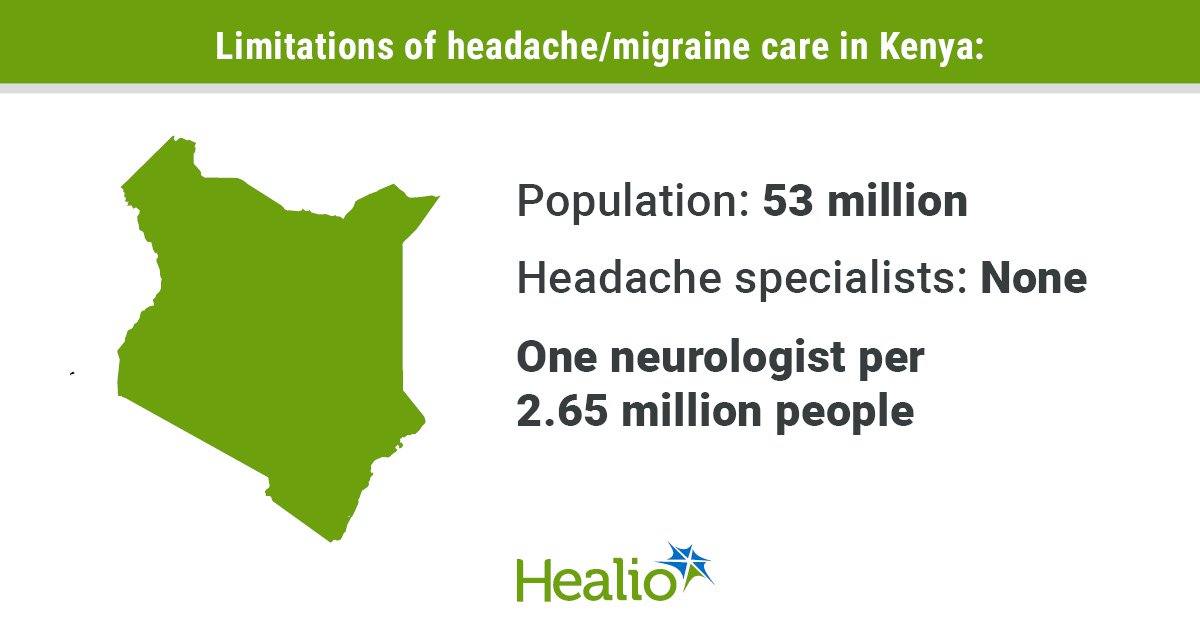
A analysis crew on the College of Barcelona’s Institute of Neurosciences (UBneuro) has found new molecular mechanisms associated to the cognitive decline related to Alzheimer’s illness, the commonest dementia. This research, carried out on animal fashions with the illness, describes for the primary time the decisive function of the RTP801 protein in cells often known as astrocytes in the course of the development of this neurodegenerative illness.
The paper, revealed in Alzheimer’s & Dementia, opens a brand new state of affairs for describing new therapeutic targets within the struggle towards the illness.
The research was carried out by researcher Almudena Chicote and members of the crew led by Professor Cristina Malagelada, from the UB’s School of Drugs and Well being Sciences and UBneuro, in collaboration with consultants from the UB’s Manufacturing and Validation Middle of Superior Therapies (Creatio), the August Pi i Sunyer Biomedical Analysis Institute (IDIBAPS) and the Biomedical Analysis Networking Middle on Neurodegenerative Illnesses (CIBERNED).
RTP801 protein, astrocytes and neurodegeneration
In Alzheimer’s illness, which nonetheless has no remedy, there’s an accumulation of β-amyloid plaques outdoors neurons and of hyperphosphorylated tau protein buds inside neurons. The RTP801 protein, encoded by the DDIT4 gene in hippocampal neurons, is concerned within the strategy of neuroinflammation, neurotoxicity and illness development, as detailed by the crew in a earlier paper.
As in different illnesses that alter mind perform and trigger cell dying, this pathology includes a posh interplay between various kinds of cells within the central nervous system.
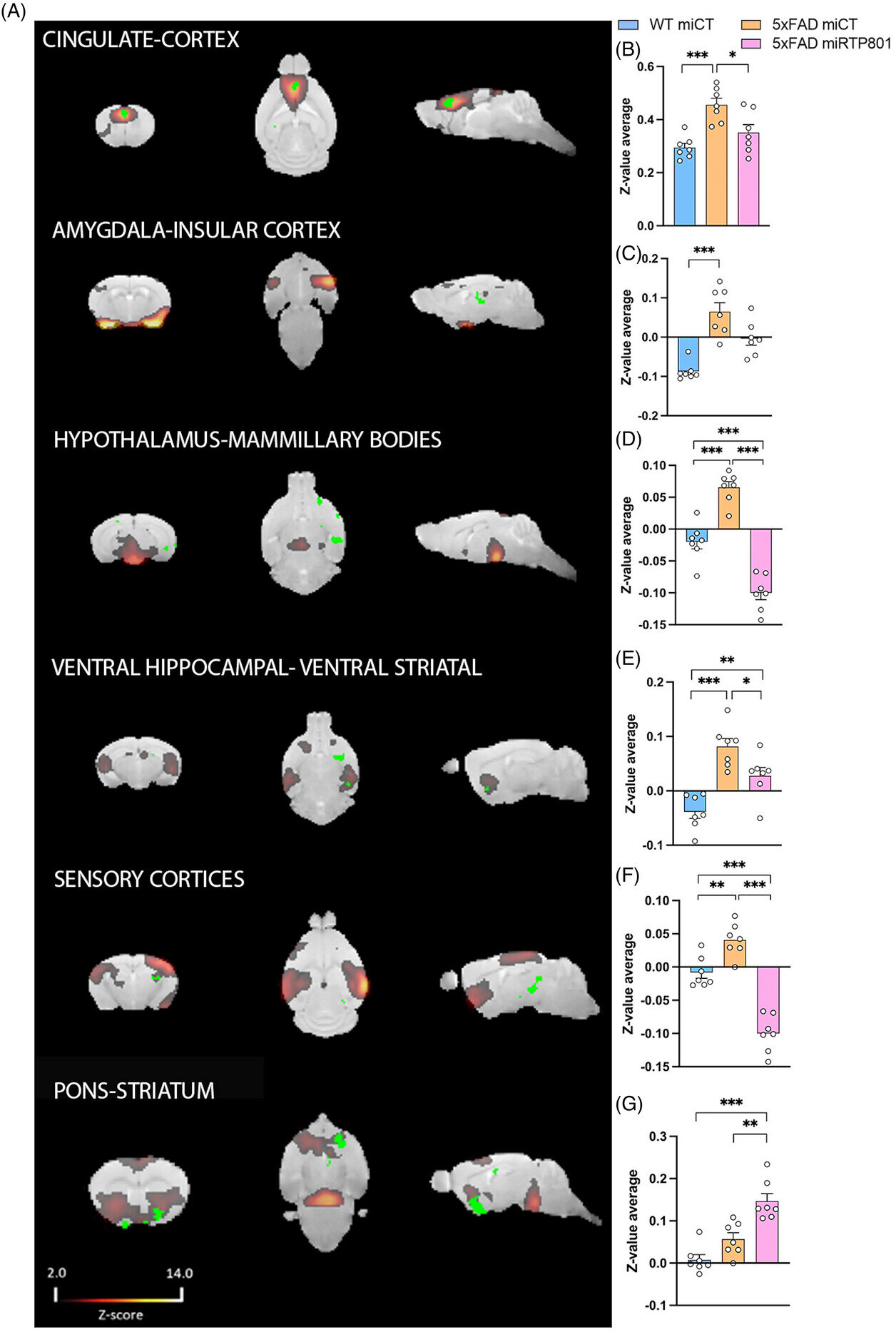
Now, the brand new research describes for the primary time the crucial function of the RTP801 protein in astrocytes, particular mind cells concerned in neuroinflammation, synaptic regulation and mind homeostasis.
“Astrocytes, beforehand thought-about passive assist cells, act as lively regulators of neurodegenerative processes, together with the upkeep of excitatory-inhibitory steadiness and neuroimmune responses. RTP801 is a stress response protein concerned in neuronal dysfunction, however its particular function in astrocytes was not well-known,” says Malagelada, from the UB’s Division of Biomedicine and CIBERNED.
Utilizing gene remedy strategies, the crew explored the consequences of silencing RTP801 protein expression in dorsal hippocampal astrocytes in animal fashions of the illness. The research analyzed the affect of gene silencing on spatial reminiscence, parvalbumin-positive (PV+) interneurons and practical mind connectivity, that are interconnected by the perform of inhibitory neural circuits.
“In Alzheimer’s illness, dysfunction of those circuits results in cognitive impairment, emotional dysregulation and disruption of mind community exercise, that are key features of illness development. As well as, we additionally examined its affect on neuroinflammatory markers, particularly astrogliosis, microgliosis and inflammasome activation,” explains first writer of the article Chicote from UBneuro and CIBERNED.
In response to the research, when RTP801 ranges are lowered in astrocytes within the animal mannequin of Alzheimer’s illness, the hyperconnectivity of those mind networks additionally decreases. Subsequently, normalization of RTP801 expression would assist to revive mind community connectivity just like that of wholesome people.
Metabolic and neural modifications
The crew additionally discovered that ranges of GABA—a neurotransmitter important for inhibiting mind excitability—are lowered in animal fashions of Alzheimer’s illness. Nonetheless, this situation could be partially reversed when RTP801 protein expression in astrocytes is silenced. These metabolic modifications have been linked to the lack of a selected kind of GABA-synthesizing PV+ interneurons within the hippocampus.
“Subsequently, silencing the RTP801 protein might assist reverse among the harm to PV+ interneurons within the hippocampus, and this might assist restore sufficient GABA manufacturing and enhance mind perform,” notes Chicote.
The research additionally means that the aberrant mind community connectivity—the hyperconnectivity or elevated mind community exercise—noticed in some fashions might be defined by the toxicity of the RTP801 protein in PV+ neurons within the hippocampus, that are key producers of GABA. “The discount of RTP801 partially restored these neurons and improved GABA ranges,” says the researcher.
The crew plans to develop the traces of analysis to strengthen the in vitro findings and validate using RTP801 protein silencing in future therapeutic methods to handle Alzheimer’s illness.
Extra data:
Almudena Chicote‐González et al, Astrocytes, by way of RTP801, contribute to cognitive decline by disrupting GABAergic‐regulated connectivity and driving neuroinflammation in an Alzheimer’s illness mouse mannequin, Alzheimer’s & Dementia (2025). DOI: 10.1002/alz.70051
Quotation:
Astrocyte protein RTP801 might contribute to cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s illness (2025, Could 26)
retrieved 26 Could 2025
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2025-05-astrocyte-protein-rtp801-contribute-cognitive.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.