Key takeaways:
- Researchers expanded C. auris screenings exterior of outbreaks to incorporate particular affected person populations thought of excessive danger.
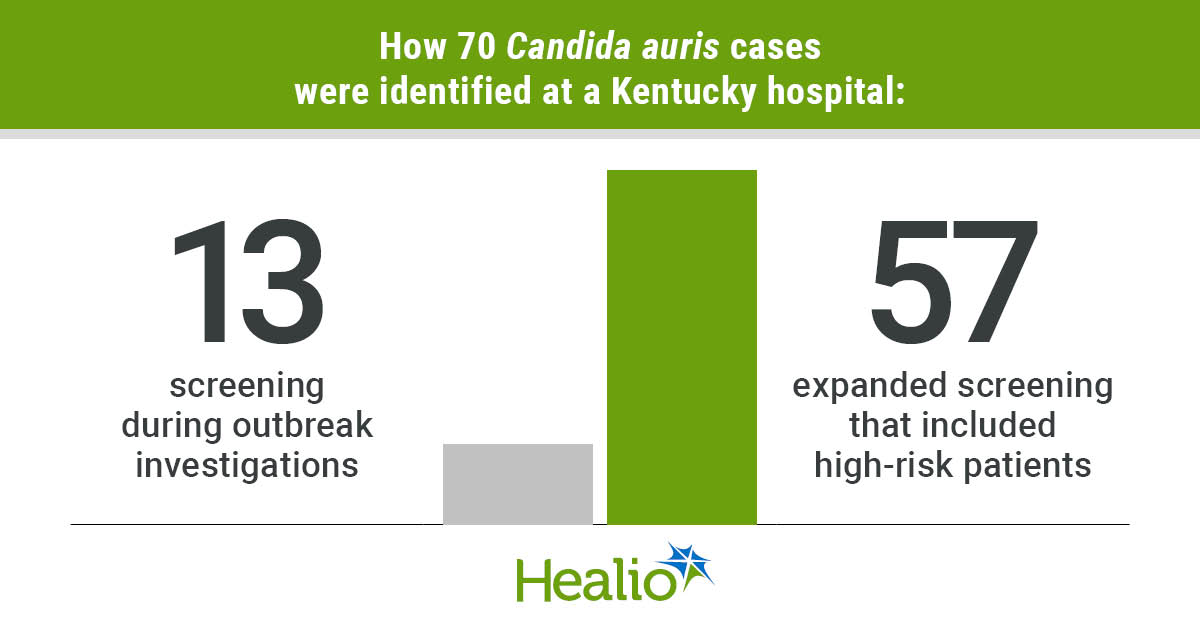
- 13 instances have been recognized earlier than expanded screening started vs. 57 after implementation.
ORLANDO — Increasing Candida auris screening to incorporate sufferers within the ICU or these with indwelling medical gadgets led to extra instances being recognized in a Kentucky hospital, in response to knowledge offered at SHEA Spring.
“We wished to try our surveillance screening program and see how efficient it truly was in capturing new C. auris sufferers and see if it was doing what we wished it to do,” Religion Fursman, BPH, MPH scholar and an infection prevention technician at College of Kentucky HealthCare (UKHC), instructed Healio.

Knowledge derived from Fursman F, et al. Summary 171. Introduced at: SHEA Spring; April 27-30, 2025; Orlando.
To take action, Fursman and colleagues performed a retrospective observational research utilizing knowledge from all grownup sufferers age screened for C. auris at UKHC between July 1, 2021, and June 30, 2024. In keeping with the researchers, the research lined two time durations — the interval previous to February 2023 when C. auris screening was solely performed throughout outbreak investigations and a post-implementation interval throughout which C. auris screening was expanded to incorporate ICU admissions, sufferers from exterior amenities with wounds or tracheostomies and sufferers with a historical past of carbapenem-resistant organism an infection. Throughout screenings axillary and groin swabs have been collected and examined by way of PCR. As soon as instances have been recognized, they have been labeled as community-onset — happening fewer than 4 days after admission — or hospital-onset — happening 4 days or extra after admission.
In whole, 13,642 C. auris exams have been carried out all through the whole research interval, resulting in the identification of 70 constructive instances — 13 instances throughout pre-implementation of which six have been community-onset and 7 hospital-onset, and 57 instances post-implementation of which 31 have been community-onset and 26 have been hospital-onset.
In keeping with the research, the principle indications for screening sufferers included ICU admission (42.86%), level prevalence surveys (17.14%) and admission from exterior amenities with wounds (5.72%).
Amongst all of the recognized instances, 10 (14.29%) have been labeled as scientific infections and 60 (85.71%) as colonization.
Fursman stated that the research revealed there have been loads of prevalent elements in scientific vs. colonization sufferers. For instance, sufferers with scientific instances have been extra more likely to have diabetes (90% vs. 48.33%; P = .0143) and indwelling medical gadgets together with tracheostomy (80% vs. 45%; P = .0404), gastrostomy tubes (90% vs. 53.33%; P = .0293), central strains (60% vs. 41.67%) and urinary catheters (60% vs. 46.67%).
She added that additionally they discovered a excessive prevalence of hypertension and power obstructive pulmonary illness or emphysema; nonetheless, Fursman stated these circumstances are closely prevalent in Kentucky the place the research was performed.
The research additionally confirmed that 30-day mortality was increased amongst scientific instances vs. colonized instances, though the researchers famous that the distinction was not statistically vital (30% vs. 25%).
Primarily based on these findings, Fursman stated that screening for C. auris — which she stated is lastly getting extra traction as a well being menace — is a crucial funding to make, however extra funding is required. She defined that some hospitals and well being care amenities could have some room of their budgets for laboratory testing; nonetheless, they might not assume it vital.
“In the event that they understand, ‘Hey, it’s vital. It’s one thing that’s prevalent and rising in our nation,’ then we’d make investments extra into it,” Fursman stated.
She added that C. auris is “an unknown till you take a look at for it.”
“You’re by no means going to know what you don’t know till you go search for it,” Fursman stated. “It’s important to look. It’s important to be that illness detective and simply see what you discover.”
For extra data
Religion Fursman, BPH, may be reached at religion.fursman@uky.edu.