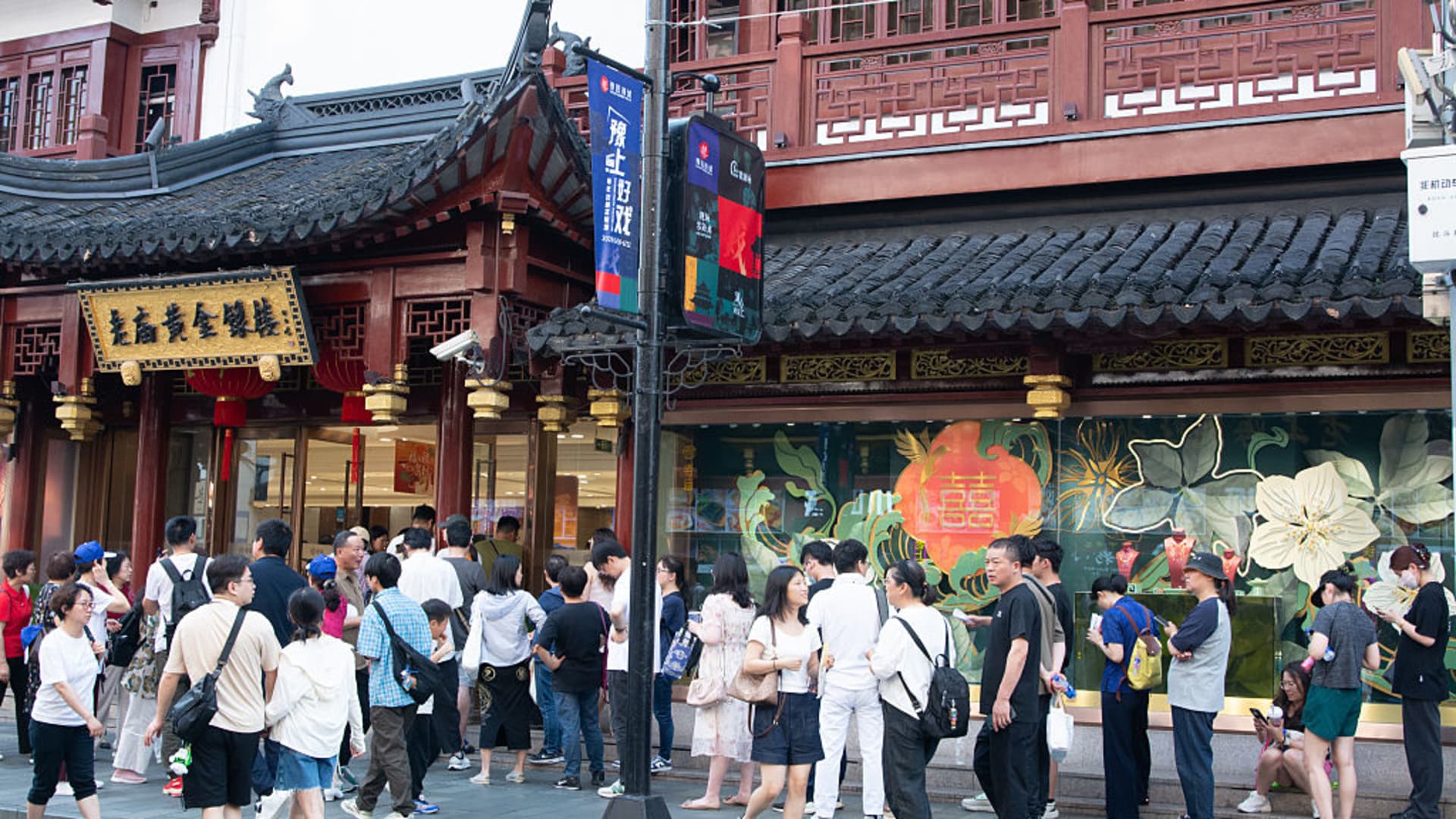
Enormous ready strains are seen in entrance of jewellery retailer shops at Yu Backyard in Shanghai, China, on Might 17, 2025, as the town provides consumption vouchers to stimulate shopper spending.
Nurphoto | Nurphoto | Getty Pictures
China’s retail gross sales in Might grew at their quickest charge since late 2023, information from Nationwide Bureau of Statistics confirmed Monday, partially helped by the prolonged Labor Day and Dragon Boat holidays.
Retail gross sales final month jumped 6.4% from a 12 months earlier, sharply beating analysts’ estimates for a 5% progress in a Reuters ballot and accelerating from the 5.1% progress within the earlier month.
Development in industrial output slowed to five.8% 12 months on 12 months in Might from 6.1% within the prior month. The newest studying got here in barely weaker than analysts’ expectations for a 5.9% rise.
Fastened-asset funding, reported on a year-to-date foundation, expanded 3.7% this 12 months as of Might from a 12 months earlier, undershooting Reuters’ forecast for a 3.9% progress and slowing from a 4% progress within the first 4 months.
Inside the fixed-asset funding, the contraction in property funding deepened, falling 10.7% within the first 5 months, authorities information confirmed.
The city survey-based unemployment charge in Might got here in at 5.0%, easing from 5.1% in April to the bottom degree since November final 12 months.
“The rise of retail gross sales got here as a shock,” probably boosted by the lasting results from shopper items trade-in program, stated Zhiwei Zhang, president and chief economist at Pinpoint asset administration, including that the falling property costs might dampen shopper sentiment.
A separate launch Monday by the NBS confirmed costs of recent properties within the extra prosperous tier 1 cities continued to say no, falling 1.7% in Might from a 12 months in the past, whereas these in tier 2 and tier 3 cities dropped 3.5% and 4.9%, respectively.
A tariff deal reached by Beijing and Washington in mid-Might gave momentary aid to the nation’s exports, prompting some companies to frontload cargo whereas doubling down on various markets. Each side struck a 90-day truce to roll again a lot of the triple-digit levies added on one another’s items in early April.
Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick instructed CNBC final week that U.S. tariffs on Chinese language imports will keep at their present degree of 55%.
China’s exports grew lower than anticipated in Might, although surging shipments to Southeast Asian nations, European Union nations and Africa helped offset the sharp decline in U.S.-bound items. China’s exports to the U.S. plunged over 34% from a 12 months in the past, their sharpest drop since February 2020.
The previous two months’ commerce information indicated resilience in China’s exports, based on Goldman Sachs, as they highlighted “the problem for bilateral tariffs to meaningfully cut back whole Chinese language exports.”
Sluggish home demand caught out as a extra urgent concern for Chinese language policymakers. Shopper costs have seen an year-on-year decline for 4 consecutive months, slumping 0.1% in Might. Deflation within the factory-gate or producer costs has additionally deepened, falling 3.3% from a 12 months in the past.
Nonetheless, Beijing could really feel much less urgency in rolling out extra easing steps as exports seem extra resilient than anticipated and the GDP progress is on monitor to exceed 5% within the first half-year, Goldman stated.