Key takeaways:
- Accelerometers confirmed a slower price of decline vs. ALSFRS-R scores, with robust correlation in motor domains.
- Longitudinal evaluation deemed accelerometer information complementary to ALSFRS-R, indicating viability.
Wrist-based accelerometry could also be a possible technique for steady monitoring for people with motor neuron illness, in response to information printed in eBioMedicine.
“Actigraphy, which leverages wearable sensors to observe motion, gives a promising platform for figuring out novel consequence measures outdoors the clinic,” Cory J. Holdom, a doctoral scholar on the Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology on the College of Queensland, and colleagues wrote.

Knowledge have been derived from Holdom CJ, et al. EBioMedicine. 2025;doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2025.105779.
Hallmarks of motor neuron illness (MND), a group of neurodegenerative situations centered round lack of neuronal perform inside the mind, embrace muscle weak spot, atrophy or spasticity, requiring measures that arrest illness development, Holdom and colleagues wrote.
As present medical measures lack the power to precisely and objectively log practical decline in each day residing of sufferers with MND, the researchers sought to evaluate and validate wrist-worn accelerometers for steady monitoring on this affected person inhabitants.
Their longitudinal, pure historical past examine included 95 people (77% male; imply age = 59.95 years) with MND who attended the Royal Brisbane and Ladies’s Hospital MND clinic with information collected between February 2017 and September 2021.
All enrollees, no matter limb incapacity, donned an ActiGraph GT9X Hyperlink system on their non-dominant wrist for 8 days, with recordings set to start simply previous to 12 p.m. on the day the system was issued.
Accelerometer information have been processed utilizing ActiLife and GGIR throughout baseline assessments in addition to follow-up, which occurred on the hospital roughly each 3 months. Longitudinal adjustments in ALS Purposeful Ranking Scale-Revised (ALSFRS-R) scores have been tracked between baseline and observe up.
For the needs of research, questions within the ALSFRS-R have been subdivided into 4 domains: bulbar, questions 1-3; higher limb, 4-5; decrease limb, 8-9; and respiratory, 10-12). As well as, there was an overlaid motor area between questions 4 and 9.
Pattern measurement estimates for members’ medical trial suitability have been generated utilizing each accelerometer- and ALSFRS-R-based outcomes, whereas principal element evaluation (PCA) in contrast accelerometer and ALSFRS-R information for analytical suitability.
Based on outcomes, accelerometer outcomes confirmed a slower price of decline (0.6 to 0.3 customary deviations monthly) in contrast with ALSFRS-R (0.1 SD/month), demonstrating stronger correlations with overlaid motor subdomains (partial r: 0.6–0.73) from the ALSFRS-R.
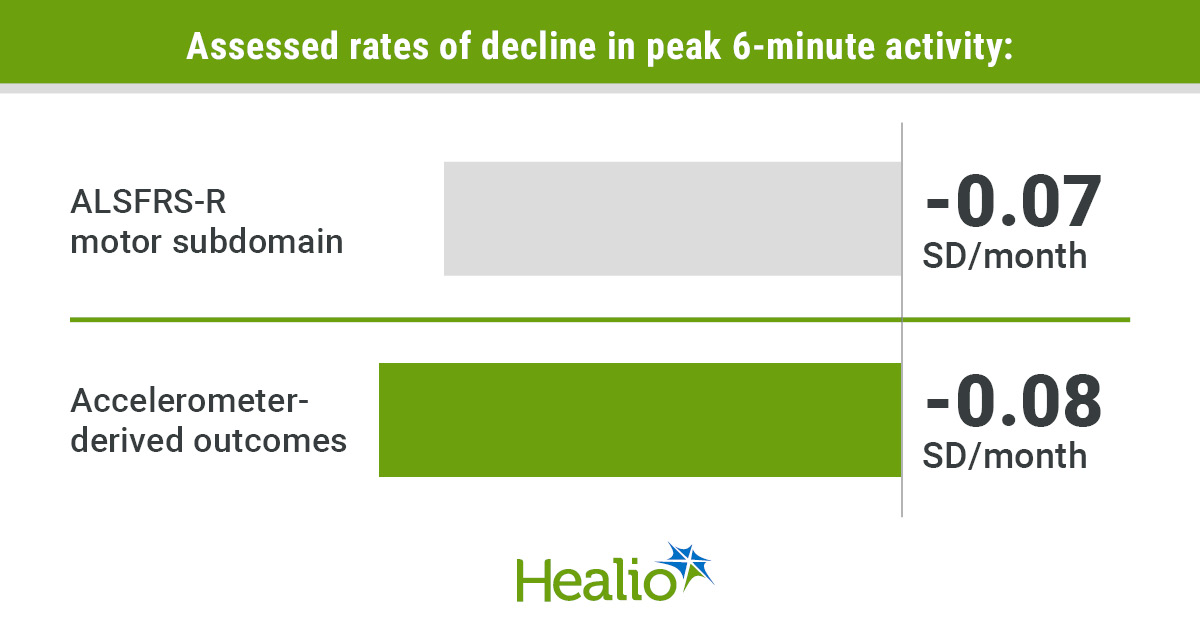
This decline, seen particularly in peak 6-minute exercise (0.07 SD monthly), in contrast favorably with the motor area from ALSFRS-R (0.08 SD monthly), suggesting suitability as a marker to detect practical variations.
The researchers additionally reported that PCA evaluation distinguished longitudinal measures of accelerometry differed from ALSFRS-R, confirming their complementary nature. Nonetheless, they reported that accelerometer-derived outcomes weren’t statistically considerably related to survival.
“By increasing the array of dependable and delicate measures and optimizing information assortment protocol, we are able to improve illness monitoring, scale back affected person burden by way of distant evaluation, and enhance the analysis of therapeutic interventions in [motor neuron disease],” Holdom and colleagues wrote.