Key takeaways:
- Sufferers with gastrointestinal cancers had considerably decrease danger for demise in the event that they obtained fluoropyrimidine chemotherapy.
- Preexisting heart problems didn’t improve danger for cardiotoxicity.
Survival advantages of fluoropyrimidine chemotherapy considerably outweighed the dangers for cardiovascular occasions for sufferers with gastrointestinal cancers, based on outcomes of an observational cohort examine.
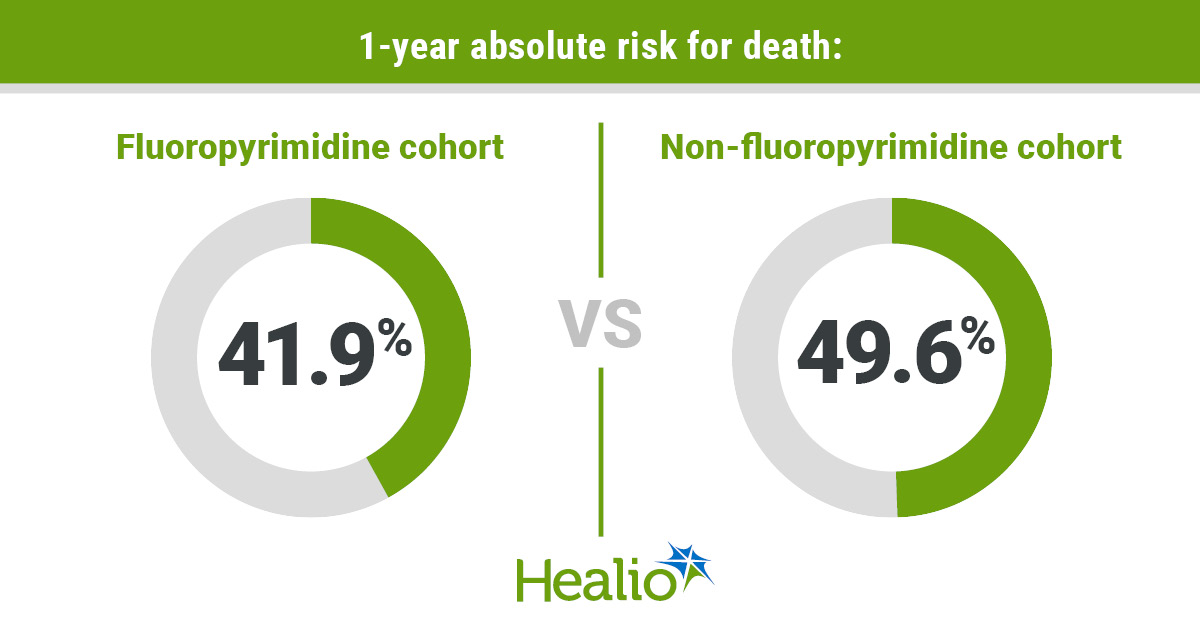
Sufferers who obtained fluoropyrimidine chemotherapy had a virtually 8% decrease absolute danger for demise at 1 yr than those that didn’t. Their danger for cardiovascular occasions throughout the identical time elevated roughly 1%.

Knowledge derived from Abiodun AT, et al. JACC CardioOncol. 2025;doi:10.1016/j.jaccao.2025.01.019.

Charlotte Manisty
“We hope it will present reassurance to oncologists and permit them to keep away from potential inappropriate therapeutic conservatism stopping these sufferers from having lifesaving most cancers therapies,” examine creator Charlotte Manisty, MD, PhD, head of scientific cardiovascular science at Institute of Cardiovascular Science at College School London and chief of cardio-oncology service at Barts Coronary heart Centre and College School Hospitals in London, instructed Healio.
Massive nationwide dataset
Fluoropyrimidine chemotherapy is a first-line remedy choice for many gastrointestinal cancers, however it will probably trigger cardiotoxicity, based on examine background.
Many people with gastrointestinal cancers have already got heart problems earlier than starting remedy.
Manisty and colleagues beforehand printed a examine in BMJ Oncology that confirmed people with gastrointestinal most cancers who had preexisting heart problems had a 27% decrease chance of receiving fluoropyrimidine.
“A few of the research recommend that when you’ve bought preexisting heart problems, you usually tend to have cardiotoxic occasions throughout [fluoropyrimidine] remedy,” Manisty stated. “Many different research say precisely the alternative, which is there doesn’t appear to be an elevated danger.
“We set out, utilizing this very giant nationwide linked dataset, to try to handle this query.”
The researchers used the Digital Cardio-Oncology Analysis Initiative program to analyze.
They included 103,110 adults recognized with gastrointestinal cancers between January 2014 and March 2018 who had fluoropyrimidine chemotherapy indicated as a first-line remedy choice.
Most contributors had colorectal most cancers (66.3%).
Researchers used a grace interval of 8 weeks and censored people who died throughout that point.
After the grace interval, the analyzed cohort included 25,401 sufferers who obtained fluoropyrimidine (imply age, 63.5 years; commonplace deviation, 11.6; 63.9% males; 91.1% white) and 64,589 who didn’t (imply age, 71 years; commonplace deviation, 12.3; 58.3% males; 91.4% white).
All-cause mortality and hospitalizations for cardiovascular occasions at 1 yr served as major endpoints.
‘Putting’ outcomes
In all, 21,110 sufferers died within the fluoropyrimidine group in contrast with 31,104 within the non-fluoropyrimidine group.
The fluoropyrimidine cohort had a decrease 1-year absolute danger for demise (41.9%; 95% CI, 41.1%-42.8%) than the non-fluoropyrimidine cohort (49.6%; 95% CI, 49.1%-50.3%) — a distinction of seven.7% (95% CI, 6.7%-8.7%). The danger ratio was 0.85 (95% CI, 0.83-0.86).
“A 7.7% absolute mortality discount at 12 months, when sufferers obtain these medicine, is absolutely placing,” Manisty stated.
The fluoropyrimidine group had 8,287 instances of composite cardiovascular occasions and the non-fluoropyrimidine group had 9,873 instances.
People who obtained fluoropyrimidine had a 0.9% (95% CI, 0%-1.9%) increased danger of cardiovascular occasions at 1 yr (RR = 1.07; 95% CI, 1-1.13).
Fluoropyrimidine remedy elevated danger for cardiac arrhythmia 0.82% (95% CI, 0.11%-1.58%) and cardiac arrest 0.34% (95% CI, 0.13%-0.47%).
Researchers didn’t observe an elevated danger for acute coronary syndrome, coronary heart failure, cardiomyopathy, cardiac intervention or cardiac demise.
Sufferers with preexisting heart problems didn’t have elevated danger of cardiovascular occasions.
“Hopefully [these data] will give oncologists the boldness that the risk-benefit steadiness favors giving these medicine to sufferers,” Manisty stated.
‘The very best’ cardiovascular, most cancers outcomes
A key query Manisty and colleagues nonetheless have is how one can rechallenge sufferers with fluoropyrimidine after they developed cardiovascular toxicities.
In follow, Manisty had performed that safely with people who developed chest pains, she stated.
“There haven’t really been giant scientific trials to show the security of that, though we’ve managed to efficiently rechallenge the vast majority of our sufferers,” she added.
Extra analysis is required to guage newer remedies, reminiscent of immune checkpoint inhibitors, and their associations with cardiotoxicities, too.
“These have revolutionized most cancers care, revolutionized most cancers outcomes, however are related to a small danger of myocarditis after which, subsequently, with acute coronary occasions,” Manisty stated. “I believe understanding the connection with preexisting heart problems, particularly in relation to myocarditis, is necessary. It not solely must be handled by way of scientific trials, but additionally by way of analyzing real-world knowledge.”
Scientific trials might higher element cardiovascular toxicities, as effectively.
“Usually, the security endpoints which can be collected are pretty broad from a cardiovascular perspective,” Manisty stated. “We might not have the suitable data with which to have the ability to monitor danger and to have the ability to establish which sufferers ought to or shouldn’t be receiving these therapies, and the way finest we must always monitor them. As trialists, we have to work intently collectively between cardiology and oncology to make sure that applicable knowledge are collected throughout the early-phase drug trials for oncology brokers.”
Communication between oncology and cardiology stays important all through care, as effectively.
“Initially, maybe oncologists felt that cardio-oncology was virtually designed to forestall sufferers from getting first-line chemotherapy, and to try to establish these sufferers who maybe would do worse,” Manisty stated. “Truly, what I want to argue, is that the majority of us working inside cardio-oncology are doing our utmost to make sure that sufferers will not be prevented from having these remedies. That they get the first-line chemotherapy, however they get it administered in a secure approach. [They get it] with applicable monitoring and clear communication traces between the oncologists and the cardiologists, in order that we will try to be sure that they get the most effective cardiovascular and most cancers outcomes.”
References:
For extra data:
Charlotte Manisty, MD, PhD, may be reached at c.manisty@ucl.ac.uk.