People are innately able to recognizing different individuals they’ve seen earlier than. This functionality finally permits them to construct significant social connections, develop their sense of id, higher cooperate with others, and establish people who may pose a threat to their security.
A number of previous research rooted in neuroscience, psychology and behavioral science have tried to make clear the neural processes underlying the power to encode different individuals’s identities. Most findings collected thus far recommend that the id of others is encoded by neurons within the amygdala and hippocampus, two mind areas identified to assist the processing of feelings and the encoding of recollections, respectively.
Based mostly on proof collected prior to now, researchers have concluded that neurons in these two mind areas reply in particular methods once we meet an individual we’re acquainted with, no matter visible options (i.e., how their face appears). A latest paper revealed in Nature Human Behaviour, nonetheless, means that this may not be the case, and that particular person neurons within the amygdala encode and characterize facial options, finally supporting the identification of others.
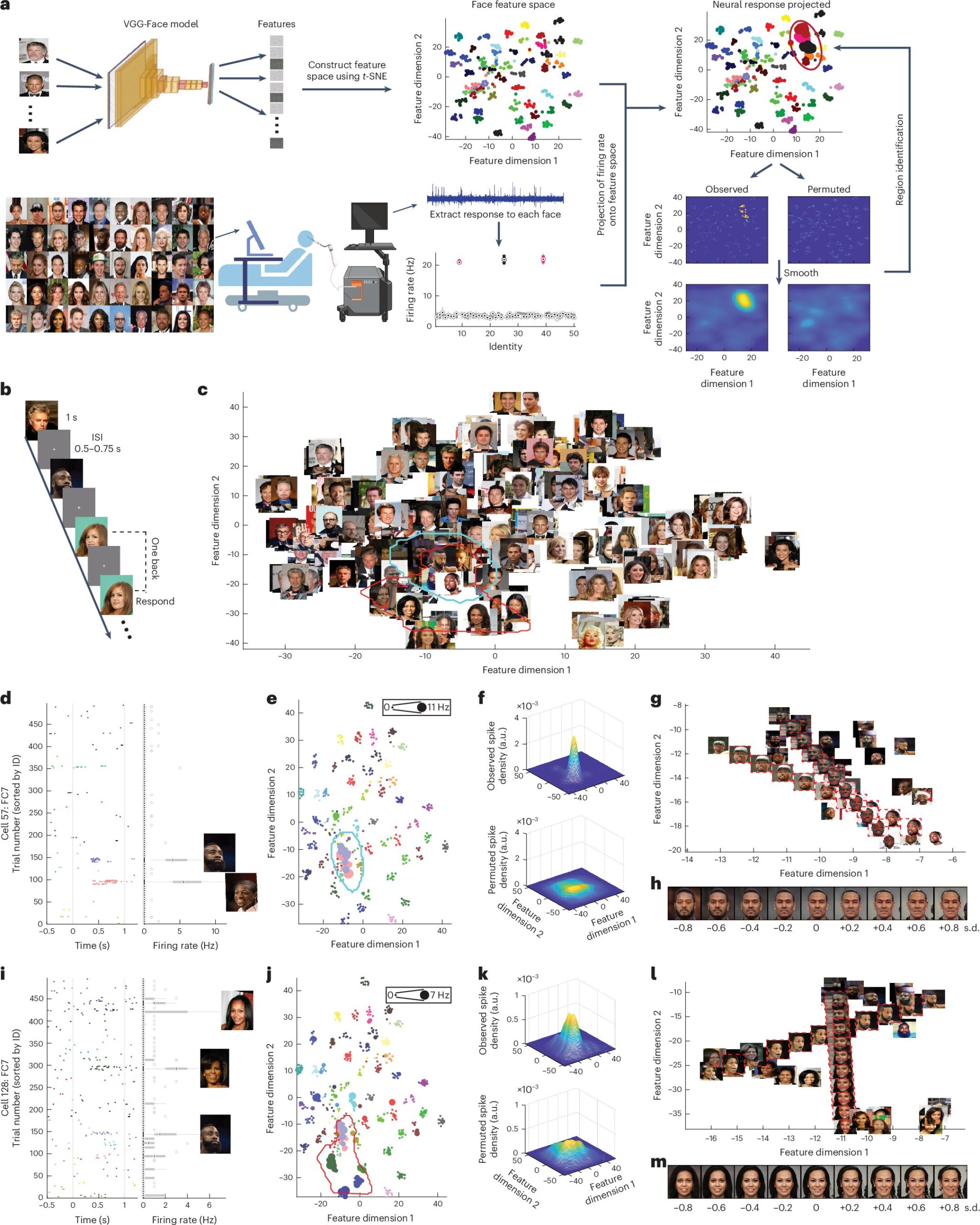
The authors of the paper, primarily based at Washington College in St Louis, West Virginia College, and different institutes, carried out 4 experiments involving 19 neurological sufferers. The sufferers had electrodes implanted of their brains as a part of their remedy for epilepsy, and the researchers used these electrodes to document the exercise of over 3,500 particular person neurons within the amygdala and hippocampus.
“Neurons within the human amygdala and hippocampus are classically thought to encode an individual’s id invariant to visible options,” wrote Runnan Cao, Jinge Wang and their colleagues of their paper. “Nonetheless, it stays largely unknown how visible data from increased visible cortical areas is translated into such a semantic illustration of a person individual.
“Throughout 4 experiments (3,581 neurons from 19 neurosurgical sufferers over 111 classes), we exhibit a region-based characteristic code for faces, the place neurons encode faces on the premise of shared visible options slightly than associations of identified ideas, opposite to prevailing views.”
The sufferers who participated within the staff’s experiment have been proven photographs of various individuals’s faces, a few of whom have been kind of acquainted to them. Whereas they seemed on the photographs, the electrodes implanted of their brains recorded the exercise of particular person neurons within the hippocampus and amygdala.
The researchers then analyzed the recordings they’d collected and located that some neurons appeared to constantly reply to particular face options, no matter the extent to which an individual was acquainted to a participant. This seems to contradict earlier theories, suggesting that some neurons within the hippocampus and amygdala do in actual fact encode visible options and will additionally play an element within the human capacity to acknowledge particular individuals.
“Function neurons encode teams of faces no matter their id, broad semantic classes or familiarity; and the coding areas (that’s, receptive fields) predict characteristic neurons’ response to new face stimuli,” wrote Cao, Wang and their colleagues.
“Collectively, our outcomes reveal a brand new class of neurons that bridge perception-driven illustration of facial options with mnemonic semantic representations, which can type the premise for declarative reminiscence.”
The brand new insights gathered by Cao, Wang and their colleagues may deepen the current understanding of id recognition. Sooner or later, it may encourage additional analysis specializing in the category of neurons recognized by the researchers, whereas additionally probably pinpointing neural processes which can be disrupted in people who wrestle to acknowledge faces, reminiscent of these identified with the cognitive dysfunction prosopagnosia.
Written for you by our writer Ingrid Fadelli,
edited by Gaby Clark
, and fact-checked and reviewed by Robert Egan —this text is the results of cautious human work. We depend on readers such as you to maintain impartial science journalism alive.
If this reporting issues to you,
please contemplate a donation (particularly month-to-month).
You will get an ad-free account as a thank-you.
Extra data:
Runnan Cao et al, Function-based encoding of face id by single neurons within the human amygdala and hippocampus, Nature Human Behaviour (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s41562-025-02218-1.
© 2025 Science X Community
Quotation:
Particular person neurons in amygdala and hippocampus encode visible options that assist acknowledge faces, examine finds (2025, June 29)
retrieved 29 June 2025
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2025-06-individual-neurons-amygdala-hippocampus-encode.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.