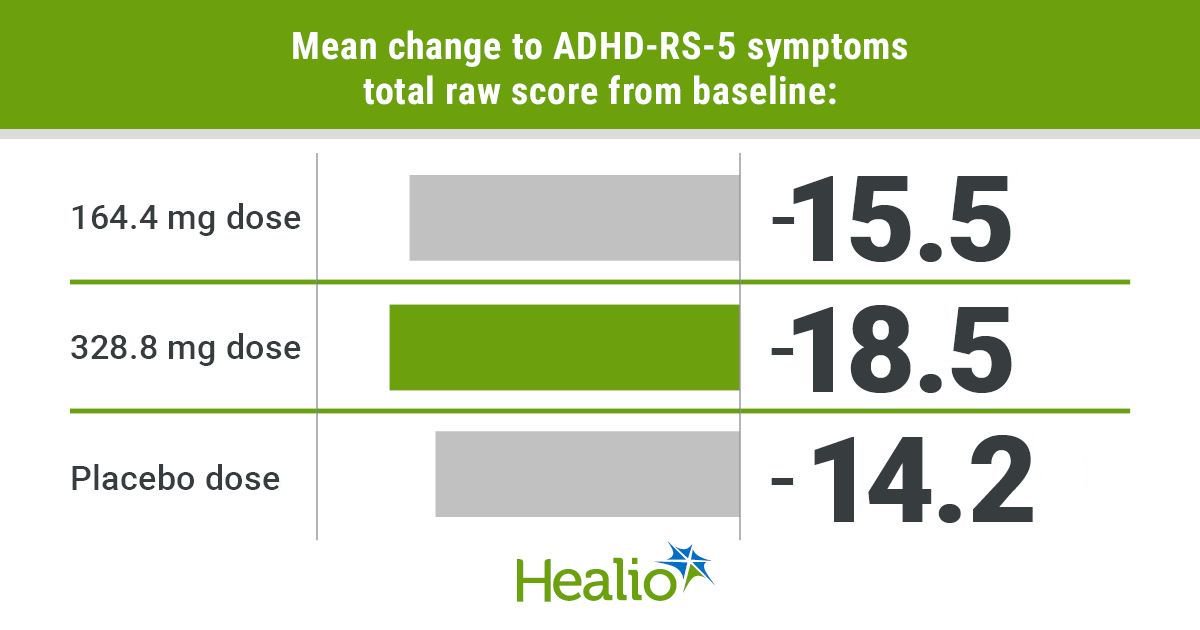
Scientists have uncovered outstanding insights into how the earliest mind connections form toddler emotional improvement, probably providing new methods to determine youngsters in danger for future behavioral and emotional challenges.
The research, led by Dr. Yicheng Zhang and Dr. Mary L. Phillips on the College of Pittsburgh College of Drugs, examined 95 infant-caregiver pairs utilizing superior mind imaging methods. Researchers found that the microstructure of white matter tracts—the mind’s data highways—at simply 3 months of age may predict how infants’ feelings and self-soothing talents would evolve over the next six months.
The research has been printed in Genomic Psychiatry.
Decoding the toddler mind’s emotional blueprint
The analysis staff employed refined Neurite Orientation Dispersion and Density Imaging (NODDI), a cutting-edge MRI method that gives unprecedented element about mind tissue group. This expertise allowed scientists to see into the growing mind’s structure with outstanding precision, revealing how the association of neural fibers influences emotional trajectories.
“What we’re seeing is that the mind’s structural group in early infancy units the stage for emotional improvement,” explains the analysis staff.
The research centered on vital white matter pathways connecting areas liable for self-awareness, consideration to vital stimuli, and cognitive management—networks that kind the muse of emotional processing all through life.
Key discoveries form understanding of emotional improvement
The findings revealed distinct patterns linking mind construction to emotional outcomes. Infants with increased neurite dispersion within the forceps minor—a bundle of fibers connecting the mind’s hemispheres—confirmed better will increase in adverse emotionality between 3 and 9 months. This implies that sure patterns of mind connectivity would possibly predispose infants to heightened emotional reactivity.
Conversely, infants with a extra complicated microstructure within the left cingulum bundle, which connects areas concerned in govt management, demonstrated bigger will increase in constructive feelings and improved self-soothing talents.
These discoveries increase intriguing questions on whether or not early interventions may probably affect these neural pathways to advertise more healthy emotional improvement.
Implications for early detection and intervention
The power to determine infants in danger for emotional difficulties earlier than behavioral signs emerge represents a major advance in developmental neuroscience. Earlier analysis has established that prime adverse emotionality in infancy correlates with elevated danger of future anxiousness and behavioral issues, whereas low constructive emotionality hyperlinks to later melancholy and social difficulties.
Dr. Phillips notes the potential affect, “Understanding these early neural markers may rework how we method toddler psychological well being, permitting for focused interventions throughout vital developmental home windows.”
The analysis staff validated their findings in an impartial pattern of 44 infants, strengthening confidence in these brain-behavior relationships.

Superior imaging reveals hidden patterns
The research’s use of NODDI expertise marks a major methodological advance in toddler mind analysis. Conventional imaging strategies typically battle to seize the nuanced group of growing mind tissue. NODDI’s capability to separate totally different tissue elements offers researchers with a clearer image of how neural pathways mature and arrange throughout this important interval.
The analysis examined three main white matter tracts: the forceps minor, cingulum bundle, and uncinate fasciculus. Every performs a significant position in connecting mind areas important for emotional processing and regulation. How would possibly variations in different mind connections affect toddler improvement? What position do environmental components play in shaping these neural pathways?
Bridging neuroscience and medical follow
The findings have fast relevance for pediatric care and early childhood improvement. By figuring out goal neural markers of emotional improvement, clinicians may probably display screen for danger components earlier than behavioral issues emerge. This proactive method may result in earlier, more practical interventions.
The analysis staff accounted for a number of components that may affect mind improvement, together with caregiver psychological well being, socioeconomic standing, and toddler traits. This complete method strengthens the research’s conclusions and means that mind microstructure represents a basic contributor to emotional improvement impartial of environmental influences.
Future instructions and unanswered questions
Whereas these findings signify a major advance, in addition they open new avenues for investigation. How steady are these early neural patterns all through childhood? Can focused interventions modify white matter improvement to advertise emotional resilience? The analysis staff’s ongoing work goals to deal with these questions via longitudinal research following infants into later childhood.
The research additionally highlights the significance of the primary yr of life as a vital interval for mind improvement. Throughout this time, speedy modifications in white matter group lay the muse for lifelong emotional and behavioral patterns. Understanding these processes at a neural stage may inform every little thing from parenting practices to public well being insurance policies supporting toddler improvement.
A brand new period in developmental neuroscience
This analysis exemplifies the ability of superior neuroimaging to disclose beforehand hidden features of mind improvement. As expertise continues to evolve, scientists acquire more and more refined instruments to grasp how the mind’s earliest group shapes human habits and expertise.
The College of Pittsburgh staff’s findings contribute to a rising physique of proof suggesting that many features of emotional and behavioral improvement have roots within the mind’s earliest structural patterns. By figuring out these patterns, researchers transfer nearer to growing focused interventions that would stop or mitigate future psychological well being challenges.
The implications prolong past particular person youngsters to broader questions on human improvement. How do genetic and environmental components work together to form these early mind patterns? What evolutionary benefits would possibly totally different patterns of emotional improvement confer? These basic questions drive continued analysis on this quickly advancing subject.
The research demonstrates that even within the earliest months of life, the mind’s structural group profoundly influences emotional improvement. This information opens new prospects for supporting wholesome improvement from the very starting of life.
Extra data:
Early toddler white matter tract microstructure predictors of subsequent change in emotionality and emotional regulation, Genomic Psychiatry (2025). DOI: 10.61373/gp025a.0026
Offered by
Genomic Press
Quotation:
Mind connections at 3 months predict toddler emotional improvement (2025, June 3)
retrieved 3 June 2025
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2025-06-brain-months-infant-emotional.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.