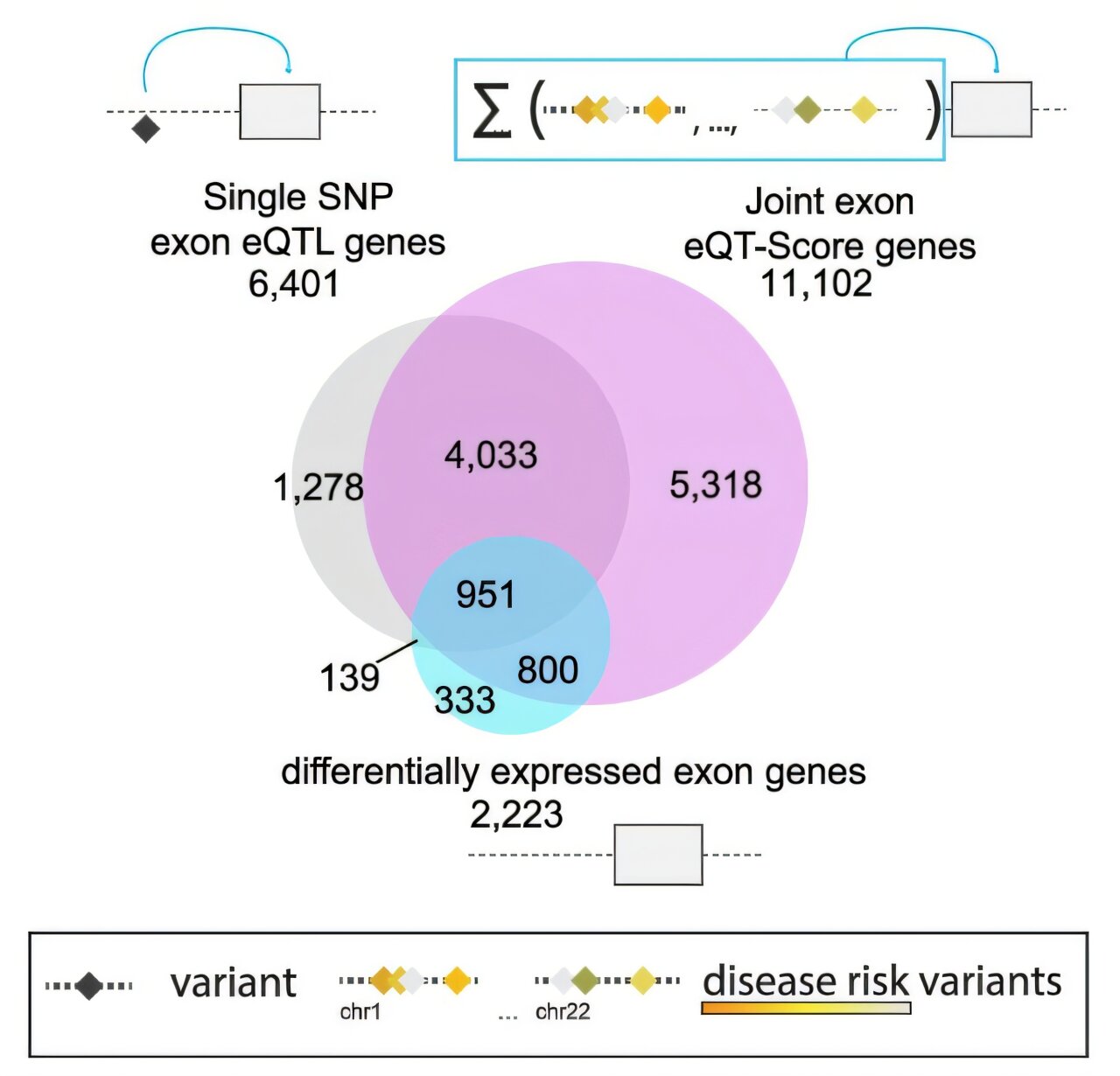
Researchers on the Max Planck Institute of Psychiatry (MPI), Helmholtz Munich and the College of Sydney have recognized organic mechanisms which might be shared throughout psychiatric issues.
To take action, the crew analyzed postmortem mind tissue samples from the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC). The DLPFC is the middle for reasoning and feelings within the mind, and is usually implicated in psychiatric issues. Samples from affected people, most of whom had been schizophrenia sufferers, and wholesome controls had been included within the examine, now revealed in Translational Psychiatry.
The analysis crew mixed a number of completely different layers of genetic information. “In distinction to research that take a look at gene expression as a complete, we analyzed the exon degree to raised perceive the construction of the genes. This detailed method gave us a greater understanding of how genetic variation influences illness danger,” first writer Karolina Worf explains.
Exons are the important, information-containing segments of a gene. Along with offering the blueprint for constructing proteins, additionally they decide which variations of a protein finally come up from a gene. This occurs by way of various splicing, a course of that happens in additional than 95% of human genes.
Together with the exon degree within the evaluation was an vital step: Whereas samples from psychiatric sufferers and wholesome controls weren’t considerably completely different on the gene degree, they had been considerably completely different on the exon degree. “The danger of creating a psychiatric dysfunction appears to due to this fact not simply rely upon what genes you will have, however how your genes are expressed,” explains Janine Knauer-Arloth, chief of the Venture Group Medical Genomics on the MPI.
The crew built-in completely different genetic information, together with variations in particular person base pairs of DNA (single nucleotide polymorphisms, or SNPs), uncommon genetic variants and polygenic danger scores, which summarize an individual’s illness danger by aggregating all related genetic variants. This fashion, the researchers found disruptions in pathways associated to the circadian rhythm, the discharge of the stress hormone cortisol, and the neurotransmitter dopamine—throughout all three included issues.
These outcomes present that psychiatric issues share a typical organic foundation. Within the long-term, this data can assist researchers to categorise psychiatric issues not solely based mostly on signs, but in addition based mostly on organic mechanisms. This paradigm shift is a major step towards extra exact diagnoses and therapy.
Extra info:
Karolina Worf et al, Exon-variant interaction and multi-modal proof establish endocrine dysregulation in extreme psychiatric issues impacting excitatory neurons, Translational Psychiatry (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s41398-025-03366-8
Quotation:
Genetic evaluation reveals shared organic mechanisms in melancholy, bipolar dysfunction and schizophrenia (2025, June 2)
retrieved 2 June 2025
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2025-06-genetic-analysis-reveals-biological-mechanisms.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.