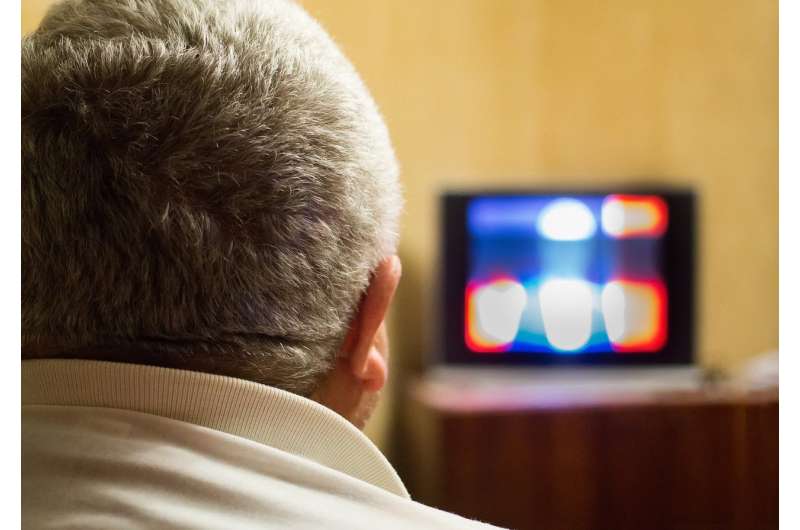
Individuals who sit or stay sedentary for greater than 14 hours a day, on common, could have the next threat of a cardiovascular occasion or dying within the 12 months after remedy at a hospital for signs of a coronary heart assault comparable to chest ache, based on new analysis revealed in Circulation: Cardiovascular High quality and Outcomes.
Earlier analysis by the examine authors discovered that individuals who had skilled a coronary heart assault had been spending as much as 12 to 13 hours every day being sedentary, outlined as any awake exercise that concerned little-to-no bodily motion.
On this examine, the researchers used a wrist accelerometer to trace the period of time every participant spent shifting or being sedentary for a median of 30 days after discharge from a hospital’s emergency division.
Wrist accelerometers measure the acceleration of movement in three instructions—forwards and backwards, side-to-side, and up and down. These measurements allowed the researchers to deduce the depth of a participant’s bodily exercise, they usually present extra correct measurements of the contributors’ time spent shifting, relatively than asking contributors to recollect.
Some examples of moderate-intensity bodily actions are brisk strolling, water aerobics, dancing, taking part in doubles tennis or gardening, and examples of vigorous-intensity actions are working, lap swimming, heavy yardwork comparable to steady digging or hoeing, taking part in singles tennis or leaping rope.
“Present remedy pointers after a cardiac occasion focus primarily on encouraging sufferers to train usually,” stated examine lead creator Keith Diaz, Ph.D., the Florence Irving Affiliate Professor of Behavioral Drugs at Columbia College Medical Middle in New York Metropolis, an authorized train physiologist and a volunteer member of the American Coronary heart Affiliation’s Bodily Exercise Science Committee.
“In our examine, we explored whether or not sedentary time itself could contribute to cardiovascular threat.”
Researchers adopted greater than 600 adults, ages 21 to 96, handled for a coronary heart assault or chest ache within the emergency division at a single hospital system in New York Metropolis.
Members wore a wrist accelerometer for a median of 30 consecutive days after hospital discharge to measure the period of time they spent sitting or being inactive every day. Further cardiac occasions and deaths had been evaluated one 12 months after hospital discharge by way of cellphone surveys with sufferers, digital well being data and the Social Safety Dying Index.
The examine was targeted on understanding the chance of sedentary habits and figuring out modifiable threat components that will enhance long-term outcomes on this high-risk group.
The evaluation discovered:
- In comparison with contributors within the group with the best bodily exercise stage, these within the group with the bottom exercise stage had a 2.58 instances greater threat of getting one other coronary heart downside or dying inside the subsequent 12 months.
- Changing half-hour of sedentary time with half-hour of reasonable to vigorous bodily exercise, every day, decreased the chance of hostile cardiovascular occasions or dying by 61%; changing the sedentary time with light-intensity bodily exercise decreased threat by 50%; and changing the sedentary time with half-hour of sleep lowered threat by 14%.
- Based on accelerometer knowledge, contributors in probably the most bodily lively group had common every day bodily exercise measures of 143.8 minutes of sunshine bodily exercise; 25 minutes of moderate-to-vigorous bodily exercise; 11.7 hours spent sedentary; and eight.4 hours of sleep.
- Members within the least bodily lively group had every day averages of 82.2 minutes every day of sunshine bodily exercise; 2.7 minutes of moderate-to-vigorous bodily exercise; 15.6 hours spent sedentary; and 6.6 hours of sleep.
- Members within the group between most and least bodily lively had every day averages of 109.2 minutes of sunshine depth bodily exercise; 11.4 minutes of moderate-to-vigorous depth bodily exercise; 13.5 hours spent sedentary and seven.8 hours of sleep.
“We had been stunned that changing sedentary time with sleep additionally lowered threat. Sleep is a restorative habits that helps the physique and thoughts get well, which is particularly necessary after a critical well being occasion like a coronary heart assault,” Diaz stated.
“Our examine signifies that one would not have to start out working marathons after a cardiovascular occasion to see advantages. Sitting much less and shifting or sleeping somewhat extra could make an actual distinction. Extra bodily exercise and extra sleep are more healthy than sitting, so we hope these findings help well being professionals to maneuver towards a extra holistic, versatile and individualized method for bodily exercise in sufferers after a coronary heart assault or chest ache.”
Bodily exercise and sleep are each key elements of the American Coronary heart Affiliation’s Life’s Important 8, an inventory of well being behaviors and components that help optimum cardiovascular well being. Poor sleep is a identified threat issue for heart problems, which claims extra lives annually within the U.S. than all types of most cancers and power decrease respiratory illness mixed, based on the American Coronary heart Affiliation’s 2025 Statistical Replace.
Along with sleep period, a latest scientific assertion from the Affiliation highlighted the significance of sleep continuity, sleep timing, sleep satisfaction, sleep regularity, sleep-related daytime functioning and sleep structure in cardiometabolic well being.
The examine had a number of limitations, together with that the definition of sedentary habits was primarily based solely on the depth stage of bodily motion, that means that the examine could have overestimated the time contributors spent in sedentary habits. Moreover, there was no details about contributors’ earnings and traits of the neighborhoods the place they reside, which limits the examine’s means to account for social and environmental components, together with contributors’ threat of one-year cardiac occasions and deaths.
Additionally, hospital discharge details about whether or not sufferers had been despatched dwelling, referred to rehabilitation or referred to different care facilities comparable to expert nursing amenities weren’t collected. This restricted the examine’s means to totally assess whether or not the sufferers’ settings had an influence on their restoration.
“This examine gives additional help for a ‘sit much less, transfer extra’ technique and—necessary for sufferers lately hospitalized for acute coronary syndrome who could have boundaries to extra intense train—discovered that rising light-intensity actions by half-hour a day was associated to dramatic reductions within the threat of a cardiac occasion inside the subsequent 12 months,” stated Bethany Barone Gibbs, Ph.D., FAHA, a professor and chair of the division of epidemiology and biostatistics on the Faculty of Public Well being at West Virginia College in Morgantown, West Virginia, and rapid previous chair of the American Coronary heart Affiliation’s Bodily Exercise Committee.
“This examine discovered that changing sedentary time with light-intensity actions, like tidying up the home or strolling at a gradual tempo, was almost as useful as moderate-to-vigorous depth bodily actions, like biking or doing aerobics. As well as, changing simply half-hour of sedentary habits with any depth of bodily exercise greater than halved the chance of getting a cardiac occasion over the one-year follow-up,” she stated.
“These findings counsel sitting much less and doing anything—like taking a stroll, cooking, taking part in along with your canine or gardening—will aid you keep more healthy.”
Research particulars, background and design:
- The examine included 609 adults who had been handled within the hospital emergency division for signs of chest ache and coronary heart assault, suggestive of acute coronary syndrome, between September 2016 and March 2020, at Columbia College Irving Medical Middle in New York Metropolis.
- When discharged from the hospital, examine contributors obtained an accelerometer to put on on their wrists to trace their sedentary and bodily exercise habits. Members accomplished follow-up cellphone interviews at one month and one 12 months after hospital discharge.
- Members had been requested to put on the accelerometers for 30 consecutive days and most did, the researchers stated; all contributors who wore the gadget for no less than 4 consecutive days had been included within the evaluation. The median variety of days that contributors wore accelerometers was 30 days. (Of notice: The accelerometers used on this examine had a battery lifetime of ~45 days, due to this fact, they didn’t to be taken off to be charged.)
- Research contributors had been a median age of 62 years previous; 48% had been girls, and 52% had been males. Roughly 58% of contributors self-identified as Hispanic adults; 22.8% had been non-Hispanic Black adults; 11% had been non-Hispanic white adults; and eight.2% self-identified as a race or ethnicity listed underneath “Different.”
- Inside one 12 months of hospital discharge, 8.2% of sufferers (n=50) skilled a cardiac occasion or died.
- The examine was supported by grants from the Nationwide Institutes of Well being and the Nationwide Coronary heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
Extra info:
Sedentary Conduct and Cardiac Occasions and Mortality After Hospitalization for Acute Coronary Syndrome Signs: A Potential Research, Circulation Cardiovascular High quality and Outcomes (2025). DOI: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.124.011644
Quotation:
An excessive amount of sitting after coronary heart assault tied to larger probability of one other occasion (2025, Could 19)
retrieved 19 Could 2025
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2025-05-heart-greater-chance-event.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.