In a complete analysis examine, scientists have uncovered a beforehand unknown mechanism explaining how neurons survive botulinum neurotoxin sort A (BoNT/A) publicity, regardless of the toxin’s highly effective skill to dam neurotransmission.
The analysis, led by Dr. Hermona Soreq at The Hebrew College of Jerusalem, may have far-reaching implications for each medical remedies and beauty purposes of this potent bacterial toxin.
The work seems in Genomic Psychiatry.
Understanding botulinum’s twin nature
Botulinum neurotoxins are essentially the most potent organic toxins recognized, with an estimated deadly dose of roughly 1 ng/kg. Whereas they’ll trigger doubtlessly deadly paralysis, they paradoxically type the premise for quite a few therapeutic and beauty purposes. How neurons survive this potent toxin has remained a thriller—till now.
“We have lengthy recognized that botulinum toxin sort A induces paralysis with out killing neurons, in contrast to different botulinum serotypes,” explains Dr. Soreq. “This distinctive attribute has enabled its widespread therapeutic use, however the molecular mechanisms supporting neuronal survival remained largely unexplained.”
Small RNAs play outsized position
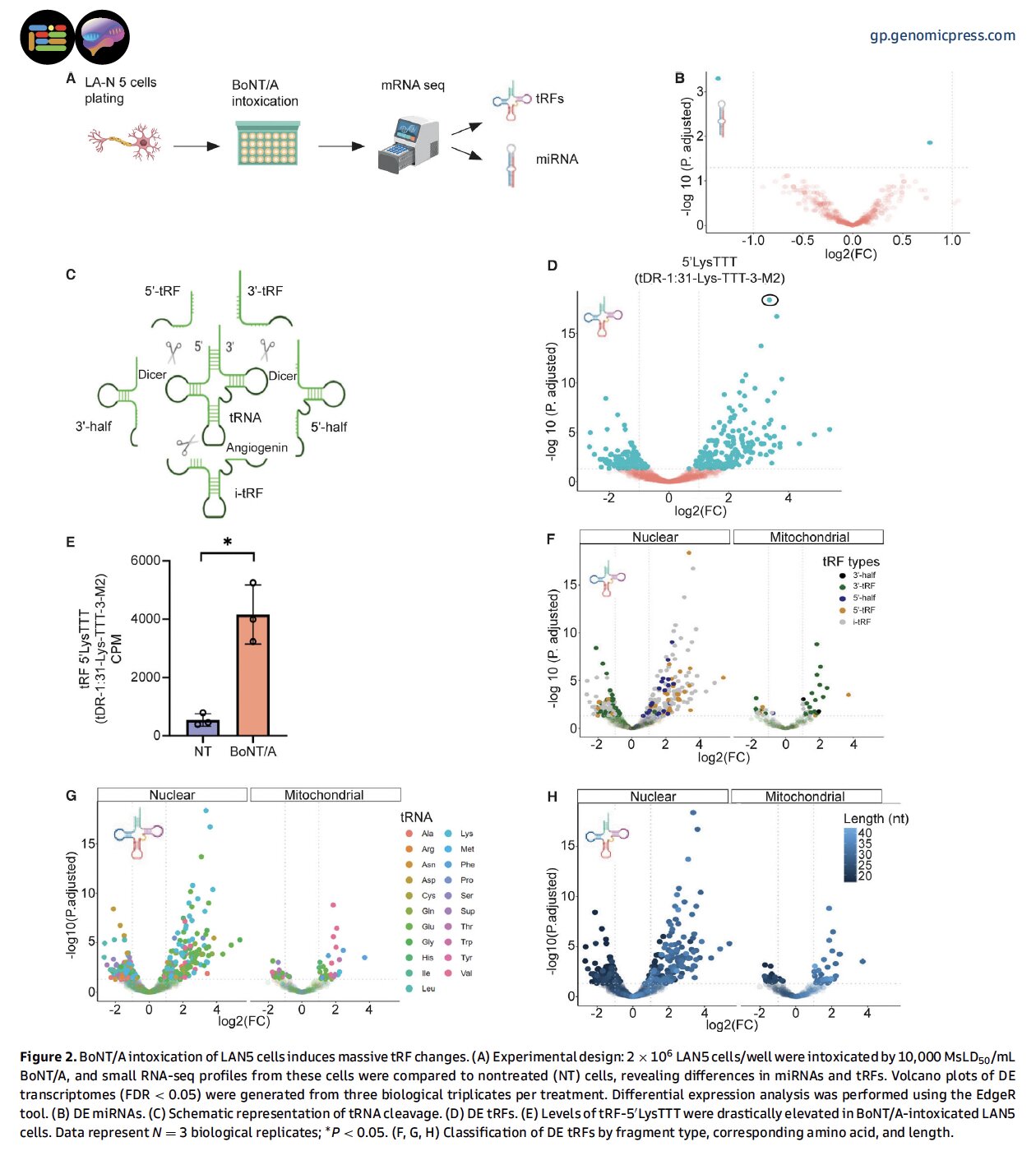
The examine utilized superior genomic applied sciences to investigate molecular adjustments in human neuroblastoma cells following BoNT/A publicity. Whereas earlier analysis centered totally on protein-level adjustments, this examine revealed dramatic alterations in small RNA molecules, significantly switch RNA fragments (tRFs).
Researchers found that following BoNT/A intoxication, neurons accumulate particular tRFs, particularly these derived from lysine tRNA (often known as 5’LysTTT tRFs). These fragments work together with key proteins and RNA molecules concerned in regulating ferroptosis, a type of programmed cell dying characterised by iron-dependent lipid peroxidation.
“What stunned us most was the huge accumulation of tRFs in comparison with minimal adjustments in microRNAs,” notes Dr. Arik Monash, first creator of the examine. “This implies that tRFs function major regulators of the mobile response to BoNT/A poisoning.”
Blocking cell dying whereas sustaining therapeutic results
The analysis workforce demonstrated that 5’LysTTT tRFs assist neuronal survival by concurrently focusing on a number of mechanisms that may in any other case set off ferroptosis. These tRFs work together with a protein referred to as HNRNPM and the CHAC1 mRNA, successfully blocking cell dying pathways whereas permitting the toxin’s therapeutic results to proceed.
What mechanism permits neurons to stay alive whereas their operate is blocked? This query has puzzled researchers since botulinum toxin was first developed for medical use. The present examine means that particular tRNA fragments act as mobile lifeguards, stopping neurons from present process ferroptosis regardless of the worrying circumstances induced by the toxin.
May these protecting tRFs be harnessed therapeutically in different circumstances the place stopping neuronal dying is essential? The researchers imagine this chance warrants additional investigation.
Evolutionary conservation and amplification mechanisms
One of the intriguing findings was that roughly 20% of the BoNT/A-induced tRFs contained an an identical 11-nucleotide sequence motif: “CCGGATAGCTC.” This shared motif suggests a coordinated mobile response to intoxication that has been conserved throughout species.
“Discovering this repetitive motif in each human cell cultures and rat tissues signifies we have recognized a elementary protecting mechanism,” explains Dr. Joseph Tam, co-senior creator. “The conservation of this response throughout mammalian species suggests its evolutionary significance.”
How does this repetitive motif amplify safety? The researchers hypothesize that by producing quite a few tRFs carrying the identical protecting sequence, cells can quickly mount a strong protection in opposition to toxin-induced stress. This “tRF storm” could also be extra environment friendly than producing particular person protecting molecules.
Has this regulatory mechanism advanced particularly to counter botulinum intoxication, or does it signify a broader mobile technique for surviving stress? This represents an intriguing space for future analysis.
Potential purposes past beauty use
Whereas BoNT/A is extensively recognized for its beauty purposes in lowering wrinkles, it additionally performs an important position in treating numerous medical circumstances, together with dystonia, hyperhidrosis, and important tremors.
“Understanding the molecular mechanisms behind BoNT/A’s results may result in improved therapeutic formulations with optimized length and efficacy,” explains Dr. Osnat Rosen, co-senior creator. “This might be significantly useful for sufferers requiring common remedies for persistent circumstances.”
May manipulating these tRF pathways lengthen or shorten the length of botulinum results? The researchers imagine this represents a promising space for drug improvement that might enable physicians to customise remedy length based mostly on particular person affected person wants.
The examine additionally reveals why completely different botulinum serotypes have various security profiles. Whereas BoNT/A preserves neuronal viability via the tRF-mediated safety of ferroptosis, different serotypes like BoNT/C and BoNT/E lack this protecting mechanism, doubtlessly explaining their increased neurotoxicity.
Future instructions and scientific implications
The analysis opens a number of avenues for future investigation, together with the potential improvement of novel therapies focusing on tRF pathways to guard neurons in neurodegenerative ailments or to reinforce the therapeutic results of botulinum toxin.
Dr. Soreq’s workforce is now exploring whether or not related protecting mechanisms function in different contexts, reminiscent of neurodegenerative ailments or traumatic mind accidents, the place stopping neuronal dying is essential.
“These findings not solely improve our understanding of how botulinum toxin works but in addition present insights into elementary mobile survival mechanisms,” concludes Dr. Soreq. “The identification of tRFs as key mediators of neuronal safety may result in completely new therapeutic approaches for a spread of neurological circumstances.”
Extra data:
5’LysTTT tRNA fragments assist survival of botulinum-intoxicated neurons by blocking ferroptosis, Genomic Psychiatry (2025). DOI: 10.61373/gp025a.0047
Offered by
Genomic Press
Quotation:
How neurons survive botulinum neurotoxin sort A publicity (2025, Could 20)
retrieved 20 Could 2025
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2025-05-neurons-survive-botulinum-neurotoxin-exposure.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.