• Axial Seamount is the best-monitored submarine volcano on the earth.
• It’s probably the most lively undersea volcano closest to California.
• It might erupt by the tip of the yr.
A mysterious and extremely lively undersea volcano off the Pacific Coast might erupt by the tip of this yr, scientists say.
Practically a mile deep and about 700 miles northwest of San Francisco, the volcano often called Axial Seamount is drawing rising scrutiny from scientists who solely found its existence within the Nineteen Eighties.
Positioned in a darkened a part of the northeast Pacific Ocean, the submarine volcano has erupted thrice since its discovery — in 1998, 2011 and 2015 — in line with Invoice Chadwick, a analysis affiliate at Oregon State College and an knowledgeable on the volcano.
Luckily for residents of California, Oregon and Washington, Axial Seamount doesn’t erupt explosively, so it poses zero danger of any tsunami.
“Mt. St. Helens, Mt. Rainier, Mt. Hood, Crater Lake — these sort of volcanoes have much more gasoline and are extra explosive on the whole. The magma is extra viscous,” Chadwick mentioned. “Axial is extra just like the volcanoes in Hawaii and Iceland … much less gasoline, the lava could be very fluid, so the gasoline can get out with out exploding.”
The damaging drive of explosive eruptions is known: when Mt. Vesuvius blew in 79 AD, it worn out the traditional Roman metropolis of Pompeii; when Mt. St. Helens erupted in 1980, 57 individuals died; and when the Hunga Tonga-Hunga Haʻapai volcano in Tonga’s archipelago exploded in 2022 — a once-in-a-century occasion — the ensuing tsunami, which reached a most peak of 72 paymentt, triggered injury throughout the Pacific Ocean and left at the very least six useless.
Axial Seamount, against this, is a volcano that, throughout eruptions, oozes lava — just like the kind of eruptions in Kilauea on the Huge Island of Hawaii. Consequently, Axial’s eruptions usually are not noticeable to individuals on land.
It’s a really completely different story underwater.
Warmth plumes from the eruption will rise from the seafloor — maybe half a mile — however gained’t attain the floor, mentioned William Wilcock, professor of oceanography on the College of Washington.

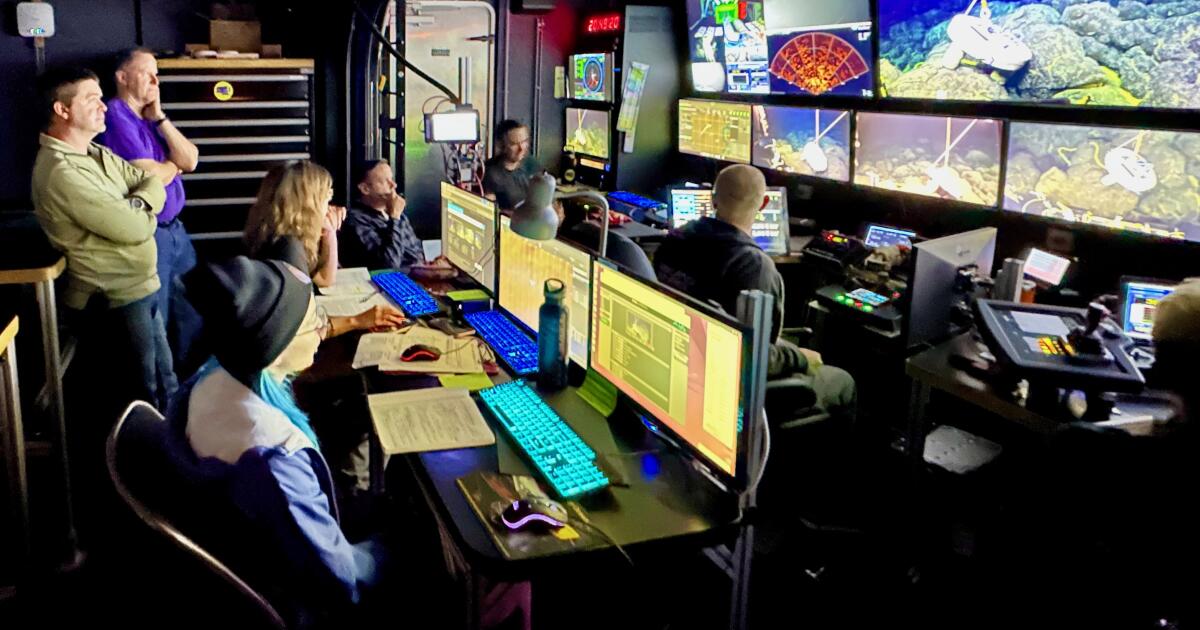
Jason is a remotely operated automobile (ROV) system designed to permit scientists to have entry to the seafloor with out leaving the ship.
(Dave Caress/MBARI)
The outermost layer of the lava circulation will virtually instantly cool and kind a crust, however the inside of the lava circulation can stay molten for a time, Chadwick mentioned. “In some locations … the lava comes out slower and piles up, after which there’s all this warmth that takes a very long time to dissipate. And on these thick flows, microbial mats can develop, and it virtually seems to be like snow over a panorama.”
Sea life can die if buried by the lava, which additionally dangers destroying or damaging scientific tools put in across the volcano to detect eruptions and earthquakes. However the eruption most likely gained’t have an effect on sea life corresponding to whales, that are “too near the floor” to be bothered by the eruption, Wilcock mentioned.
Additionally, eruptions at Axial Seamount aren’t anticipated to set off a long-feared magnitude 9.0 earthquake on the Cascadia subduction zone. Such an earthquake would most likely spawn a catastrophic tsunami for Washington, Oregon and California’s northernmost coastal counties. That’s as a result of Axial Seamount is situated too far-off from that main fault.
Axial Seamount is one in every of numerous volcanoes which are underwater. Scientists estimate that 80% of Earth’s volcanic output — magma and lava — happens within the ocean.
Axial Seamount has drawn intense curiosity from scientists. It’s now the best-monitored underwater volcano on the earth.
The volcano is a prolific erupter partly due to its location, Chadwick mentioned. Not solely is it perched on a ridge the place the Juan de Fuca and Pacific tectonic plates unfold other than one another — creating new seafloor within the course of — however the volcano can be planted firmly above a geological “scorching spot” — a area the place plumes of superheated magma rise towards the Earth’s floor.
For Chadwick and different researchers, frequent eruptions supply the tantalizing alternative to foretell volcanic eruptions weeks to months prematurely — one thing that’s very tough to do with different volcanoes. (There’s additionally a lot much less probability anybody will get mad if scientists get it mistaken.)
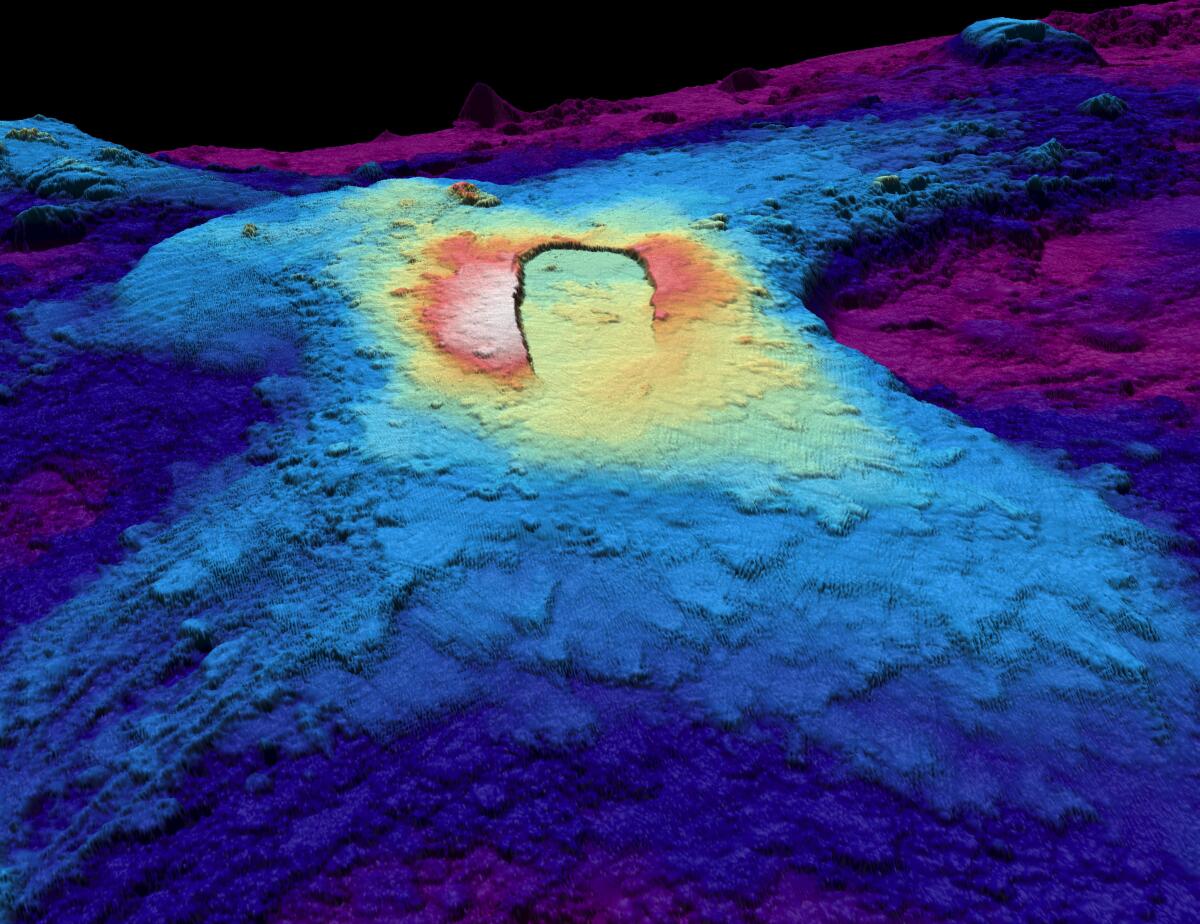

A 3-dimensional topographic depiction displaying the summit caldera of Axial Seamount, a extremely lively undersea volcano off the Pacific Coast. Hotter colours point out shallower surfaces; cooler colours point out deeper surfaces.
(Susan Merle / Oregon State College)
“For lots of volcanoes all over the world, they sit round and are dormant for lengthy durations of time, after which immediately they get lively. However this one is fairly lively on a regular basis, at the very least within the time interval we’ve been finding out it,” Chadwick mentioned. “If it’s not erupting, it’s preparing for the subsequent one.”
Scientists know this as a result of they’ve noticed a sample.
“Between eruptions, the volcano slowly inflates — which suggests the seafloor rises. … After which throughout an eruption, it should, when the magma comes out, the volcano deflates and the seafloor drops down,” Wilcock mentioned.
Eruptions, Chadwick mentioned, are “like letting some air out of the balloon. And what we’ve seen is that it has inflated to an identical stage every time when an eruption is triggered,” he mentioned.
Chadwick and fellow scientist Scott Nooner predicted the volcano’s 2015 eruption seven months earlier than it occurred after they realized the seafloor was inflating fairly shortly and linearly. That “made it simpler to extrapolate into the long run to stand up to this threshold that it had reached earlier than” eruption, Chadwick mentioned.
However making predictions since then has been more difficult. Chadwick began making forecast home windows in 2019, however round that point, the speed of inflation began slowing down, and by the summer time of 2023, “it had virtually stopped. So then it was like, ‘Who is aware of when it’s going to erupt?’”

A deep-sea octopus explores the lava flows 4 months after the Axial Seamount volcano erupted in 2015.
(Invoice Chadwick, Oregon State College / Woods Gap Oceanographic Establishment / Nationwide Science Basis)
However in late 2023, the seafloor slowly started inflating once more. For the reason that begin of 2024, “it’s been sort of cranking alongside at a reasonably regular charge,” he mentioned. He and Nooner, of the College of North Carolina at Wilmington, made the newest eruption prediction in July 2024 and posted it to their weblog. Their forecast stays unchanged.
“On the charge of inflation it’s going, I count on it to erupt by the tip of the yr,” Chadwick mentioned.
However based mostly on seismic knowledge, it’s not going the volcano is about to erupt imminently. Whereas scientists haven’t mastered predicting volcanic eruptions weeks or months forward of time, they do a good job of forecasting eruptions minutes to hours to days forward of time, utilizing clues like an elevated frequency of earthquakes.
At this level, “we’re not on the excessive charge of seismicity that we noticed earlier than 2015,” Chadwick mentioned. “It wouldn’t shock me if it erupted tomorrow, however I’m considering that it’s not going to be anytime quickly on the entire.”
He cautioned that his forecast nonetheless quantities to an experiment, albeit one which has change into fairly public. “I really feel prefer it’s extra sincere that approach, as a substitute of doing it looking back,” Chadwick mentioned in a presentation in November. The forecast began to garner consideration after he gave a chat on the American Geophysical Union assembly in December.
On the intense facet, he mentioned, “there’s no downside of getting a false alarm or being mistaken,” as a result of the predictions gained’t have an effect on individuals on land.
If the predictions are appropriate, “possibly there’s classes that may be utilized to different extra hazardous volcanoes all over the world,” Chadwick mentioned. Because it stands now, although, making forecasts for eruptions for a lot of volcanoes on land “are simply extra sophisticated,” with out having a “repeatable sample like we’re seeing at this one offshore.”
Scientists elsewhere have checked out different methods to forecast undersea eruptions. Scientists started noticing a repeatable sample within the rising temperature of hydrothermal vents at a volcano within the East Pacific and the timing of three eruptions in the identical spot over the past three many years. “And it form of labored,” Chadwick mentioned.
Loads of luck allowed scientists to {photograph} the eruption of the volcanic website often called “9 levels 50 minutes North on the East Pacific Rise,” which was simply the third time scientists had ever captured photographs of lively undersea volcanism.
However Chadwick doubts researchers will probably be lucky sufficient to videotape Axial Seamount’s eruption.
Though scientists will probably be alerted to it by the Nationwide Science Basis-funded Ocean Observatories Initiative Regional Cabled Array — a sensor system operated by the College of Washington — getting there in time will probably be a problem.
“It’s a must to be in the proper place on the proper time to catch an eruption in motion, as a result of they don’t final very lengthy. Those at Axial most likely final per week or a month,” Chadwick mentioned.
After which there’s the problem of getting a ship and a remotely operated automobile or submarine to seize the photographs. Such vessels are usually scheduled far prematurely, maybe a yr or a yr and a half out, and initiatives are tightly scheduled.
Chadwick final went to the volcano in 2024 and is predicted to exit subsequent in the summertime of 2026. If his predictions are appropriate, Axial Seamount may have already erupted.