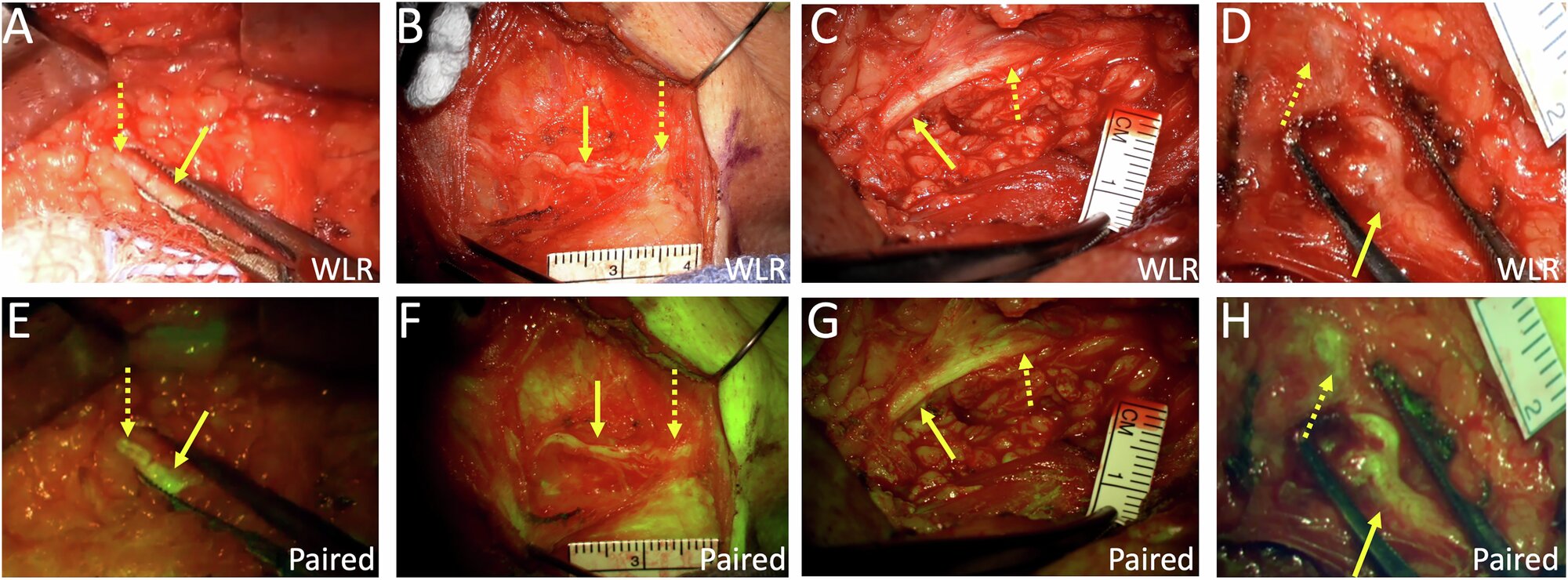
When surgeons dissect tissue to take away a tumor or make a restore, they need to work cautiously, counting on electrophysical screens and their very own anatomical data to keep away from reducing nerves, which may complicate the affected person’s restoration.
A College of New Mexico surgeon has helped develop and check a first-of-its-kind drug that binds to nerve tissue and fluoresces (emits gentle), enabling surgeons to raised see the nerves they’re attempting to work round.
A newly printed research in Nature Communications stories that bevonescein—a brief chain of amino acids connected to a fluorescing molecule—was protected to make use of and highlighted longer stretches of nerves than can be seen to the bare eye, bettering the chances of working with out inflicting damage.
“The way in which that I clarify this drug to sufferers is that I believe if we can assist surgeons see issues higher, they’ll do quicker, extra environment friendly, safer surgical procedure,” mentioned Ryan Orosco, MD, an affiliate professor and otolaryngologist (head and neck surgeon) within the UNM College of Drugs who co-authored the paper.
The journal article reported on a small Section 1–2 research of the drug, which was examined on 27 most cancers sufferers to judge its security and efficacy.
“The trial was for sufferers having a neck dissection to take away lymph nodes or a parotid surgical procedure or a thyroid surgical procedure,” he mentioned. “In all of these circumstances, there are cranial nerves which might be vital to determine, work round and defend.”
A bigger Section 3 research at present underway contains sufferers at UNM Hospital and is predicted to be accomplished by this summer season, Orosco mentioned. It’s going to assess whether or not use of the imaging agent meaningfully improves total surgical outcomes, one thing the preliminary trial was not designed to find out.
Orosco’s involvement within the improvement of the drug dates again to his ENT residency on the College of California, San Diego, the place he spent a year-long analysis fellowship within the lab of Quyen Nguyen, MD, Ph.D. She had labored intently with the late biochemist Roger Tsien, Ph.D., who received the Nobel Prize in 2008 for locating inexperienced fluorescent protein, enabling the event of strategies to “tag” particular molecules and tissue sorts, corresponding to most cancers cells.
Nguyen’s analysis ultimately led to the event of bevonescein. Orosco, who went on to do a head and neck most cancers fellowship at Stanford earlier than becoming a member of the UCSD college, performed a job in creating the medical trial protocol and carried out lots of the surgical procedures within the research.
He joined the UNM college in late 2022 and now serves because the nationwide principal investigator for the Section 3 trial of the drug, which now contains 10 websites.
Sufferers within the trials obtain an IV infusion of the drug previous to surgical procedure, however it’s shortly cleared by the kidneys, Orosco mentioned.
“We will picture them 5, six, seven, eight hours later, and it nonetheless stays certain to the nerves, however it flushes out of the physique inside 12 hours.”
Within the working room, surgeons use microscopes with particular lights and filters that illuminate the surgical website at a selected frequency that causes the drug to fluoresce. The nerves seem as wormlike yellowish-green buildings that thread by means of the encircling tissue.
An upcoming section of the analysis will consider using specifically modified headband-mounted magnifying loupes of the type that surgeons put on, quite than the microscope.
“Testing these loupes in a derivative trial is a crucial and sensible step towards real-world implementation,” Orosco mentioned.
If the Section 3 trial reveals clear medical profit from using bevonescein throughout head and neck surgical procedure, it may win FDA approval, resulting in wider use in surgical procedures all through the physique.
“As soon as the FDA has authorized it for a sure indication, then it will be on the cabinets,” he mentioned. “Surgeons can even use it off-label for no matter they need. Then the large query is, how does that go? Who begins utilizing it and during which forms of surgical procedures?”
Extra data:
Yu-Jin Lee et al, Intraoperative nerve-specific fluorescence visualization in head and neck surgical procedure: a Section 1 trial, Nature Communications (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-60737-x
Quotation:
A brand new drug causes nerve tissue to emit gentle, enabling quicker, safer surgical procedure (2025, July 3)
retrieved 6 July 2025
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2025-07-drug-nerve-tissue-emit-enabling.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.