A brand new malware marketing campaign is distributing a novel Rust-based info stealer dubbed EDDIESTEALER utilizing the favored ClickFix social engineering tactic initiated by way of faux CAPTCHA verification pages.
“This marketing campaign leverages misleading CAPTCHA verification pages that trick customers into executing a malicious PowerShell script, which in the end deploys the infostealer, harvesting delicate information akin to credentials, browser info, and cryptocurrency pockets particulars,” Elastic Safety Labs researcher Jia Yu Chan mentioned in an evaluation.
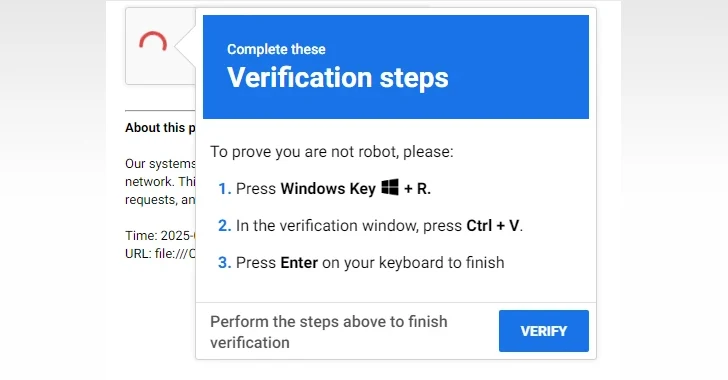
The assault chains start with menace actors compromising reliable web sites with malicious JavaScript payloads that serve bogus CAPTCHA test pages, which immediate website guests to “show you aren’t [a] robotic” by following a three-step course of, a prevalent tactic known as ClickFix.
This includes instructing the potential sufferer to open the Home windows Run dialog immediate, paste an already copied command into the “verification window” (i.e., the Run dialog), and press enter. This successfully causes the obfuscated PowerShell command to be executed, ensuing within the retrieval of a next-stage payload from an exterior server (“llll[.]match”).
The JavaScript payload (“gverify.js”) is subsequently saved to the sufferer’s Downloads folder and executed utilizing cscript in a hidden window. The primary objective of the intermediate script is to fetch the EDDIESTEALER binary from the identical distant server and retailer it within the Downloads folder with a pseudorandom 12-character file title.
Written in Rust, EDDIESTEALER is a commodity stealer malware that may collect system metadata, obtain duties from a command-and-control (C2) server, and siphon information of curiosity from the contaminated host. The exfiltration targets embody cryptocurrency wallets, internet browsers, password managers, FTP shoppers, and messaging apps.
“These targets are topic to vary as they’re configurable by the C2 operator,” Elastic defined. “EDDIESTEALER then reads the focused recordsdata utilizing normal kernel32.dll features like CreateFileW, GetFileSizeEx, ReadFile, and CloseHandle.”
The collected host info is encrypted and transmitted to the C2 server in a separate HTTP POST request after the completion of every job.
Moreover incorporating string encryption, the malware employs a customized WinAPI lookup mechanism for resolving API calls and creates a mutex to make sure that just one model is operating at any given time. It additionally incorporates checks to find out if it is being executed in a sandboxed surroundings, and if that’s the case, deletes itself from disk.
“Based mostly on an identical self-deletion method noticed in Latrodectus, EDDIESTEALER is able to deleting itself by way of NTFS Alternate Knowledge Streams renaming, to bypass file locks,” Elastic famous.
One other noteworthy characteristic constructed into the stealer is its skill to bypass Chromium’s app-bound encryption to realize entry to unencrypted delicate information, akin to cookies. That is completed by together with a Rust implementation of ChromeKatz, an open-source software that may dump cookies and credentials from the reminiscence of Chromium-based browsers.
The Rust model of ChromeKatz additionally incorporates adjustments to deal with eventualities the place the focused Chromium browser shouldn’t be operating. In such instances, it spawns a brand new browser occasion utilizing the command-line arguments “–window-position=-3000,-3000 https://google.com,” successfully positioning the brand new window far off-screen and making its invisible to the consumer.
In opening the browser, the goal is to allow the malware to learn the reminiscence related to the community service youngster course of of Chrome that is recognized by the “-utility-sub-type=community.mojom.NetworkService” flag and in the end extract the credentials.
Elastic mentioned it additionally recognized up to date variations of the malware with options to reap operating processes, GPU info, variety of CPU cores, CPU title, and CPU vendor. As well as, the brand new variants tweak the C2 communication sample by preemptively sending the host info to the server earlier than receiving the duty configuration.
That is not all. The encryption key used for client-to-server communication is hard-coded into the binary, versus retrieving it dynamically from the server. Moreover, the stealer has been discovered to launch a brand new Chrome course of with the –remote-debugging-port=
“This adoption of Rust in malware growth displays a rising development amongst menace actors looking for to leverage trendy language options for enhanced stealth, stability, and resilience towards conventional evaluation workflows and menace detection engines,” the corporate mentioned.
The disclosure comes as c/aspect revealed particulars of a ClickFix marketing campaign that targets a number of platforms, akin to Apple macOS, Android, and iOS, utilizing methods like browser-based redirections, faux UI prompts, and drive-by obtain methods.
The assault chain begins with an obfuscated JavaScript hosted on a web site, that when visited from macOS, initiates a sequence of redirections to a web page that guides victims to launch Terminal and run a shell script, which ends up in the obtain of a stealer malware that has been flagged on VirusTotal because the Atomic macOS Stealer (AMOS).
Nevertheless, the identical marketing campaign has been configured to provoke a drive-by obtain scheme when visiting the online web page from an Android, iOS, or Home windows machine, resulting in the deployment of one other trojan malware.
The disclosures coincide with the emergence of recent stealer malware households like Katz Stealer and AppleProcessHub Stealer concentrating on Home windows and macOS respectively, and are able to harvesting a variety of data from contaminated hosts, in line with Nextron and Kandji.
Katz Stealer, like EDDIESTEALER, is engineered to bypass Chrome’s app-bound encryption, however another way by using DLL injection to acquire the encryption key with out administrator privileges and use it to decrypt encrypted cookies and passwords from Chromium-based browsers.
“Attackers conceal malicious JavaScript in gzip recordsdata, which, when opened, set off the obtain of a PowerShell script,” Nextron mentioned. “This script retrieves a .NET-based loader payload, which injects the stealer right into a reliable course of. As soon as energetic, it exfiltrates stolen information to the command and management server.”
AppleProcessHub Stealer, then again, is designed to exfiltrate consumer recordsdata together with bash historical past, zsh historical past, GitHub configurations, SSH info, and iCloud Keychain.
Assault sequences distributing the malware entail the usage of a Mach-O binary that downloads a second-stage bash stealer script from the server “appleprocesshub[.]com” and runs it, the outcomes of that are then exfiltrated again to the C2 server. Particulars of the malware have been first shared by the MalwareHunterTeam on Could 15, 2025, and by MacPaw’s Moonlock Lab final week.
“That is an instance of a Mach-O written in Goal-C which communicates with a command and management server to execute scripts,” Kandji researcher Christopher Lopez mentioned.