Keep knowledgeable with free updates
Merely signal as much as the UK inflation myFT Digest — delivered on to your inbox.
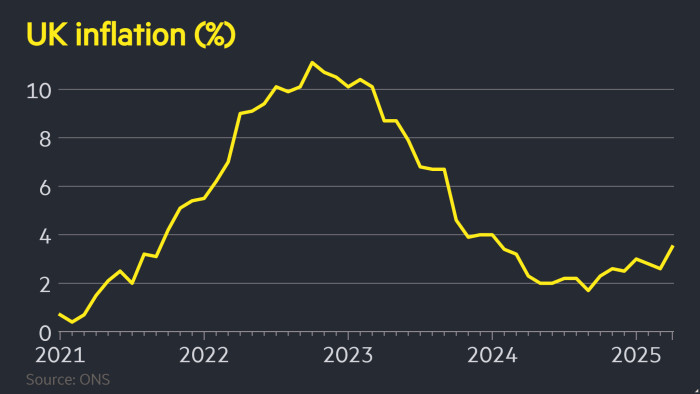
UK inflation rose greater than anticipated to a 15-month excessive of three.5 per cent in April after increased utility payments and tax rises kicked in, prompting merchants to cost in only one rate of interest lower over the subsequent 12 months.
Wednesday’s determine from the Workplace for Nationwide Statistics was each increased than the three.3 per cent predicted by analysts polled by Reuters and March’s 2.6 per cent.
The rise was pushed by increased vitality prices after regulators raised the family value cap, in addition to jumps in water payments and street tax, the ONS mentioned. Greater airfares additionally contributed.
Companies inflation, a key measure of underlying value pressures for rate-setters, climbed to five.4 per cent in April, eclipsing the 4.8 per cent anticipated by analysts and March’s determine of 4.7 per cent.
Suren Thiru, economics director at accountants’ physique the ICAEW, mentioned final month’s enhance “highlights the brutal hit to family and enterprise funds from April’s multitude of eye-watering invoice rises and tax hikes”. James Smith, an economist at ING, mentioned the numbers put “the ultimate nail within the coffin of a Financial institution of England charge lower in June”.
Merchants trimmed their bets again to completely pricing in only one quarter-point charge lower by this time subsequent 12 months, in contrast with two earlier than the information, in keeping with ranges implied by swaps markets. The pound climbed to its highest degree in opposition to the greenback since early 2022 at $1.347. It later fell again to $1.344.
The Labour authorities’s enhance in employer nationwide insurance coverage contributions can be stoking costs, analysts mentioned. Stuart Morrison, analysis supervisor on the British Chambers of Commerce, mentioned corporations have been going through a “good storm of value pressures” together with nationwide insurance coverage, a minimal wage rise and international tariffs.
The UK’s CPI inflation charge was nicely above readings in Germany and France, in addition to the EU degree.
The BoE has vowed to stick with a “cautious and gradual” method to extra charge cuts after reducing borrowing prices 4 instances since August.
However the Financial Coverage Committee was cut up over this month’s resolution to chop charges by a quarter-point to their lowest degree since 2023. On Tuesday, chief economist Huw Tablet mentioned he feared the BoE was lowering charges too quickly and that the momentum behind falling inflation was “stuttering”.
The numbers got here as a setback to chancellor Rachel Reeves, who has been making an attempt to capitalise on stronger-than-expected first-quarter development figures in addition to a trio of commerce offers.
Reacting to the inflation numbers, Reeves mentioned she was “dissatisfied” and acknowledged that “value of dwelling pressures are nonetheless weighing down on working individuals”.
She added: “We’re a good distance from the double digit inflation we noticed below the earlier administration, however I’m decided that we go additional and quicker to place extra money in individuals’s pockets.”
The BoE has predicted that inflation will attain 3.7 per cent later this 12 months earlier than falling again to its goal of two per cent in 2027. However analysts warned that the April knowledge confirmed indicators of upper than anticipated inflation in some components of the financial system. Core inflation, which excludes vitality and meals, was forward of forecasts at 3.8 per cent, whereas providers inflation was nicely forward of the BoE’s personal forecast, printed this month.
Air fares jumped sharply partially as a result of April’s value assortment dates coincided with the Easter holidays, analysts mentioned, in contrast to in 2024.
The query for the BoE will probably be whether or not they choose a hefty share of April’s acceleration was pushed by erratic or one-off components, or whether or not there are indicators that underlying inflation stays too scorching. One space of concern is fast wage development, with annual development in common weekly wages working at 5.6 per cent, excluding bonuses, within the three months to March.
“Though a lot of the rise in inflation in April may be put right down to increased utility payments, airfares, and a hike in street tax, the massive image stays that underlying inflation is just too robust for the BoE to realize its 2 per cent inflation goal,” mentioned Andrew Wishart at Berenberg financial institution.
Two-year authorities bond yields, that are delicate to adjustments in rate of interest expectations, rose 0.04 share factors to 4.09 per cent in late-morning buying and selling.
“Households are paying the value for the Labour chancellor’s selections,” mentioned Mel Stride, shadow chancellor. “Greater inflation may additionally imply rates of interest keep increased for longer, hitting household funds arduous.”