Mycetoma is a persistent and progressively debilitating illness that impacts hundreds of individuals dwelling in tropical and subtropical areas, notably these in low-resource settings. Characterised by painful swelling, pores and skin nodules, and pus-discharging sinuses, the situation primarily impacts people who come into frequent contact with soil, resembling agricultural and handbook employees.
Regardless of its severe well being and socioeconomic penalties, mycetoma has been largely neglected by world medical analysis, leading to restricted diagnostic instruments and few efficient therapy choices.
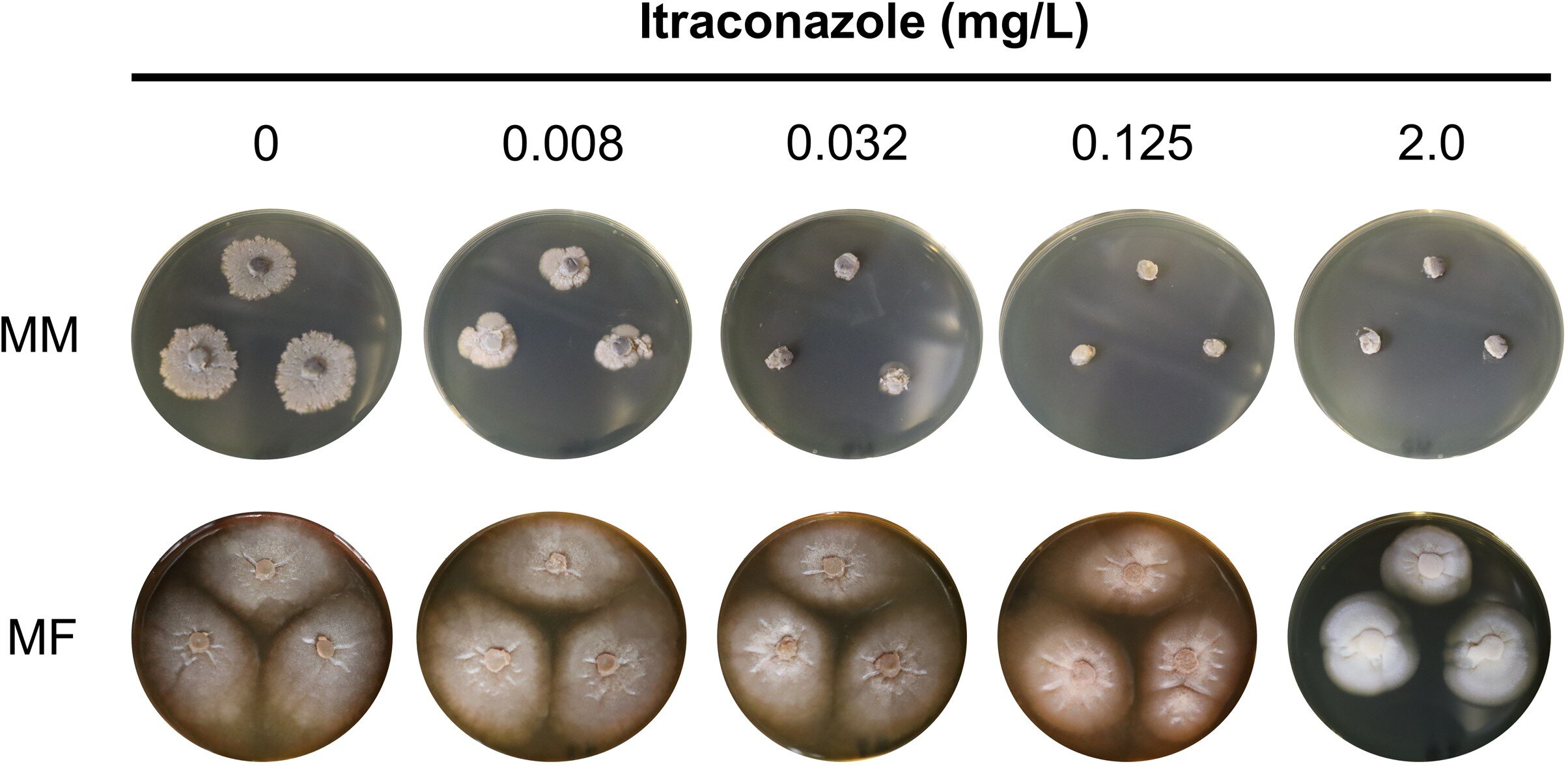
To deal with the fungal type of mycetoma, referred to as eumycetoma, physicians have relied on itraconazole—an antifungal treatment that targets a key fungal enzyme. Nonetheless, instances attributable to Madurella fahalii, a lesser-known fungal species, have repeatedly proven resistance to this drug, leaving sufferers with few alternate options. Till lately, the explanations behind this resistance remained poorly understood.
In an effort to handle this data hole, a analysis crew led by Affiliate Professor Takashi Yaguchi from the Medical Mycology Analysis Middle, Chiba College, investigated the molecular mechanisms behind itraconazole resistance in M. fahalii. Of their newest research, printed on March 27, 2025, in PLOS Uncared for Tropical Illnesses, the researchers used superior genetic and biomolecular chemistry instruments to uncover why this well-established therapy fails towards M. fahalii however not different Madurella species.
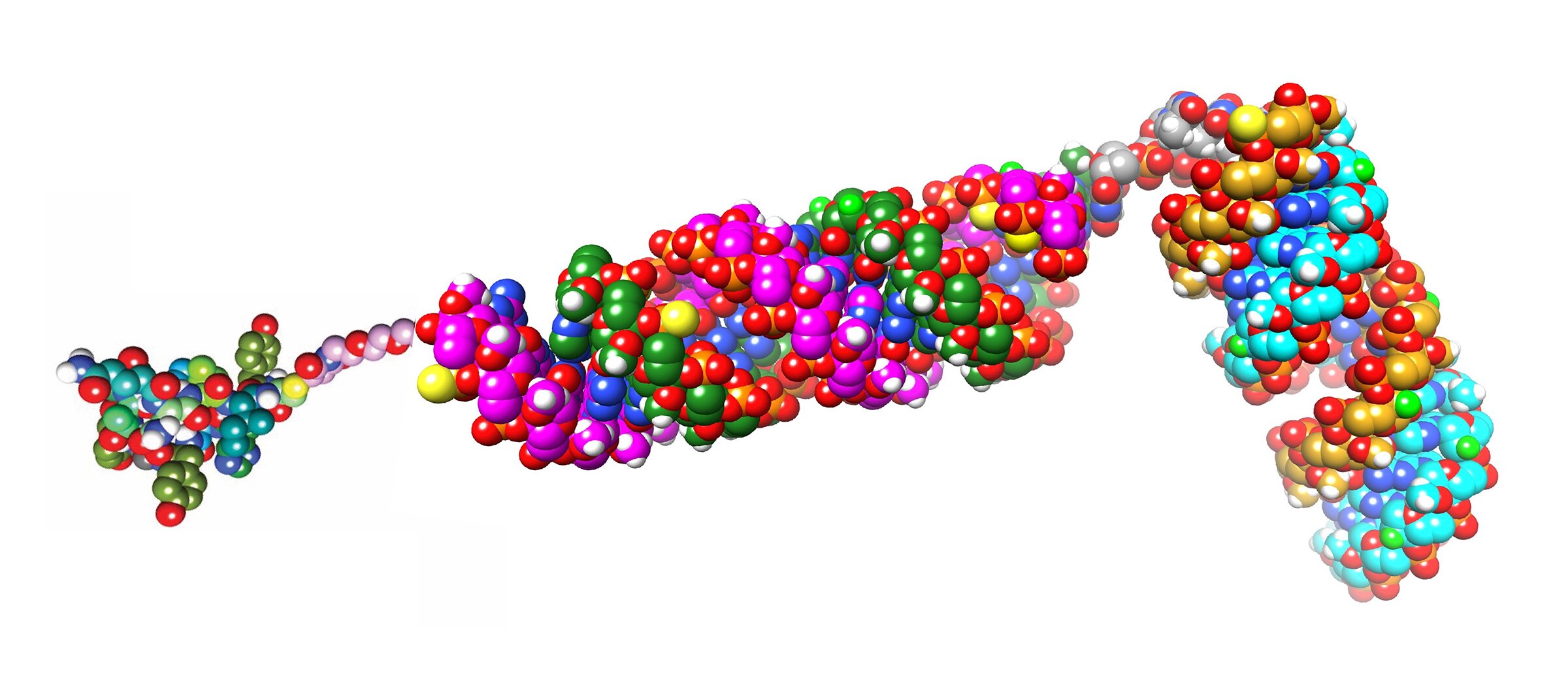
Utilizing genome sequencing and genetic engineering strategies, the researchers recognized that, not like its treatable cousin M. mycetomatis, M. fahalii possesses a further gene encoding the enzyme cytochrome P450 14-α sterol demethylase (CYP51). This second copy of the M. fahalii-specific gene (Mfcyp51A2), which encodes the precise goal of itraconazole, has key purposeful and structural variations in comparison with the gene widespread with M. mycetomatis (Mfcyp51A1), successfully neutralizing the drug’s affect.
The crew confirmed their discovery by means of a number of approaches. They demonstrated that each copies of the gene turn out to be extra lively when the fungus is uncovered to itraconazole, with the distinctive Mfcyp51A2 gene exhibiting notably sturdy activation—a typical defensive response. When the researchers transplanted these genes into yeast cells for additional testing, cells carrying the Mfcyp51A2 gene have been markedly much less vulnerable to itraconazole in comparison with these with the usual gene model.

Moreover, laptop simulations revealed that whereas itraconazole can bind to each variations of the enzyme, its interplay with the variant encoded by Mfcyp51A2 is weaker, explaining why the drug turns into much less efficient towards M. fahalii infections.
“This research represents the primary report on the physiological traits of Madurella species utilizing genetic engineering strategies,” remarks Dr. Yaguchi, “These findings spotlight the potential of molecular strategies in uncovering drug resistance mechanisms in uncared for fungal pathogens.”
Total, this work marks an necessary step ahead in addressing a extreme illness that primarily impacts impoverished communities. By understanding how drug resistance develops on the molecular degree, scientists can now work on focused approaches to beat it, bringing hope to hundreds of sufferers worldwide who’ve restricted entry to specialised well being care.
“Our findings will hopefully pave the best way for more practical therapy methods for eumycetoma attributable to M. fahalii sooner or later,” concludes Dr. Yaguchi.
As mycetoma continues to pose challenges in areas with restricted medical infrastructure, research like this reveal the position of primary science in addressing real-world well being issues. By exploring the genetic foundation of therapy resistance, researchers are constructing the muse for focused, efficient therapies that would profit hundreds worldwide.
Different members of the analysis crew included Dr. Isato Yoshioka from the Medical Mycology Analysis Middle, Chiba College, Prof. Ahmed Hassan Fahal from Mycetoma Analysis Middle, College of Khartoum, Prof. Satoshi Kaneko from the Faculty of Tropical Drugs and International Well being, Nagasaki College, and Assistant Professor Wei Cao from the Analysis Institute for Science and Engineering, Waseda College.
Extra data:
Isato Yoshioka et al, Itraconazole resistance in Madurella fahalii linked to a definite homolog of the gene encoding cytochrome P450 14-α sterol demethylase (CYP51), PLOS Uncared for Tropical Illnesses (2025). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012623
Quotation:
Tropical illness fungus thwarts therapy with gene duplication that blocks key drug (2025, Could 22)
retrieved 22 Could 2025
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2025-05-tropical-disease-fungus-thwarts-treatment.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.