Key takeaways:
- A 14-gene molecular assay might assist predict adjuvant chemotherapy profit in early NSCLC.
- Sufferers assigned adjuvant chemotherapy based mostly on molecular danger exhibited a 78% discount in danger for recurrence.
CHICAGO — A 14-gene molecular assay might assist predict which sufferers with early-stage non-small cell lung most cancers will profit from adjuvant chemotherapy, in accordance with outcomes of the AIM HIGH trial introduced at ASCO Annual Assembly.
“That is the primary potential randomized trial to point out enchancment in DFS with a molecular-risk discriminator in stage IA via stage IIA nonsquamous non-small cell lung most cancers,” David Spigel, MD, FASCO, chief scientific officer at Sarah Cannon Analysis Institute, stated throughout a press convention. “Utilization of this 14-gene assay to exactly direct systemic adjuvant remedy … might considerably cut back charges of early recurrence and dying.”

Information derived kind Spigel DR, et al. Summary LBA8027. Offered at: ASCO Annual Assembly; Could 30-June 3, 2025; Chicago.
An estimated 226,650 new instances of lung most cancers are identified annually, and about 70,000 of these are stage I or stage II NSCLC, in accordance with examine background. Roughly 70% of NSCLC instances are nonsquamous histology.
Sufferers with early-stage lung most cancers typically bear surgical procedure. Lower than 65% of sufferers with stage IA NSCLC who bear surgical procedure stay recurrence free after 5 years, Spigel stated.
Adjuvant remedy just isn’t beneficial for sufferers with stage IA illness, and it typically is deferred for these with stage 1B or stage IIA illness.
“Figuring out sufferers who’re on the highest danger for recurrence is a precedence,” Spigel stated.
Present protocols depend on illness stage and tumor dimension to find out the potential advantage of adjuvant remedy. Molecular assays that may establish modifications or modifications in genes or proteins could possibly assist information that dedication.

David Spigel
Spigel and colleagues evaluated if a business 14-gene assay (RiskReveal, Razor Genomics) might assist establish sufferers who might profit from adjuvant chemotherapy however in any other case may not have been supplied it.
The AIM HIGH trial included adults with fully resected stage IA to stage IIA nonsquamous NSCLC. All had adenocarcinoma — the affected person inhabitants wherein the assay had been validated in 2012 — and all had ECOG efficiency standing of 0 or 1.
Researchers used the assay to check tissue samples to characterize molecular danger. These characterised as low danger didn’t proceed on the examine.
Researchers randomly assigned these labeled as intermediate danger or excessive danger to statement (n = 111) or 4 cycles of platinum-based doublet chemotherapy (n = 89). Most of these assigned chemotherapy obtained carboplatin/pemetrexed (35%), cisplatin/pemetrexed (29%) or cisplatin/vinorelbine (20%).
The management and adjuvant chemotherapy teams appeared balanced for age (median, 66 years vs. 63 years), intercourse (53% males in each), proportion of sufferers with stage I illness (55% in each) and smoking historical past (86% vs. 90%).
Examine protocol allowed use of immunotherapy or tyrosine kinase inhibitor remedy for these with EGFR-positive illness per investigator discretion.
Routine CT surveillance continued for five years, or till illness recurrence or dying. DFS served as the first endpoint.
Median follow-up was 19.5 months within the chemotherapy group and 19 months within the statement group.
On the time of interim evaluation, median DFS had not been reached in both group.
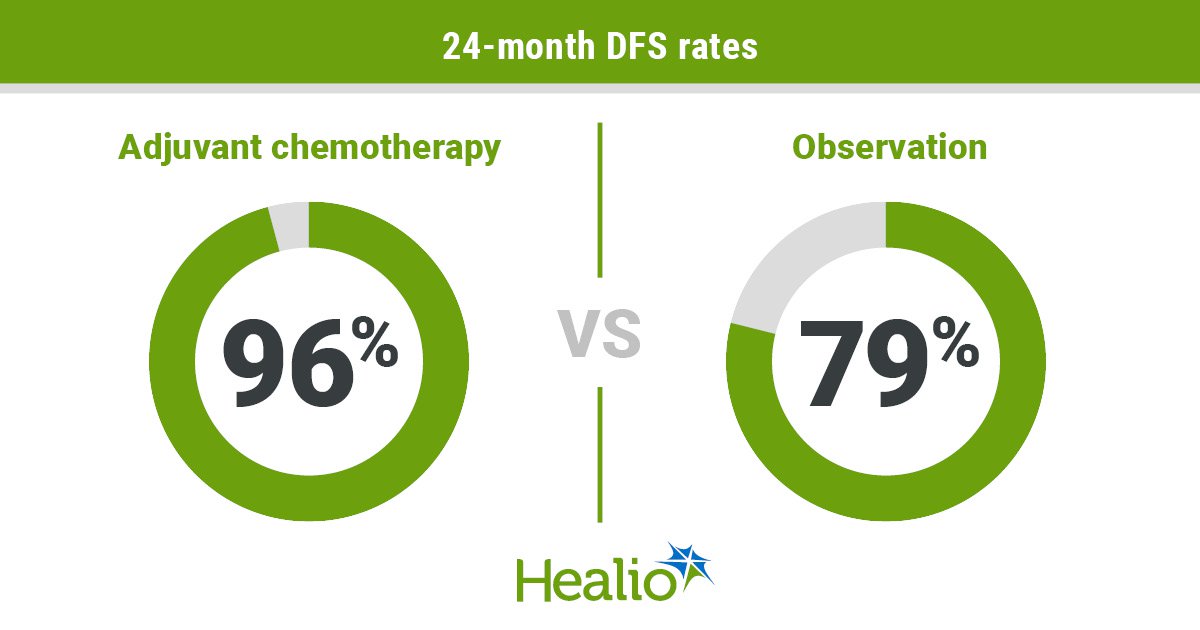
Outcomes confirmed a better proportion of sufferers assigned adjuvant chemotherapy achieved 24-month DFS (96% vs. 79%; HR = 0.22; 95% CI, 0.6-0.76).
An evaluation restricted to sufferers with stage IA illness confirmed an analogous 24-month DFS profit with adjuvant chemotherapy vs. statement (98% vs. 78%; P = .0345).
The antagonistic occasions noticed within the adjuvant chemotherapy group mirrored the established profiles of these brokers, Spigel stated.
Because of the efficacy noticed on the interim evaluation, the info security monitoring board beneficial investigators cease enrolling new sufferers. Spigel and colleagues will proceed to comply with individuals already enrolled.
When the assay was developed, outcomes from the validation cohort confirmed sufferers with stage IA illness whose scores characterised them as low danger had 5-year survival approaching 95% with out adjuvant chemotherapy, Spigel stated.
“If a affected person has a low-risk rating, it appears fairly clear chemotherapy doesn’t supply profit,” Spigel stated. “Whether or not different therapies like immunotherapy or focused remedy may gain advantage these teams stays to be seen.”
The assay might assist information shared decision-making for sufferers with stage IB or stage IIA illness, Spigel stated.
“If a doctor is planning to provide chemotherapy anyway [and] the affected person desires it, this check performs no function,” Spigel stated. “On the different excessive, if a affected person has made the choice they received’t bear chemotherapy it doesn’t matter what, this check doesn’t play a job. For these sufferers on the fence — once we perceive the dangers and advantages however we’re nonetheless undecided what to do — this check is offered with extra data to assist us make that call.”