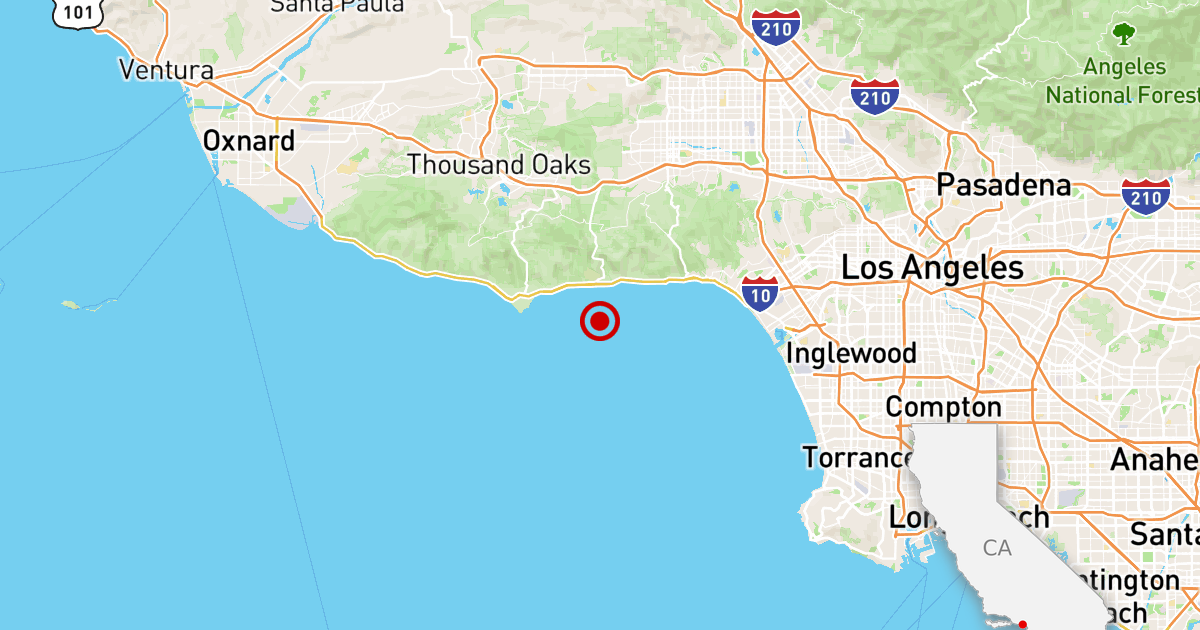
A magnitude 3.2 earthquake hit a number of miles south of Malibu on Wednesday, sending a mild jolt by way of the beachside metropolis.
The earthquake struck at 9:33 a.m., and weak shaking was felt as far-off as Los Angeles’ Westside, based on reviews submitted to the U.S. Geological Survey’s crowdsourcing web site. The epicenter was about 2.7 miles southwest of Malibu Level.
The offshore temblor comes simply three weeks after a magnitude 5.2 earthquake, centered in japanese San Diego County, rumbled throughout Southern California — shattering bottles, wine glasses and pottery however in any other case inflicting little harm.
Wednesday’s earthquake additionally provides to the notable string of seismic exercise in and across the Malibu space over the previous 16 months.
Notable current temblors embody a magnitude 4.6 earthquake on Feb. 9, 2024; a magnitude 4.7 earthquake on Sept. 12, 2024; and a magnitude 4.1 earthquake on March 9.
However whereas all have been comparatively modest and left little harm, they function an uneasy reminder that Los Angeles County and Orange County haven’t seen a serious earthquake in a very long time.
Since 1998, there was just one earthquake of magnitude 5 or higher underneath the 2 closely populated counties. That was a magnitude 5.1 earthquake centered in Brea in 2014, which brought about greater than $2.5 million in harm in that metropolis, Fullerton and La Habra.
There was additionally the magnitude 5.4 Chino Hills earthquake of 2008. Centered in San Bernardino County, however simply east of Los Angeles and Orange counties, it brought about little main harm.
It has been 31 years since the magnitude 6.7 Northridge earthquake hit Los Angeles, and greater than 35 years for the reason that magnitude 6.9 Loma Prieta earthquake ruptured in Santa Cruz County, inflicting intensive harm throughout the San Francisco Bay Space.
Amid this relative seismic drought, some communities have not too long ago made strikes to enhance seismic security.
In December, the Burbank Metropolis Council unanimously accredited a compulsory retrofit ordinance for house buildings with a flimsy first flooring, often known as a “soft-story” that may collapse in an earthquake. The well-known design flaw is commonly a results of having ground-floor carports or garages with skinny columns propping up the primary flooring, which may collapse when shaken aspect to aspect.
The regulation took impact on Jan. 19, and impacts wood-framed buildings which are not less than two tales tall and have been constructed utilizing constructing code requirements enacted previous to 1978. The Burbank regulation requires that retrofits be accomplished by 2030.
Burbank is providing refunds on constructing allow charges to property homeowners who full their retrofits early.
Greater than a half-dozen cities in Southern California have already opted to require retrofit work on soft-story house buildings — Los Angeles, Torrance, Pasadena, Santa Monica, Culver Metropolis, West Hollywood and Beverly Hills. In Northern California, the checklist contains San José, San Francisco, Oakland, Fremont, Berkeley, Albany and Mill Valley.
Nonetheless, a Instances investigation printed in November discovered that plenty of suburbs in L.A. County had no lively plans to require retrofits for a lot of these earthquake-vulnerable flats.
In Northern California, the San Francisco Board of Supervisors unanimously accredited a measure on Tuesday that can require homeowners of suspect concrete buildings to seismically consider their constructions with an engineer.
The evaluation will assist decide if particular buildings are at explicit threat of collapse or extreme harm in an earthquake.
“This laws helps us perceive the precise threat to our constructing inventory and gives concrete constructing homeowners with clear voluntary steerage and choices for retrofits,” Metropolis Administrator Carmen Chu mentioned in an announcement.
The San Francisco regulation, nonetheless, doesn’t require weak concrete buildings to be retrofitted.
Officers in San Francisco estimate that half of all deaths and accidents in a projected hypothetical magnitude 7.2 earthquake on the San Andreas fault would happen in concrete buildings.
One main flaw includes a concrete constructing being “non-ductile,” in which there’s an insufficient configuration of metal reinforcing bars, which permits concrete to blow up out of columns when shaken in an earthquake, a prelude to a catastrophic collapse. This flaw, now well-known, was found within the 1971 Sylmar quake.
Concrete buildings have beforehand collapsed in Los Angeles earthquakes, together with a Kaiser Permanente clinic constructing and a Bullock’s division retailer constructing through the 1994 Northridge earthquake, and the newly constructed Olive View Medical Heart through the 1971 earthquake.
The collapse of concrete buildings has brought about important deaths in earthquakes in Turkey, Mexico, Taiwan and New Zealand.
Cities in California that require non-ductile concrete buildings to be retrofitted embody Los Angeles, Torrance, Santa Monica and West Hollywood.
Are you prepared for when the Large One hits? Prepare for the following huge earthquake by signing up for our Unshaken publication, which breaks down emergency preparedness into bite-size steps over six weeks. Be taught extra about earthquake kits, which apps you want, Lucy Jones’ most essential recommendation and extra at latimes.com/Unshaken.
An earlier model of this story was generated by Quakebot, a pc utility that displays the newest earthquakes detected by the USGS. In case you’re interested by studying extra concerning the system, go to our checklist of often requested questions.