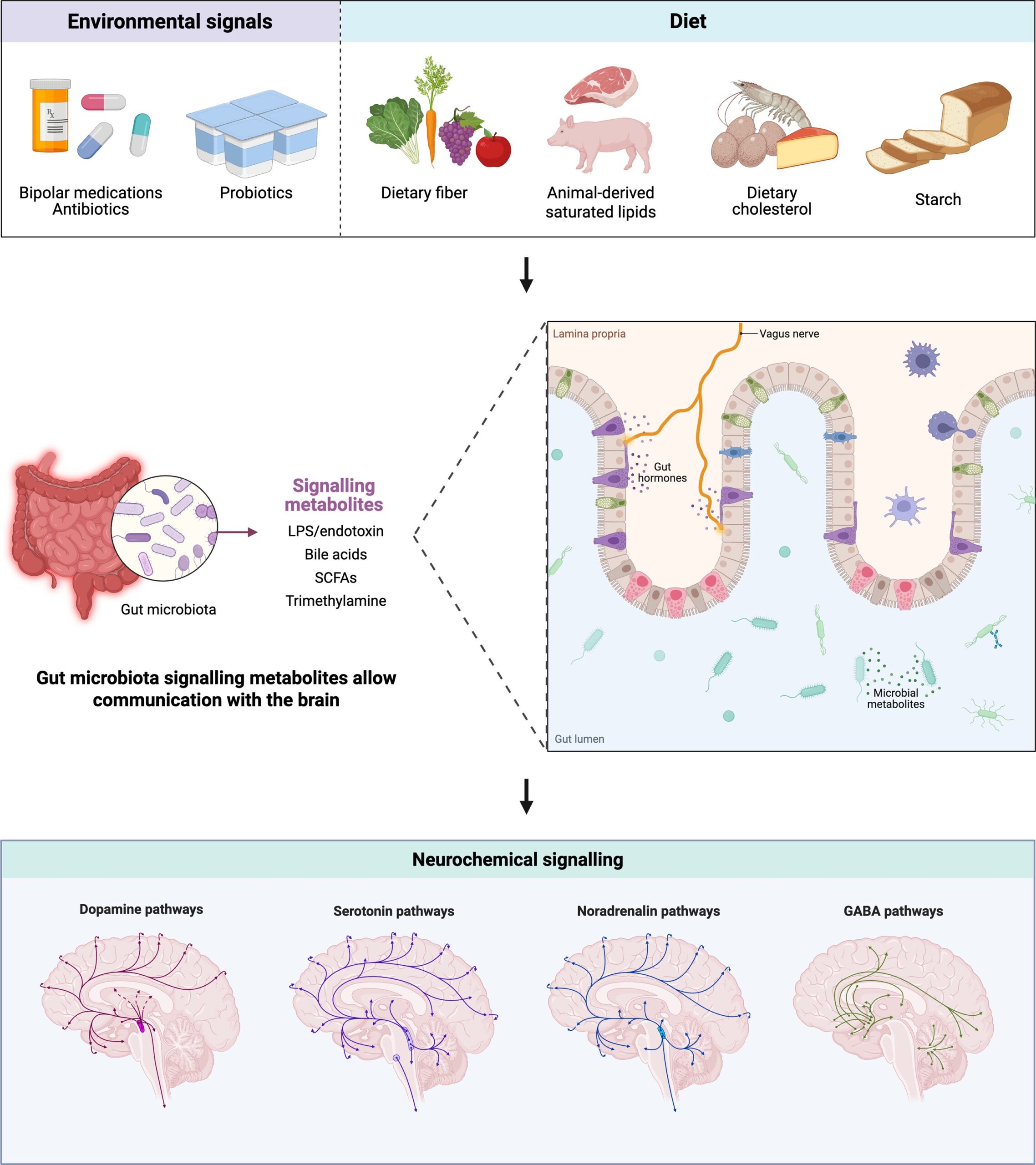
A brand new overview, revealed in Microbiology, is the primary to systematically overview the potential results of psychotropics (the medicine used to deal with bipolar dysfunction) on the intestine microbiome of handled and untreated bipolar people.
Bipolar dysfunction is a psychological well being situation characterised by unpredictable temper shifts, together with episodes of mania and melancholy. Regardless of being probably the most frequent and debilitating temper problems, affecting over 1% of the worldwide inhabitants, bipolar dysfunction is commonly misdiagnosed and undertreated.
A big variety of people with bipolar dysfunction don’t reply adequately to medicine and former research have proven that the intestine microbiome, which is the group of microbes and their surrounding surroundings (the intestine), of sufferers with bipolar dysfunction are totally different to wholesome people. This can be because of the connection between the intestine and the mind, often known as the gut-brain axis, which is a two-way communication through chemical alerts reminiscent of neurotransmitters and hormones.
Modifications to the composition of the intestine microbiome can have an effect on the best way that the mind is ready to operate. It additionally works the opposite approach, and modifications to the mind, like in bipolar dysfunction, can have an effect on the abundance and composition of the intestine microbiome.
Researchers from the College of Alberta, Canada, had been occupied with reviewing present information to learn how bipolar medicines can have an effect on the intestine microbiome, and due to this fact the mind, and whether or not the composition of the intestine microbiome might change the best way a affected person responds to therapy.
Researchers collected information from 12 present research that analyzed the consequences of bipolar medicines on the intestine microbiome. They included research that checked out variations between the intestine microbiome of adults identified with bipolar dysfunction who had been receiving medicines and in contrast them both to earlier than they started taking medicine; unmedicated individuals; or wholesome controls.
The information collected suggests that there’s a important connection between the intestine and mind in sufferers handled for bipolar dysfunction and that this impacts the methods during which a affected person responds to therapy.
Sufferers throughout a number of research who responded to therapy (indicated by alleviated melancholy signs) had markedly totally different intestine microbiome populations in comparison with those that didn’t reply. The truth is, these sufferers had intestine microbiome profiles extra alike to wholesome people. Sooner or later, this will likely assist researchers predict how a affected person will reply to therapy.
The gut-brain axis is a fancy system which could be affected by a number of elements and additional research are wanted to know the trigger and impact between the intestine microbiome and the mind.
An Bui, lead writer of the examine from the Division of Psychiatry on the College of Alberta mentioned, “We do not know the course during which this happens, whether or not the medicine change the intestine microbiome and this modifications the best way the mind capabilities, or whether or not the medicine change the best way the mind capabilities which in flip, impacts the intestine microbiome.”
Researchers hope that the outcomes of the examine might pave the best way for brand new customized therapy methods and encourage additional research wanting on the molecular mechanisms of those pathways and medical trials which concentrate on microbiome focused therapies.
Dr. Andrew Greenshaw, writer on the examine and Professor of Psychiatry and Neuroscience on the College of Alberta, Canada mentioned, “The overview is vital because it brings up extra questions and solutions for future analysis on how the intestine microbiome impacts bipolar therapy responses and vice versa. Additionally, for the reason that analysis topic remains to be new, synthesizing such numerous outcomes with heterogeneous experimental methodologies could be useful in guiding researchers design new research.”
Extra data:
Truong An Bui et al, Pharmaco-psychiatry and intestine microbiome: a scientific overview of results of psychotropic medicine for bipolar dysfunction, Microbiology (2025). DOI: 10.1099/mic.0.001568
Offered by
Microbiology Society
Quotation:
Intestine-brain axis impacts therapy outcomes in bipolar sufferers, examine finds (2025, June 18)
retrieved 18 June 2025
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2025-06-gut-brain-axis-impacts-treatment.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.